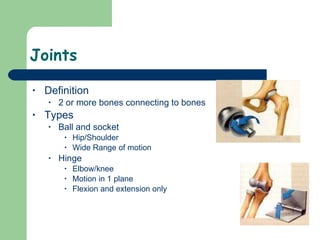
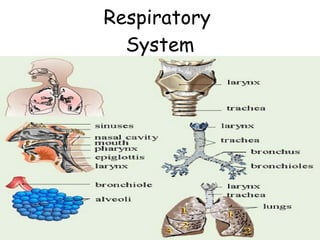
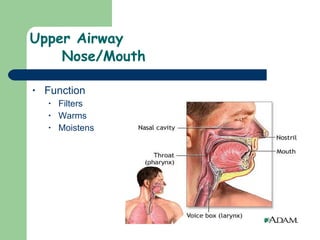
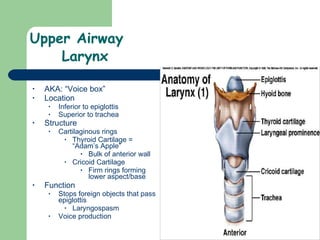
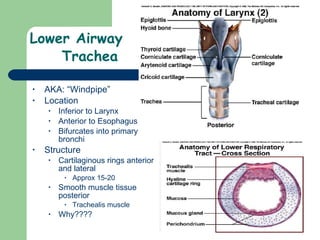
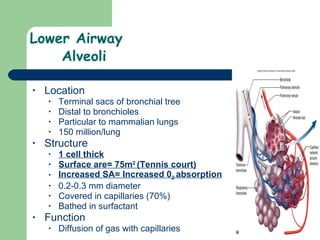
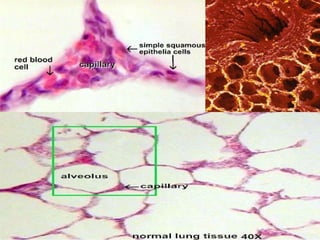
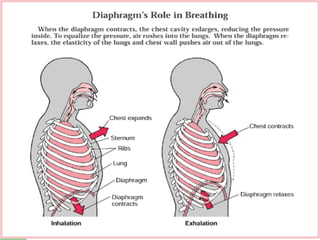
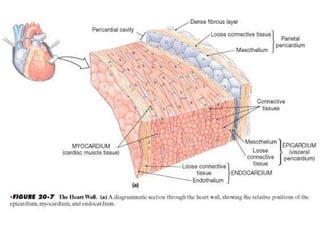
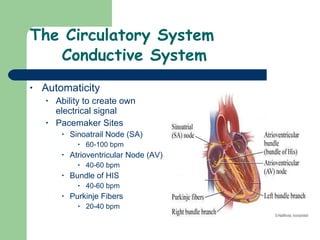
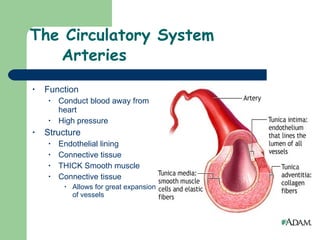
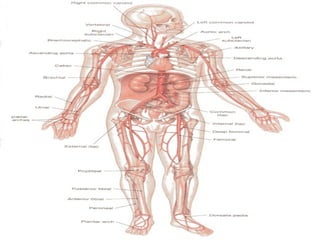
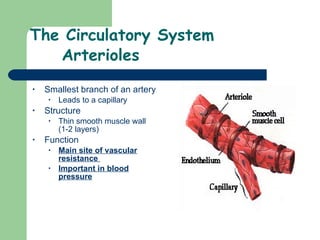
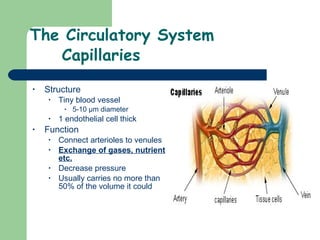
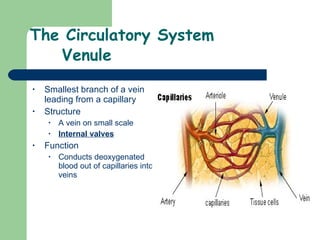
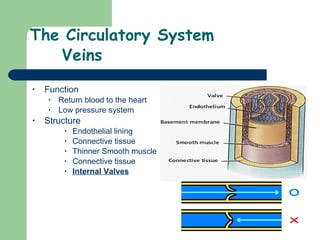
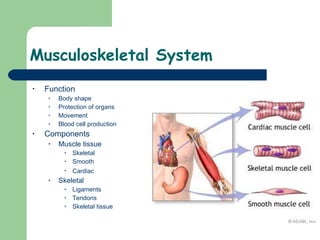
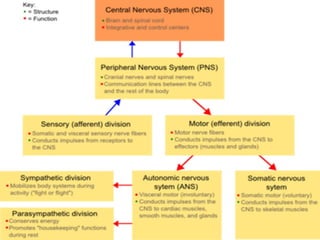
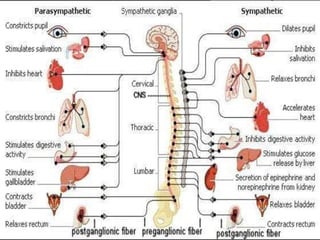
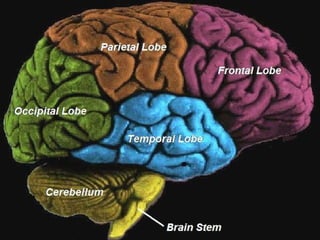
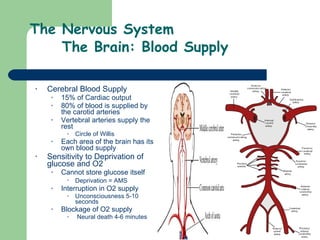
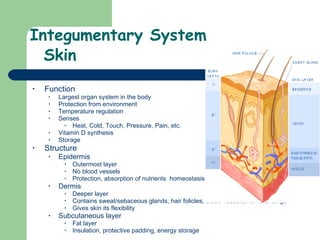
The document provides an overview of human anatomy and physiology, with a focus on the respiratory and circulatory systems. It defines anatomy and physiology, describes anatomical terms and positions, and reviews the key structures and functions of the skeletal, respiratory, and circulatory systems. The respiratory system section examines the upper airway, lower airway, gas exchange, and respiratory evaluation. The circulatory system section states its overall function of nutrient/oxygen transport and waste removal.