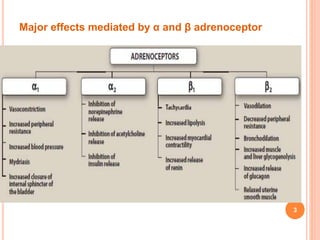
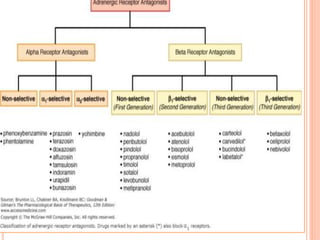
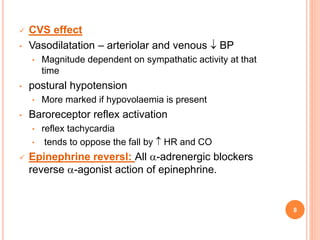
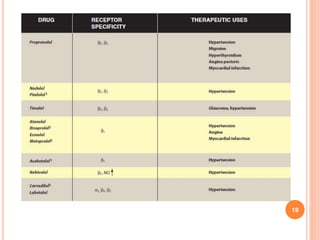
Adrenergic blockers, also known as sympatholytics, are drugs that bind to adrenergic receptors but do not trigger the usual intracellular effects. They have the opposite effect of adrenergic agents and block alpha and beta receptor sites. Major classes include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and drugs that affect neurotransmitter release or uptake. Alpha blockers are further divided into non-selective, alpha1-selective, and drugs with additional beta blocking effects. Beta blockers include non-selective, cardioselective, and those with partial agonist activity. Drugs like reserpine and guanethidine deplete neurotransmitters from nerve endings. Common uses are for hypertension, angina, migraine and