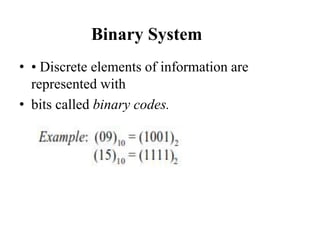
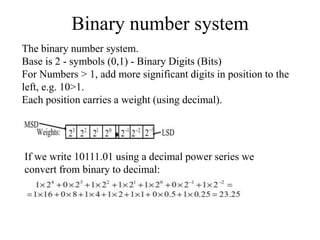
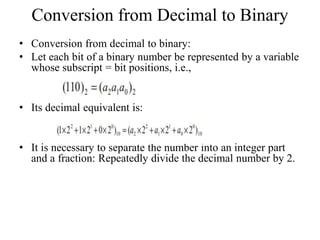
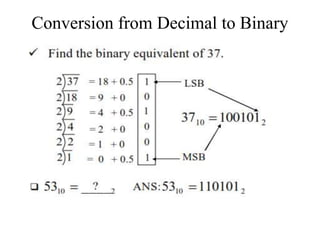
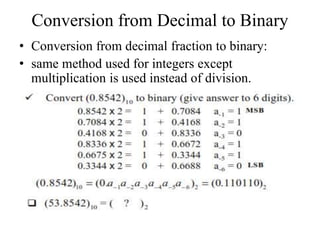
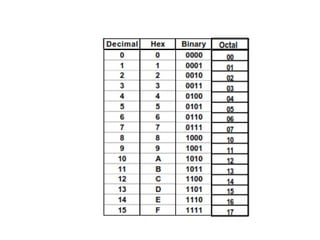
Digital systems use discrete binary values of 0s and 1s rather than continuous values. The binary number system represents numbers using a base-2 system with two digits: 0 and 1. Decimal, octal, and hexadecimal systems can be converted to and from the binary system using tables or repeated division/multiplication operations. Binary subtraction is performed using 1's or 2's complement representations of negative numbers, which involve inverting and adding 1. Digital circuits employ these binary representations and arithmetic operations to perform computations.