This document provides an overview of fractions, including:
- Defining fractions as ordered pairs of numbers where the denominator tells how many equal pieces the whole is divided into.
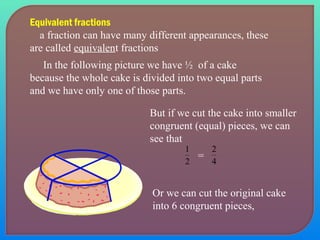
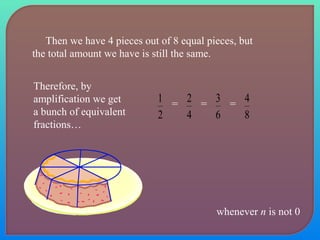
- Explaining equivalent fractions and how to reduce fractions to their simplest form.
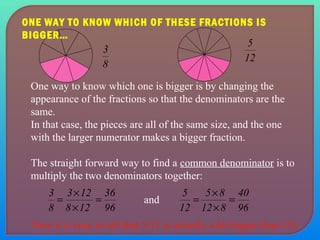
- Demonstrating how to compare fractions using cross multiplication or finding a common denominator.
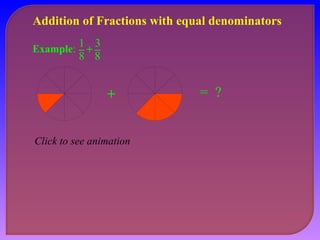
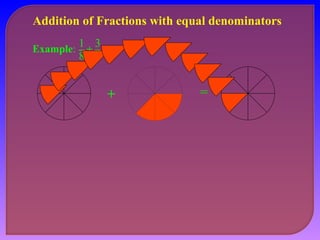
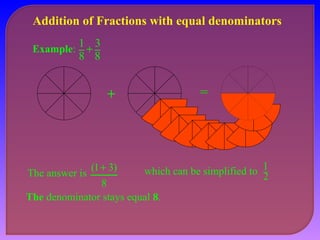
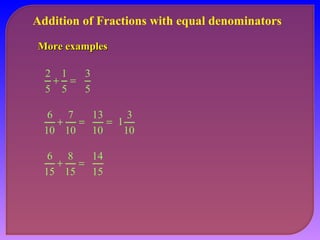
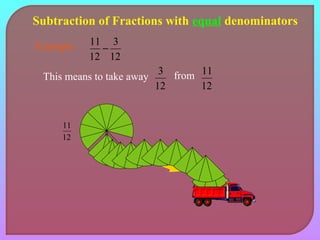
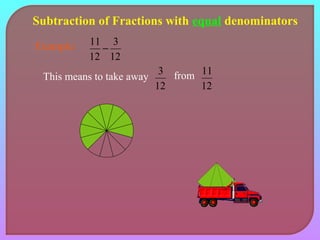
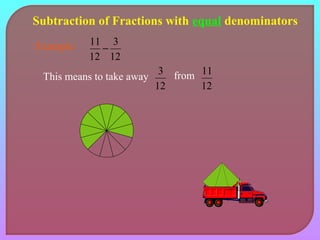
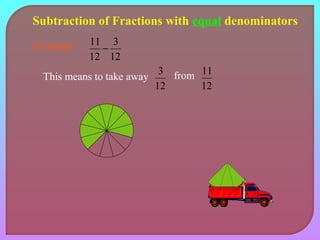
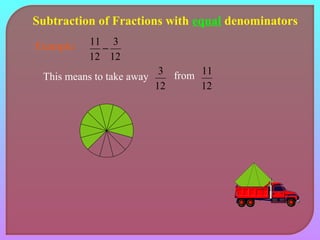
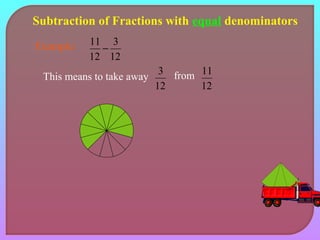
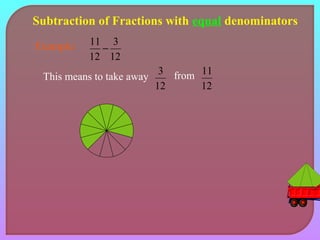
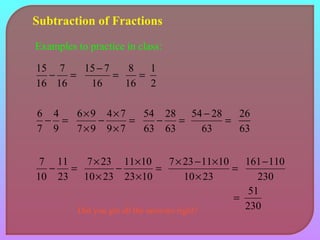
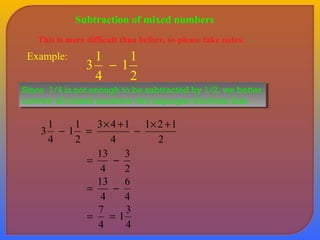
- Explaining how to perform addition and subtraction of fractions by finding a common denominator or converting to equivalent fractions with the same denominator.