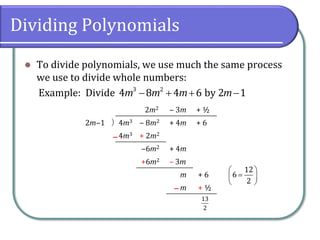
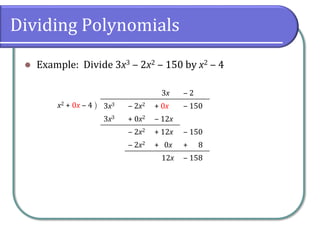
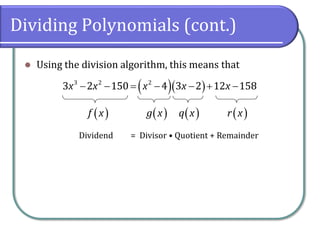
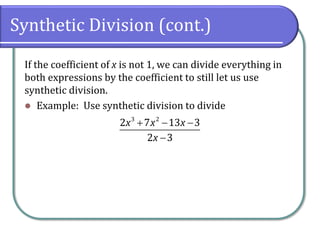
The document discusses dividing polynomials using long division and synthetic division. It provides examples of dividing polynomials using long division, including inserting placeholders for missing terms. It then introduces synthetic division as a shortcut method for dividing polynomials when the divisor is of the form x - k. Examples are provided of using synthetic division to divide polynomials.