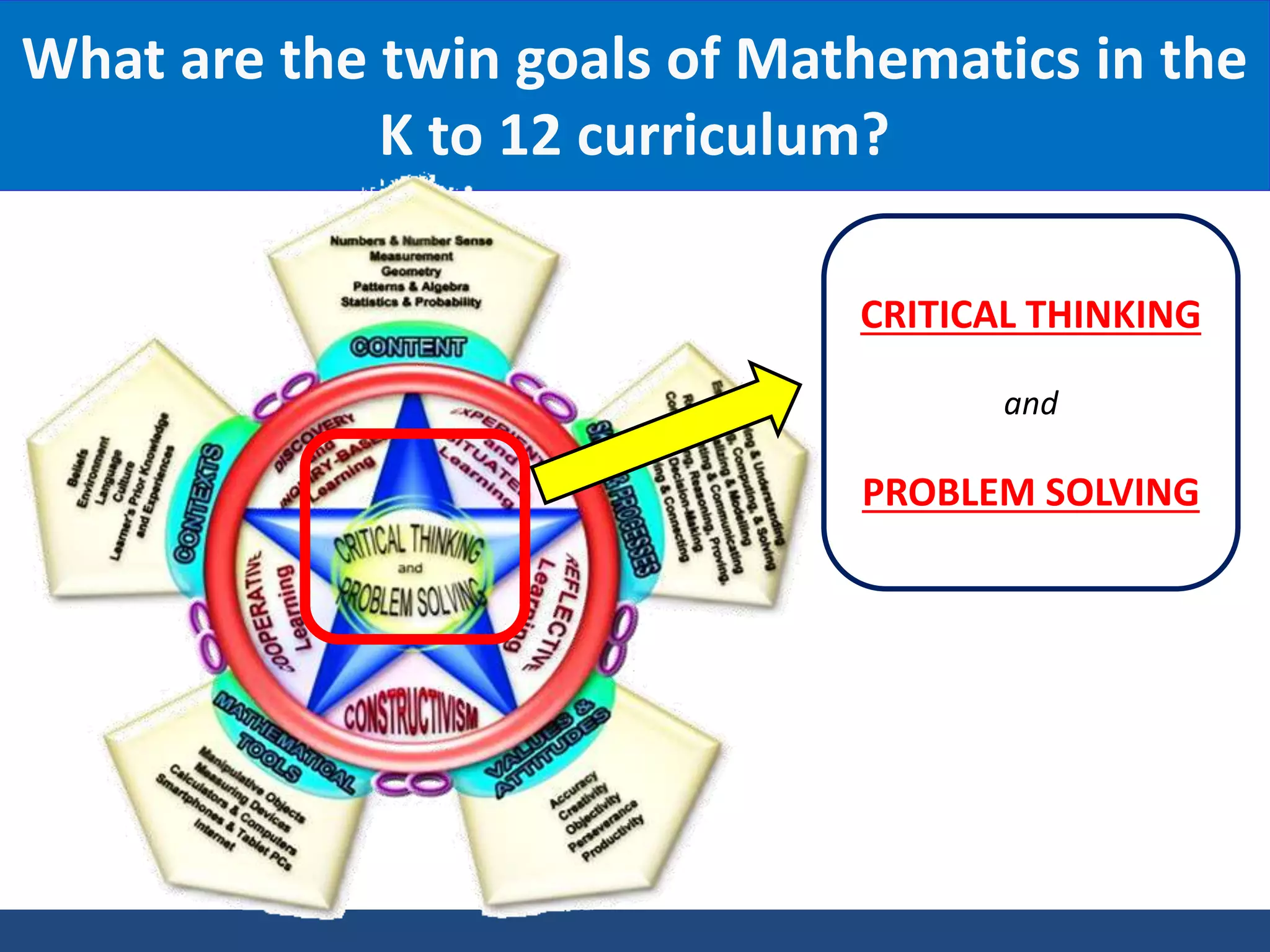
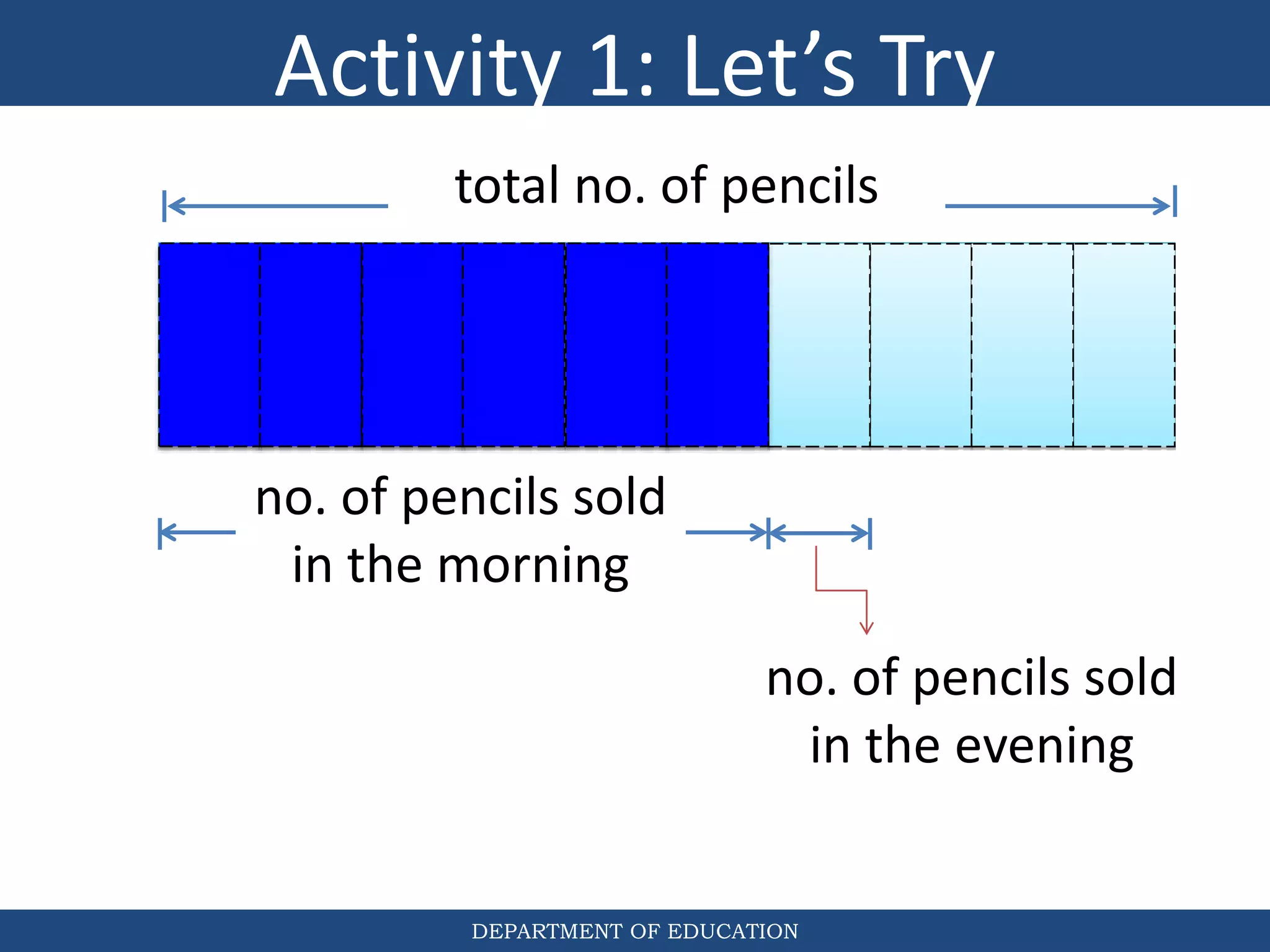
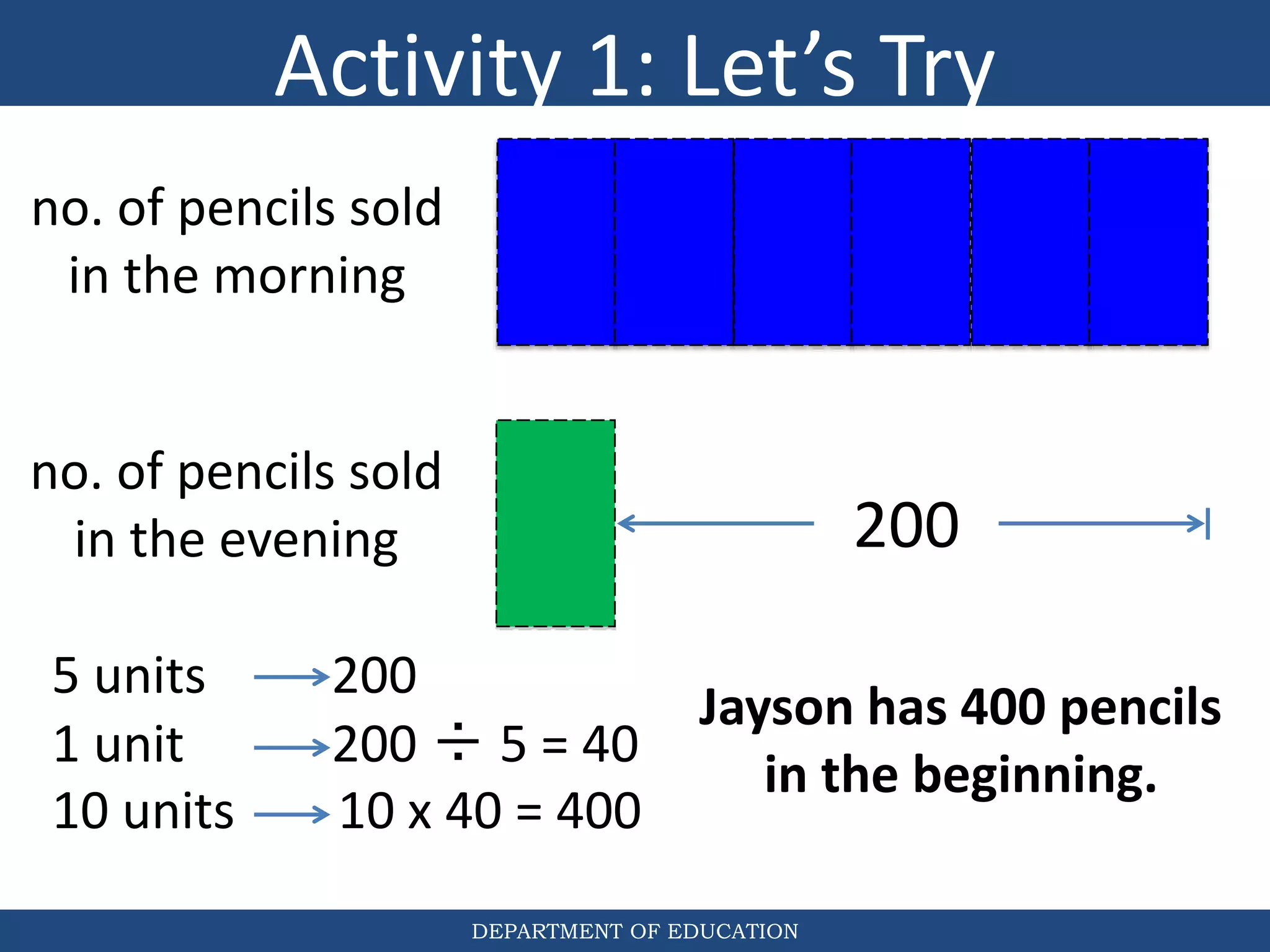
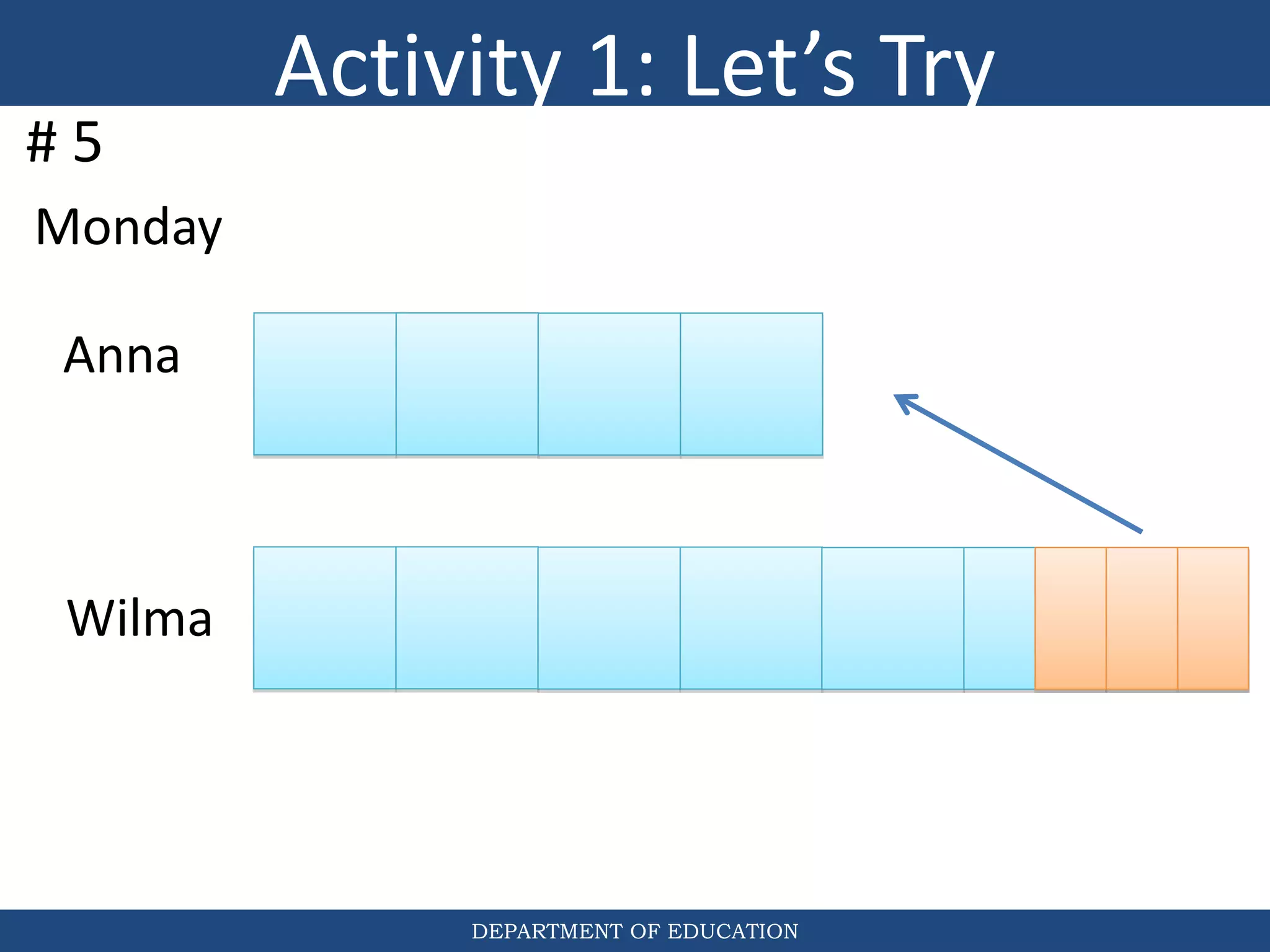
