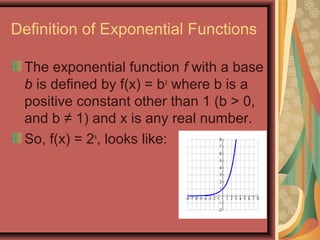
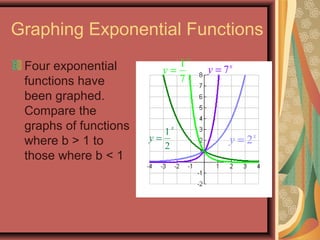
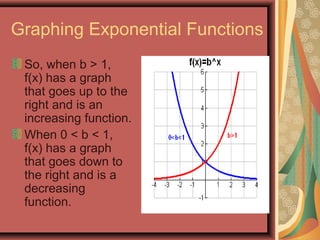
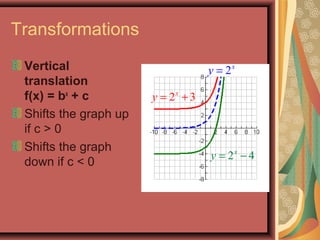
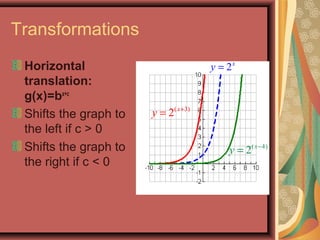
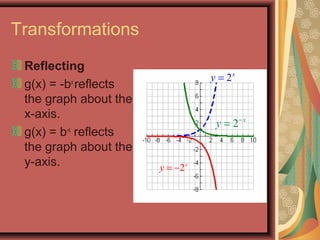
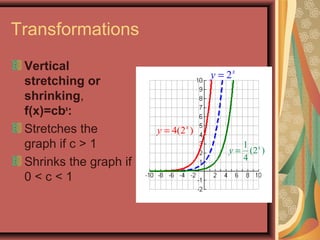
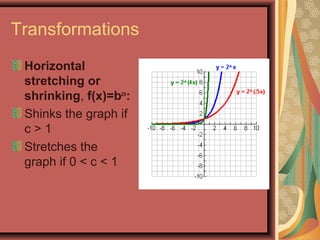
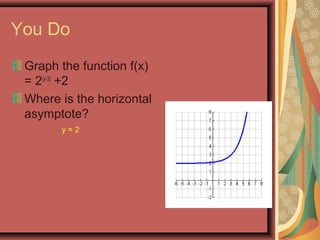
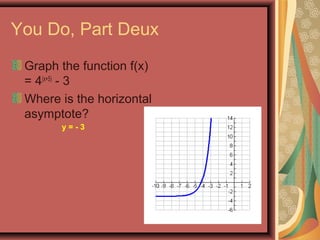
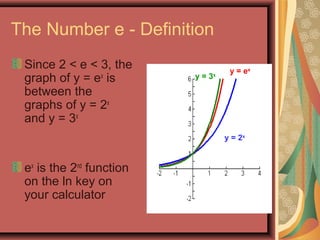
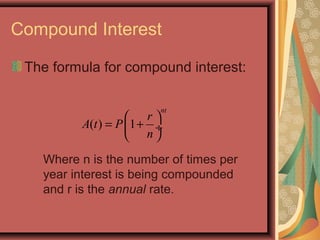
This document defines exponential functions and explores their key characteristics and transformations. Exponential functions have the form f(x) = bx, where b is a positive constant other than 1. Their graphs pass through (0,1) and have a horizontal asymptote at the x-axis. When b > 1 the graph increases to the right, and when 0 < b < 1 it decreases. Translations move the graph up/down (vertical) or left/right (horizontal). Reflections flip the graph across an axis. Stretching/shrinking changes the steepness. The number e, approximately 2.718, arises naturally in situations involving continuous growth/decay and is the base of the natural exponential function f(x