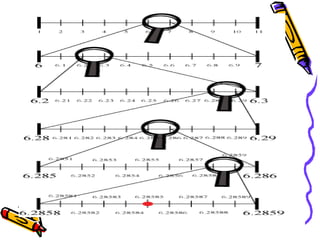
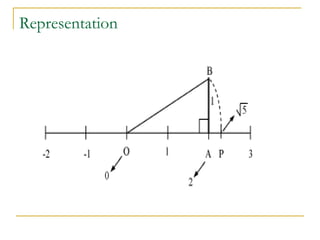
This document discusses different types of numbers and their representations. It introduces rational and irrational numbers, and explains how rational numbers can have either terminating or repeating decimal representations. Irrational numbers have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals. Examples of fractions and their decimal equivalents are provided. The document also demonstrates how to represent rational numbers on a number line using successive magnification.