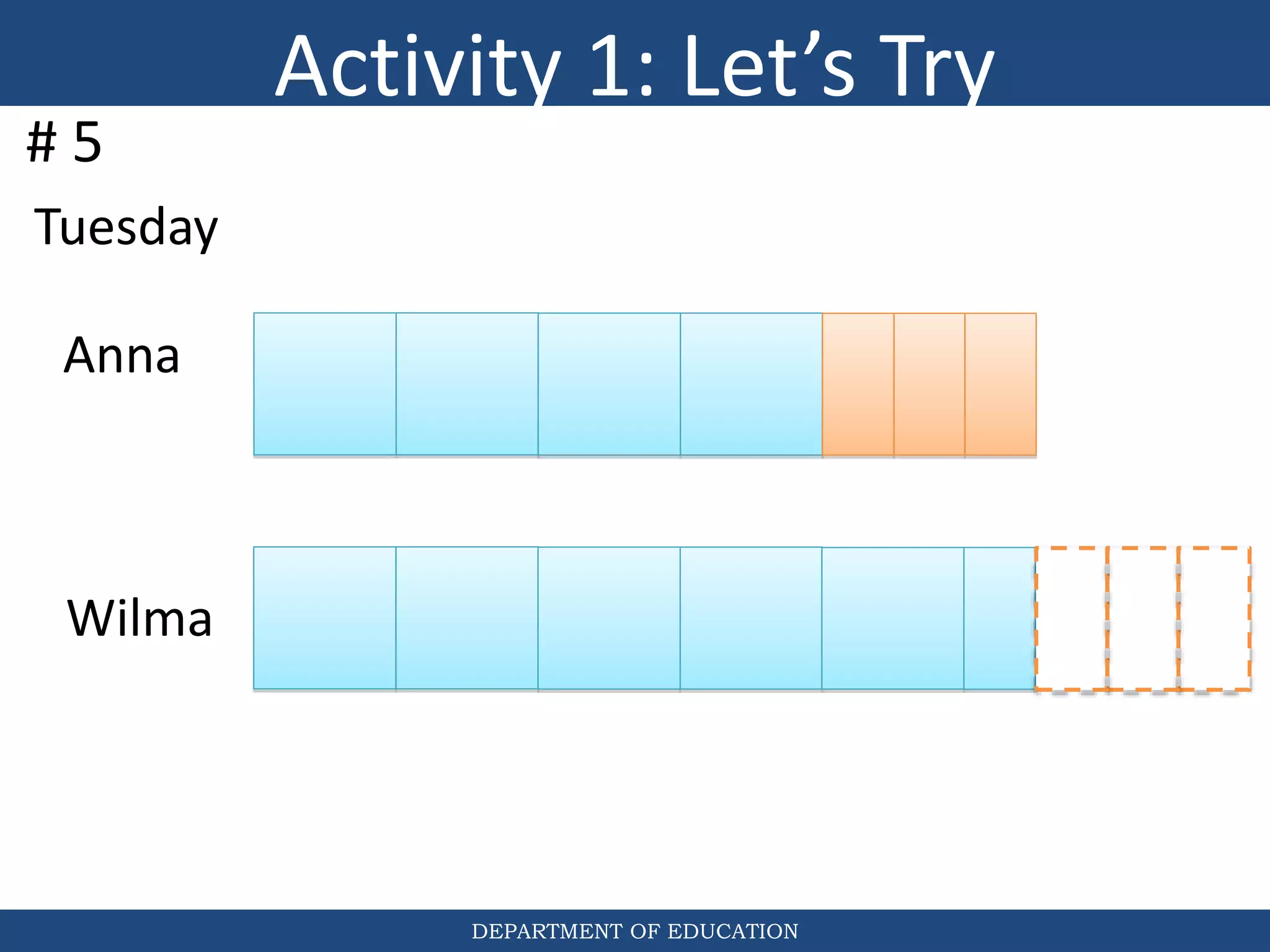
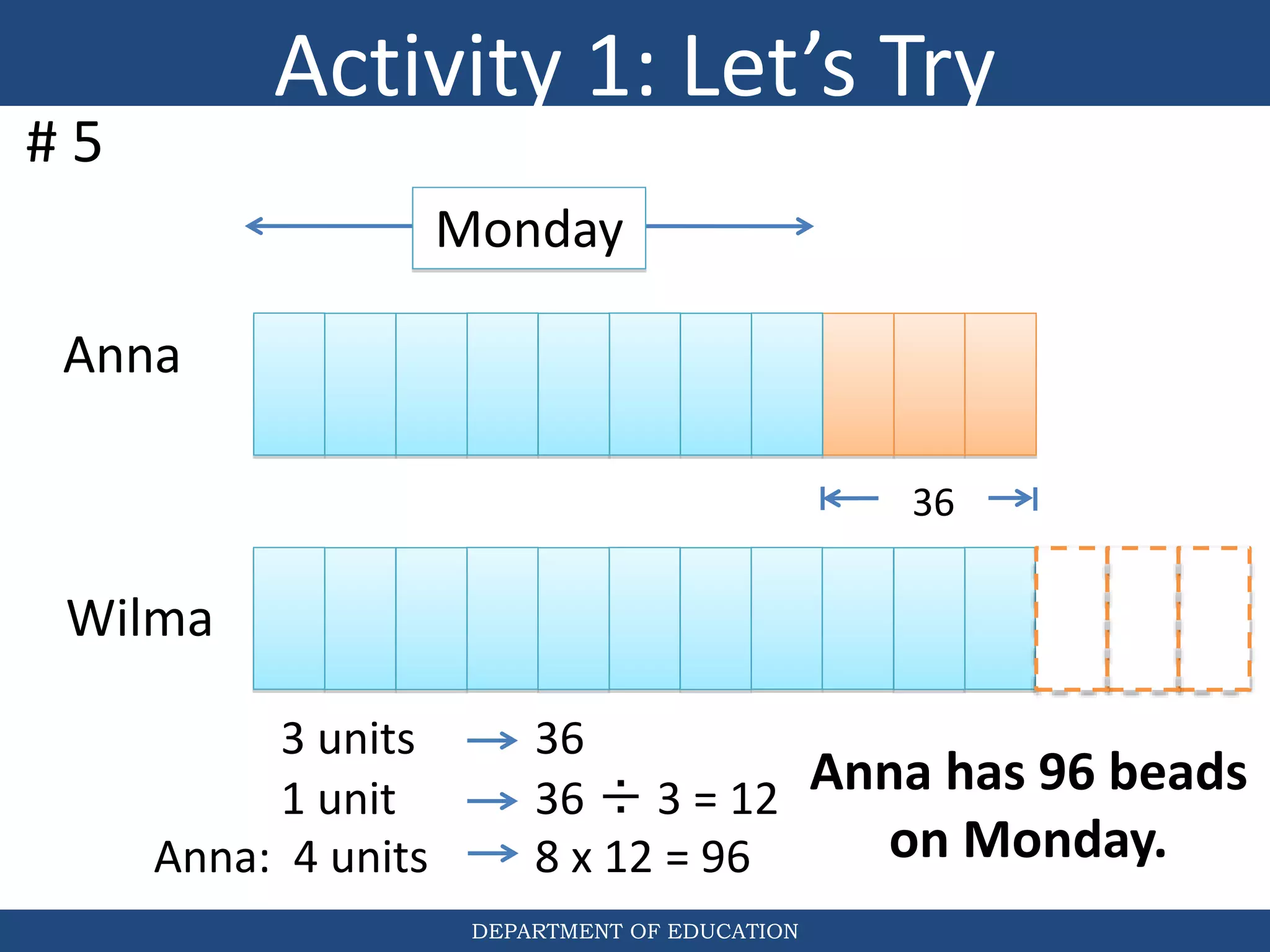
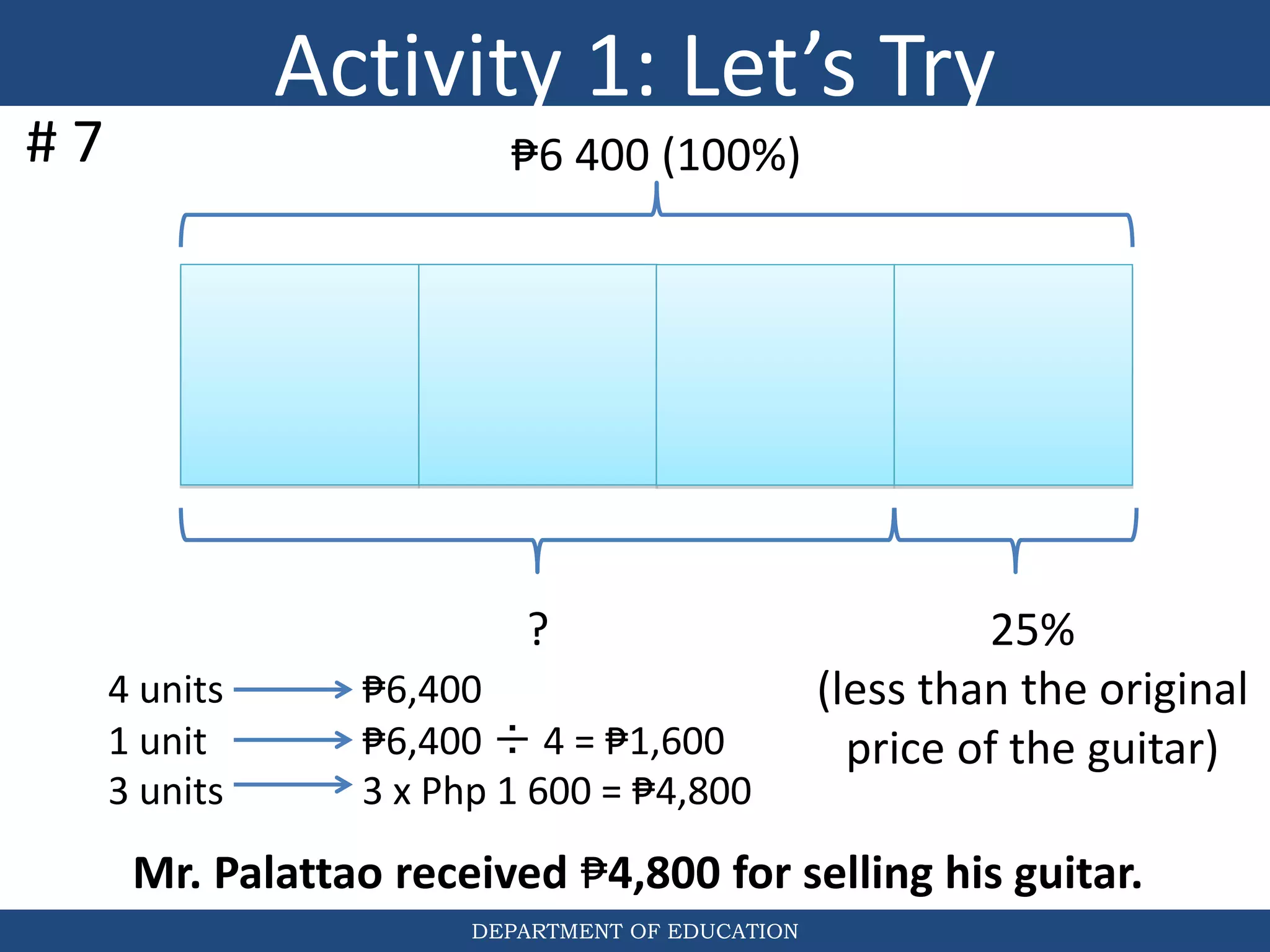
