Embed presentation
Downloaded 2,314 times

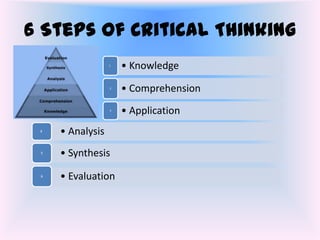



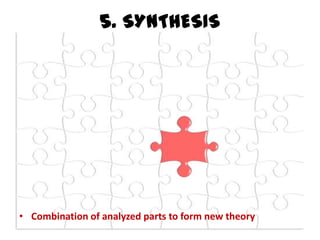


Critical thinking is defined as the process of actively and skillfully analyzing and evaluating information gathered from various sources in order to guide beliefs and actions. It involves 6 steps: 1) gaining knowledge through identification and description, 2) comprehending by explaining and summarizing, 3) applying knowledge to solve problems, 4) analyzing by breaking down information into parts, 5) synthesizing analyzed parts to form new theories, and 6) evaluating through ranking and appraising.









