Embed presentation
Downloaded 47 times


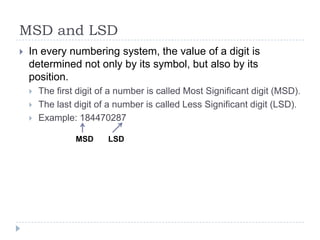


This document discusses numbering systems and conversions between systems. It defines base as the number of symbols used in a system and provides examples. The most and least significant digits in a number are defined based on their position. Binary addition and subtraction rules are covered. Methods for converting between decimal, binary, octal and hexadecimal systems are outlined, which involve repeatedly dividing by the base value and tracking the remainders or place values.