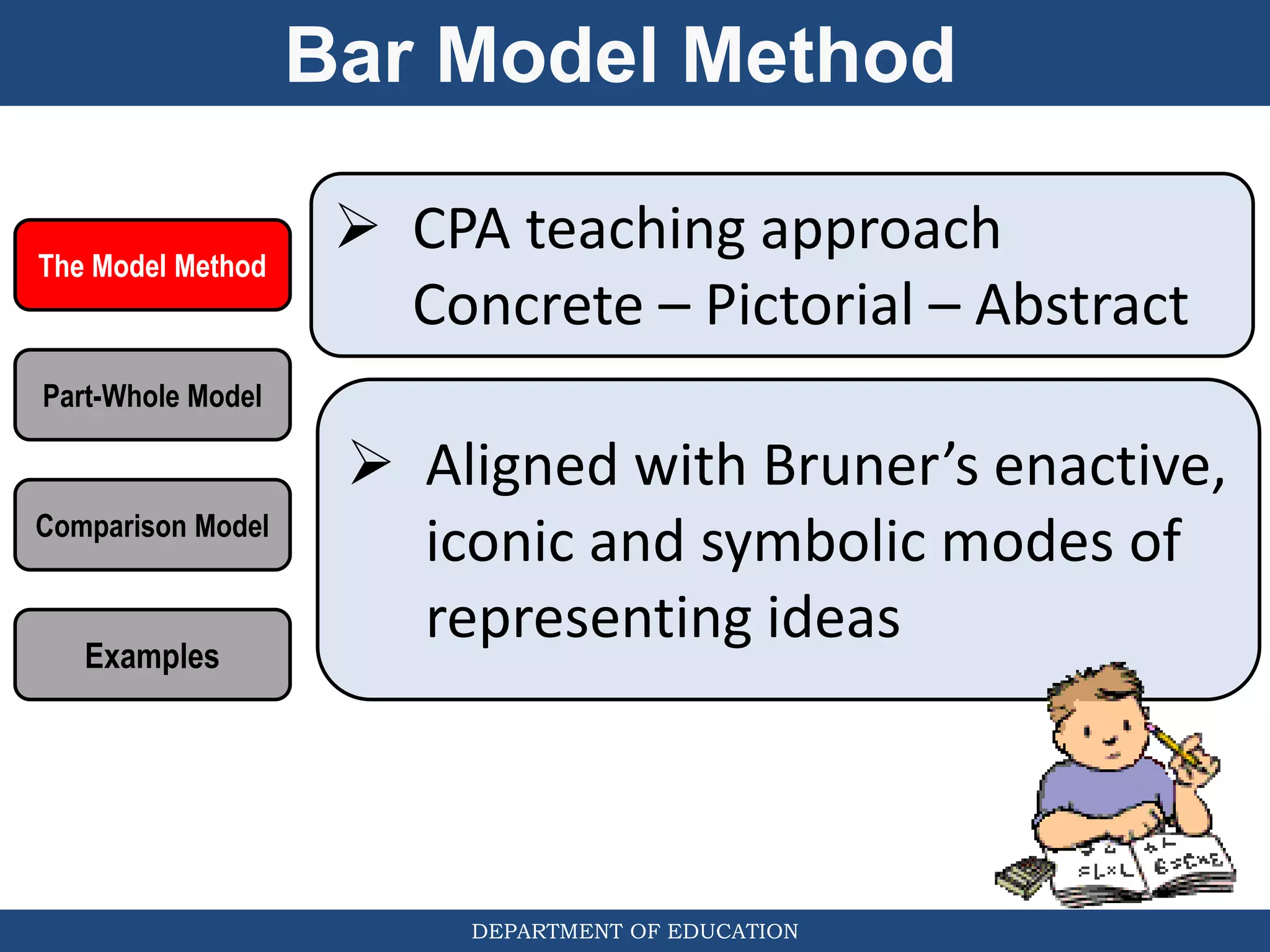
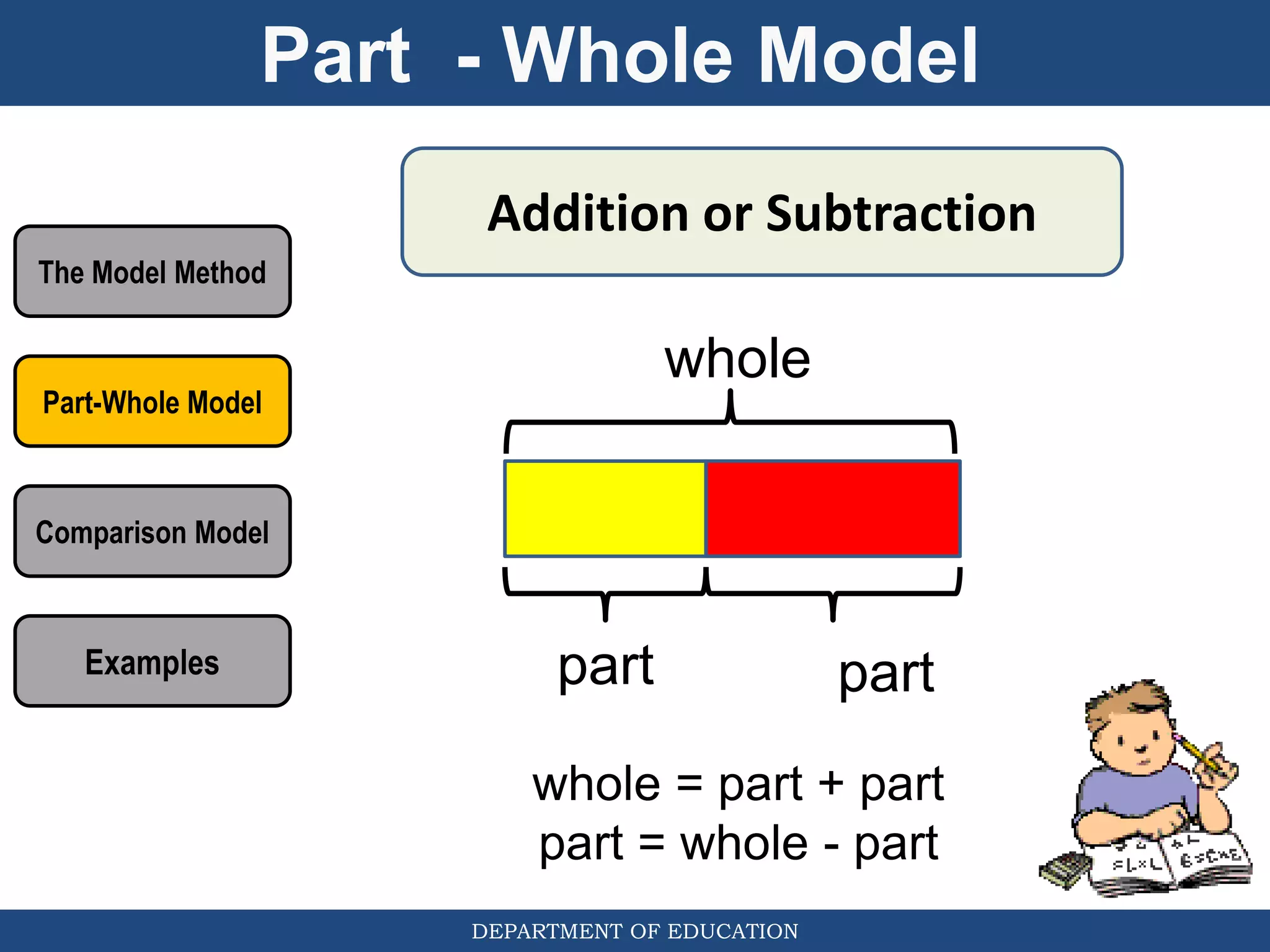
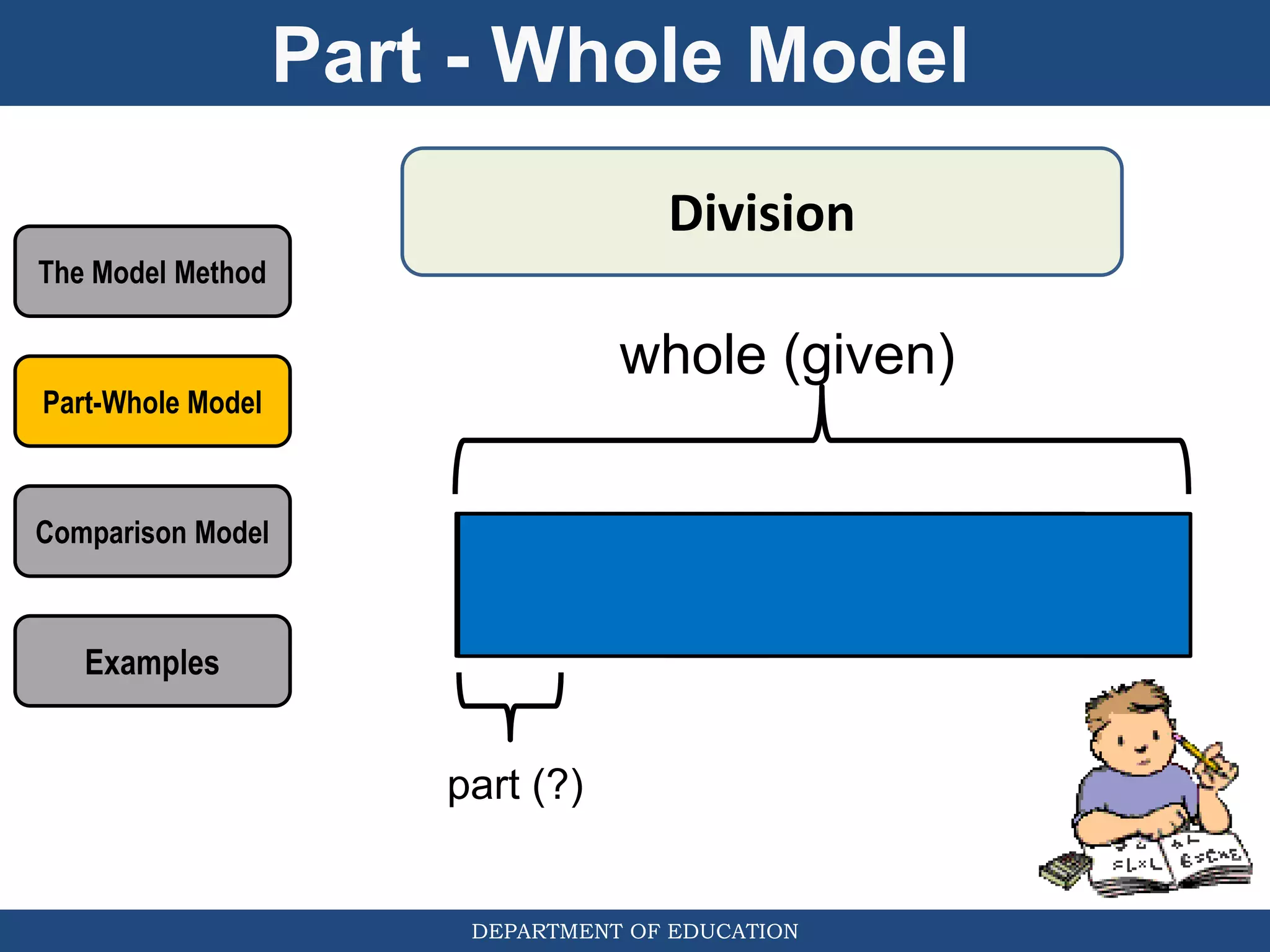
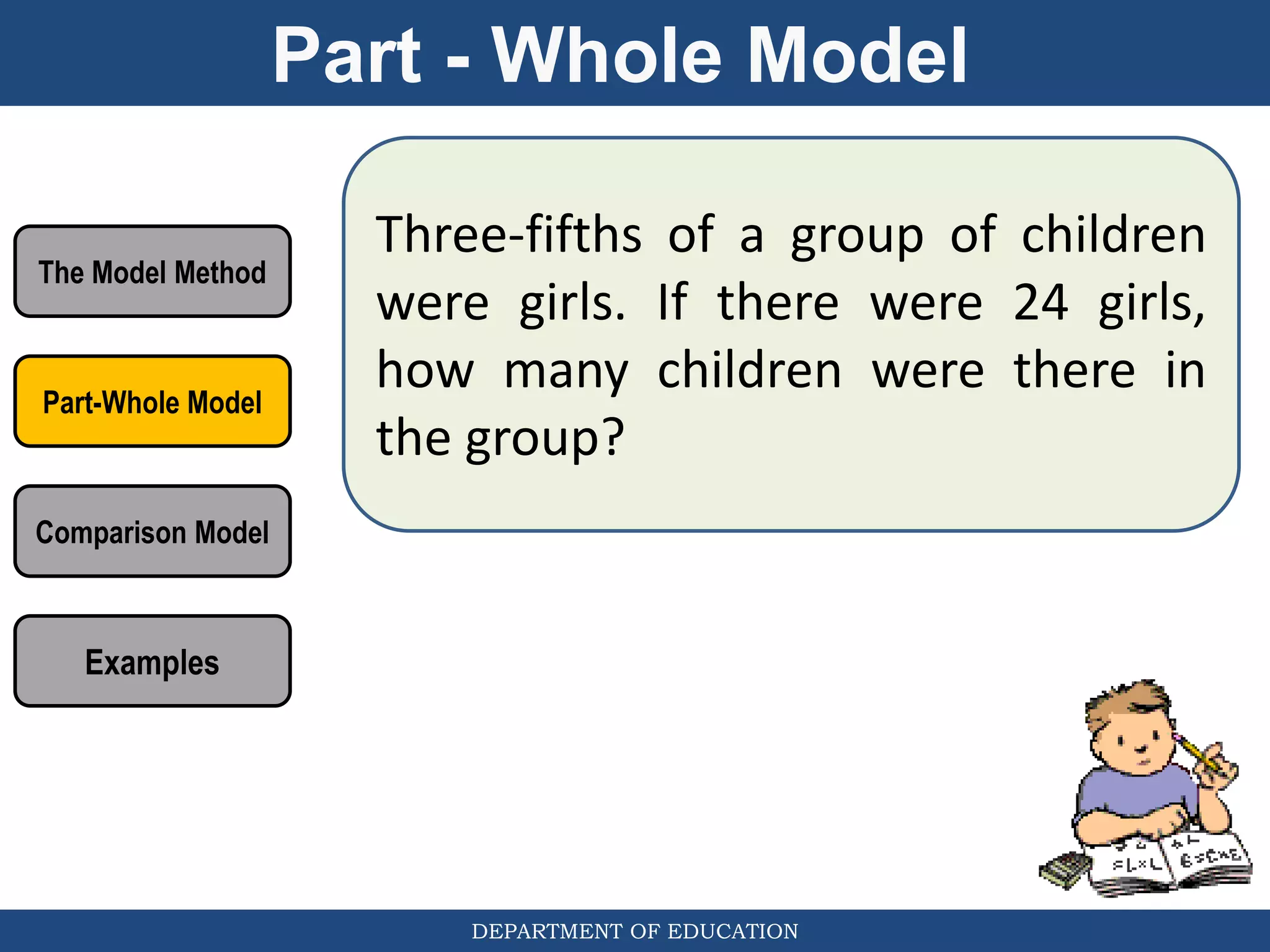
