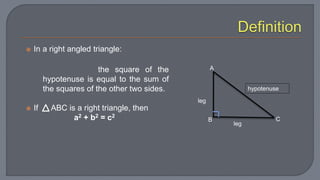
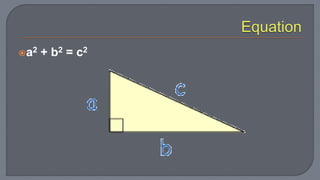
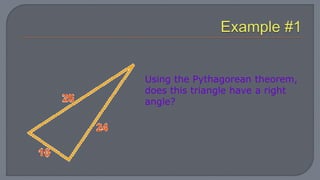
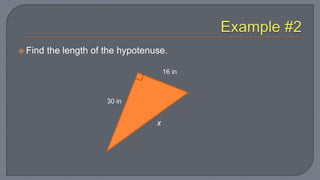
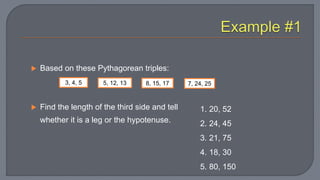
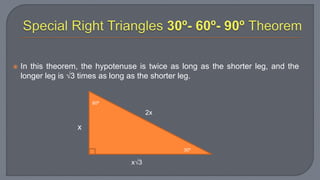
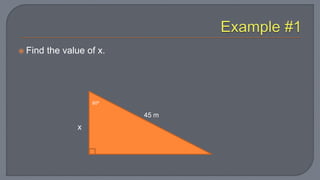
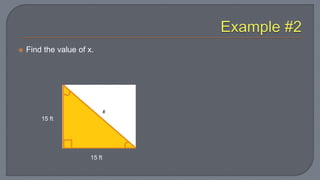
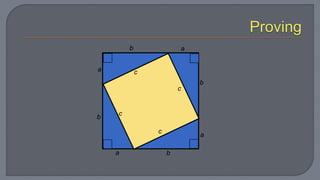
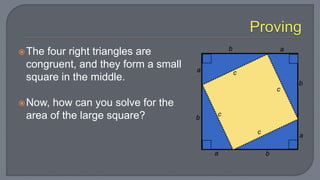
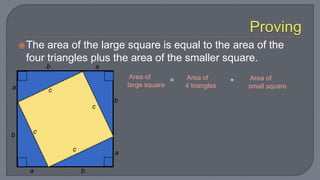
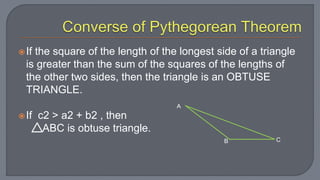
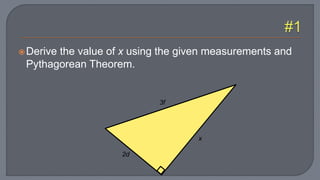
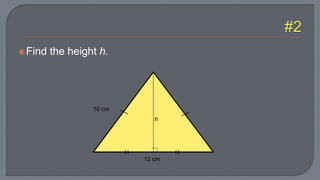
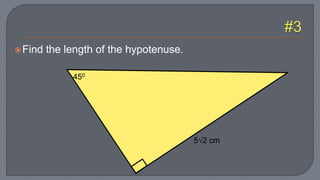
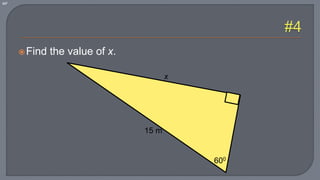
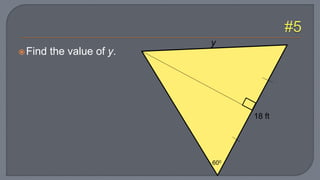
The document discusses the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. It provides examples of using the theorem to determine whether a triangle is right, acute, or obtuse based on the side lengths. It also discusses classifying triangles, finding missing side lengths, and explores Pythagorean triples.