Embed presentation
Downloaded 18 times


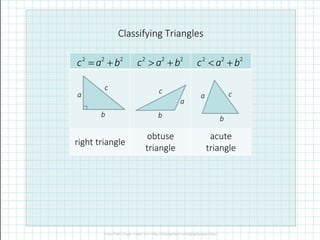


This document discusses classifying triangles using Pythagorean theorem and inequalities. It states that if a2 + b2 = c2, the triangle is right. If a2 + b2 > c2, the triangle is obtuse, and if a2 + b2 < c2, the triangle is acute. Examples are then given to classify triangles as right, obtuse or acute based on their side lengths.