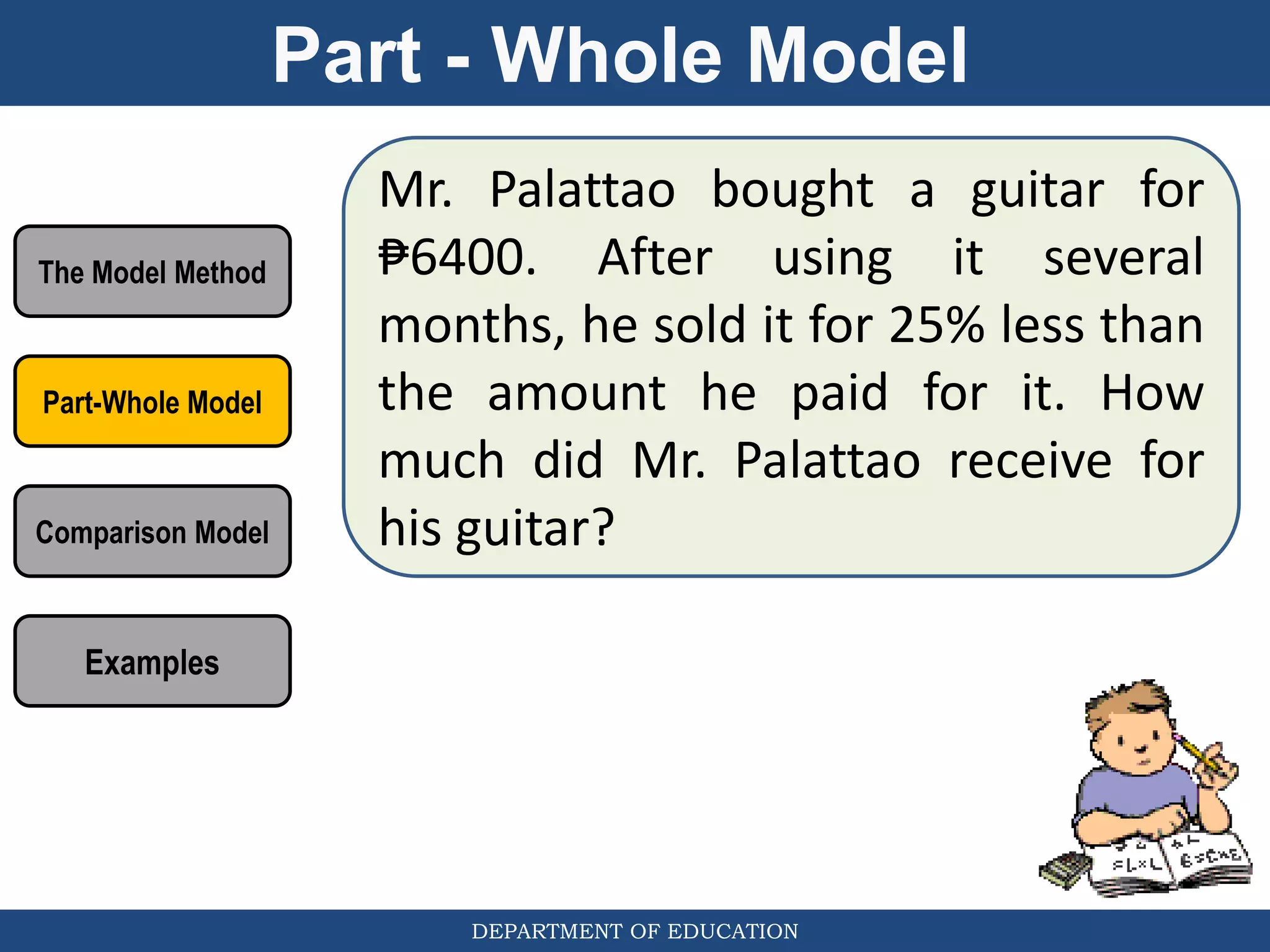
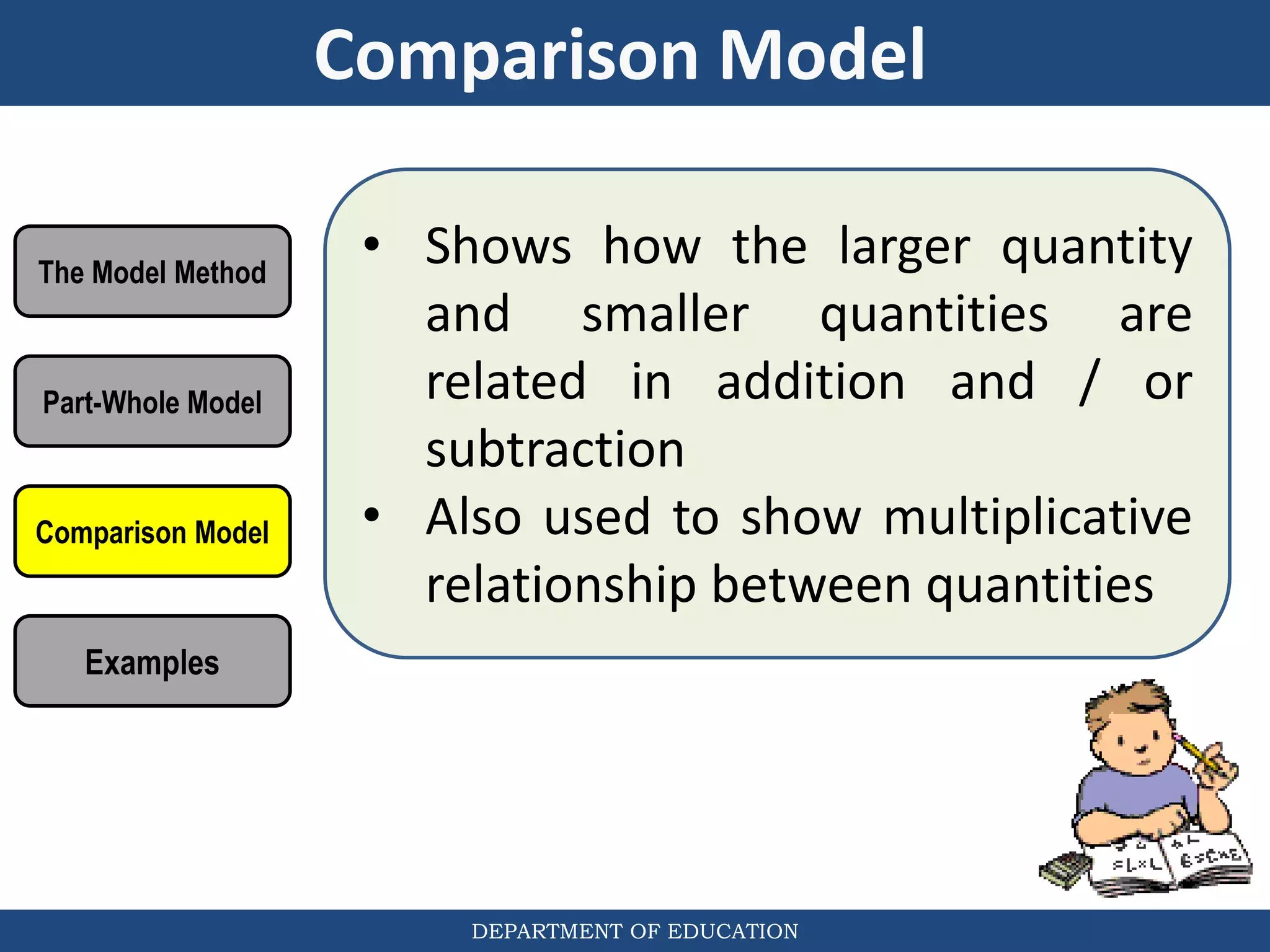
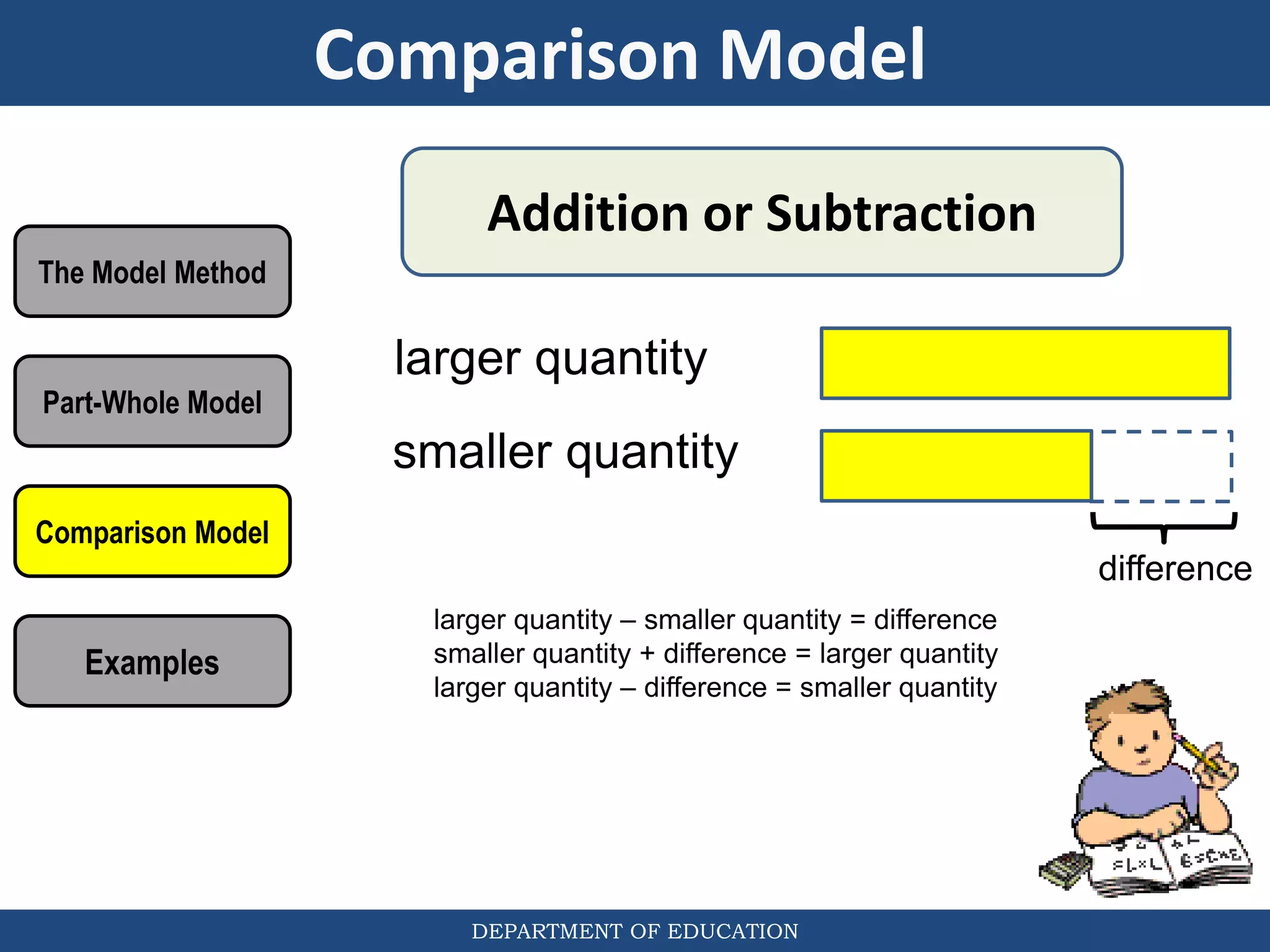
