This document provides information about chemical reactions including:
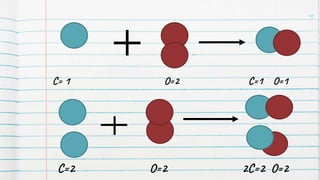
1. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances, as evidenced by changes in properties.
2. Chemical reactions are modeled using chemical formulas, symbols, and equations to represent the reactants and products.
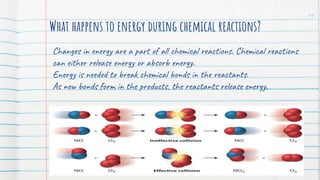
3. Chemical reactions can be endothermic, requiring energy input, or exothermic, releasing energy to the surroundings.