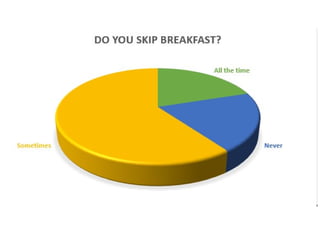
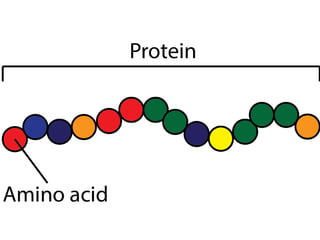
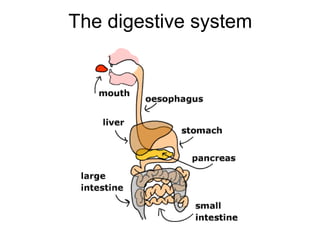
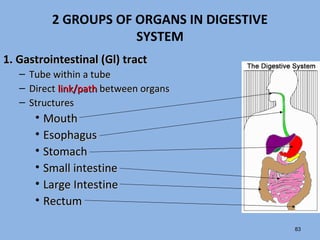
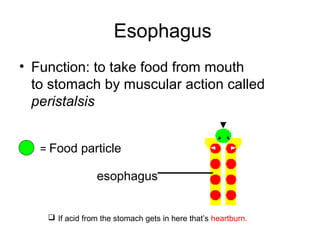
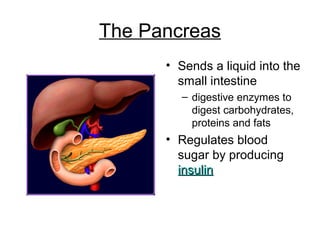
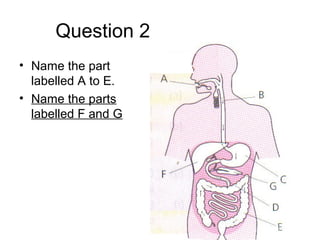
This document discusses the human digestive system and nutrition. It explains that digestion is the breakdown of food into simpler forms for absorption and use by cells. The major parts of the digestive system are named including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. The four main stages of digestion are identified as ingestion, digestion, absorption, and egestion. Carbohydrates are categorized as simple or complex, and monosaccharides like glucose, fructose and galactose are listed as examples of simple carbs.