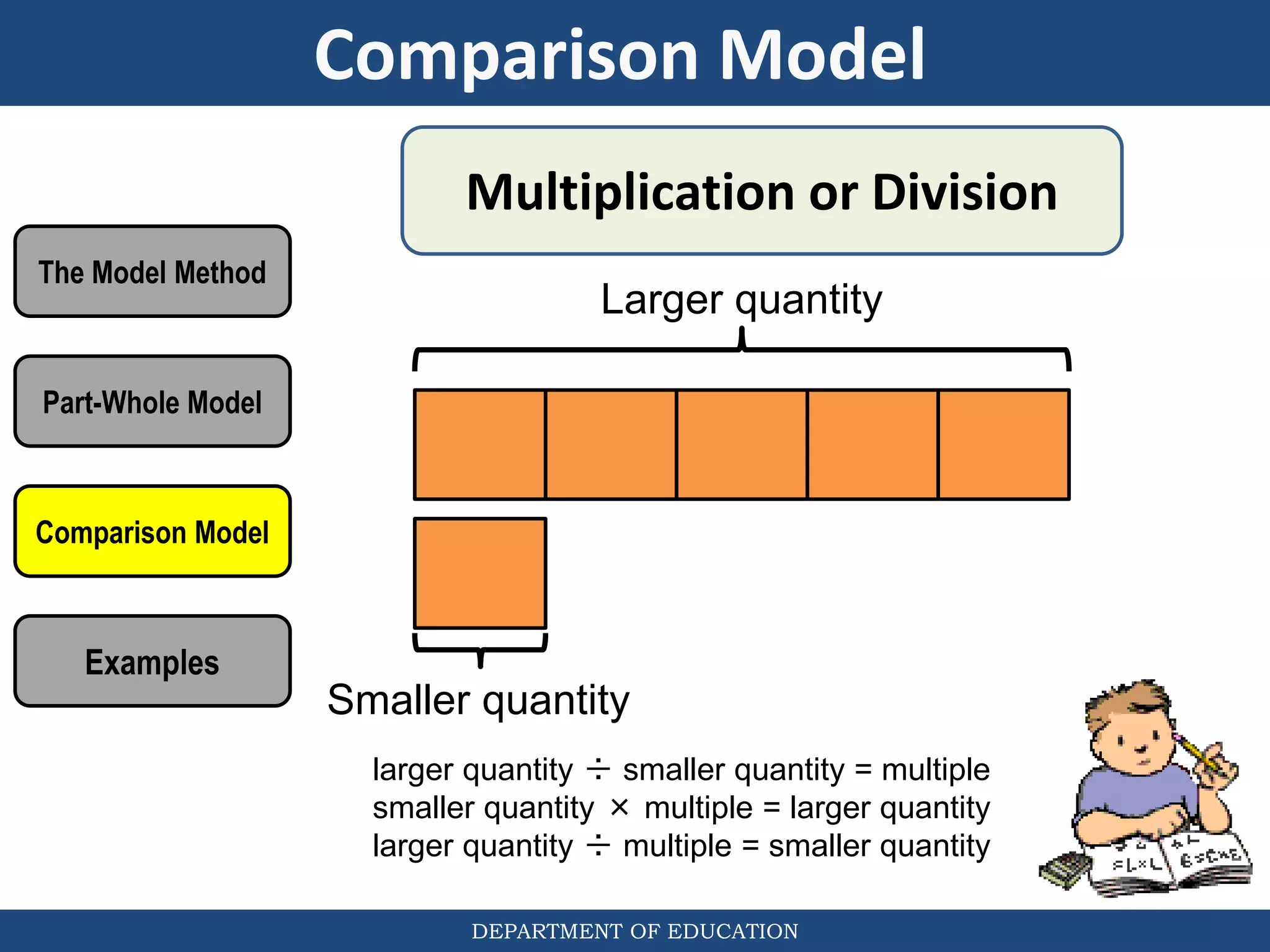
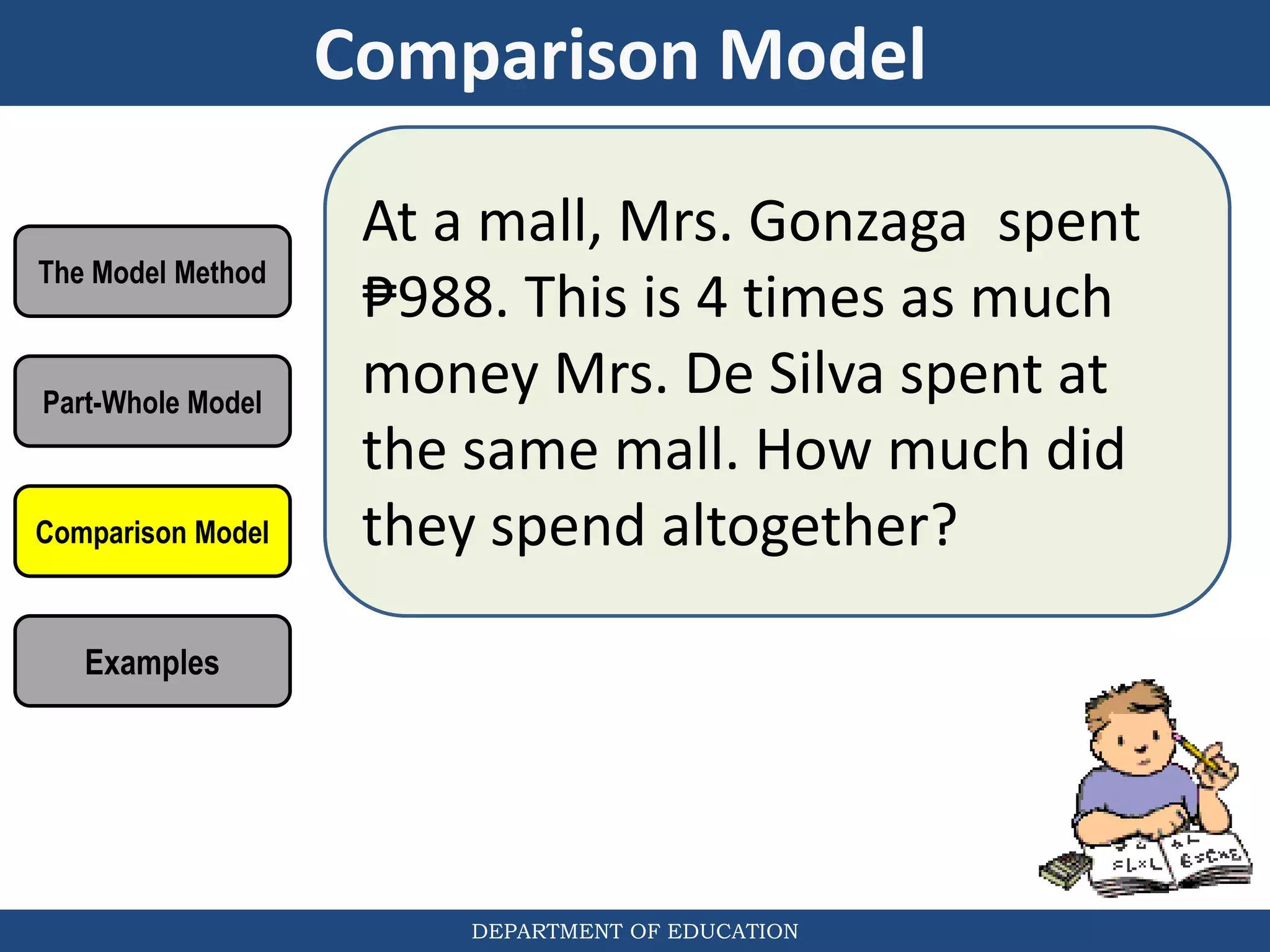
The document discusses teaching the bar model method for solving word problems in mathematics. It describes the bar model method which uses rectangular bars to represent quantities and relationships in word problems visually. Examples are provided of using part-whole and comparison bar models to solve word problems involving various mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, ratios, and percentages. Teachers lead students in activities to practice applying the bar model method to different types of word problems.