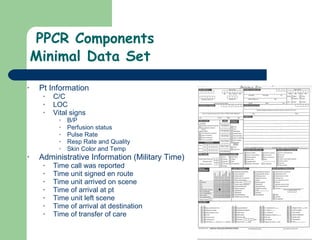
The document discusses the importance and functions of prehospital patient care reports (PPCRs). PPCRs serve several important purposes: as a medical record, for continuity of care, administrative/billing purposes, legal protection, education, and quality improvement. The document outlines the components and proper format of PPCRs, including the use of standardized templates, chronological documentation of assessments and treatments, and guidelines for special situations like mass casualty incidents or patient refusals. Accurate, objective, and complete documentation is emphasized.