Embed presentation
Downloaded 51 times





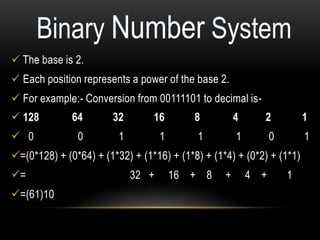
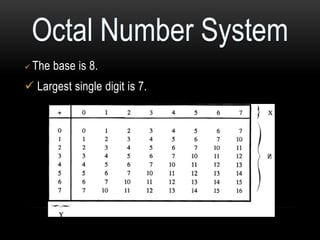
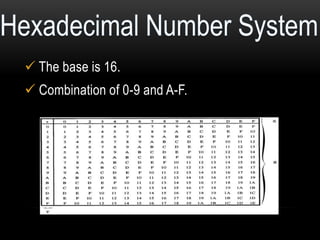
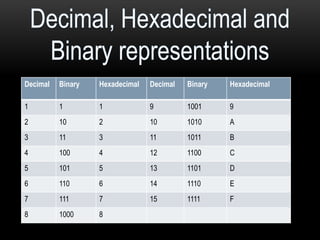

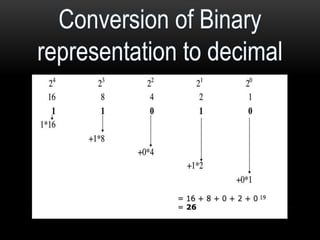
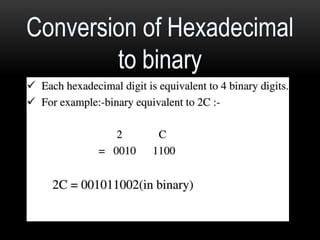








This document discusses different number systems including positional and non-positional, and how to convert between decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal numbers. It explains that positional systems use the digit's position and value to determine its overall value, and different bases determine the maximum single digit value. Conversion between number systems involves representing values in their respective bases then performing arithmetic operations.


















