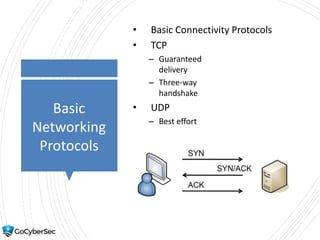
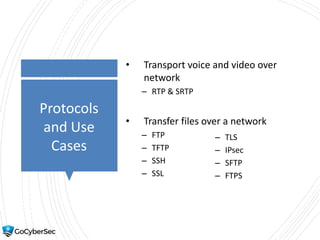
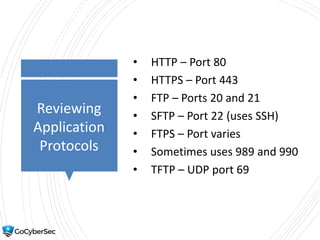
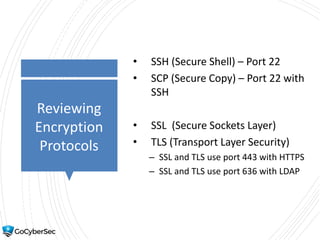
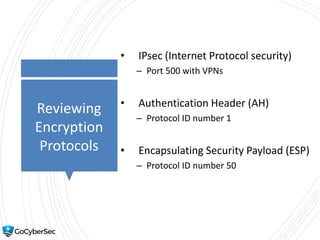
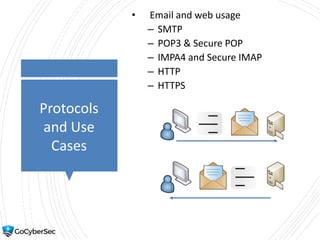
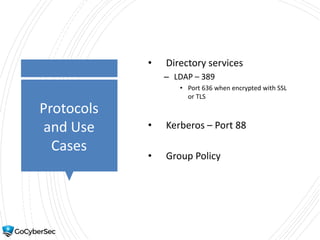
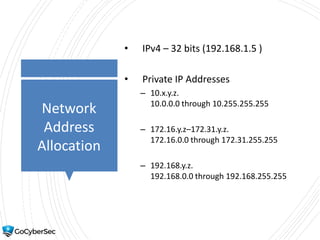
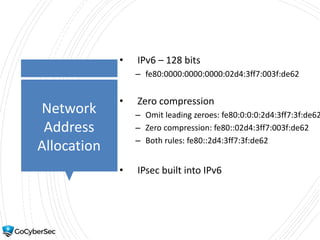
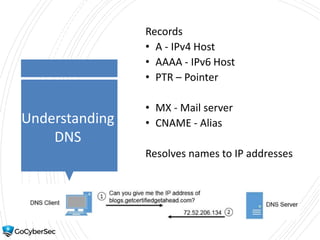
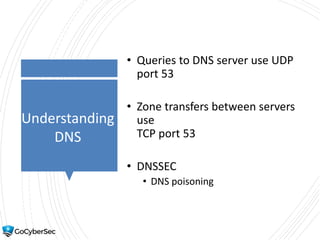
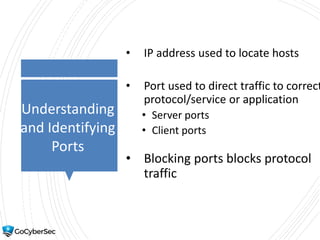
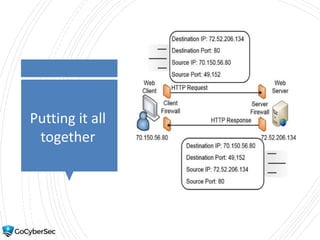
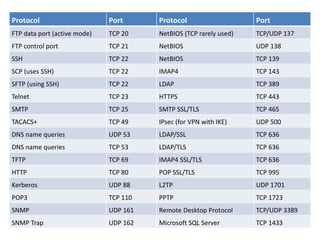
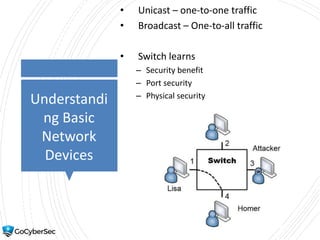
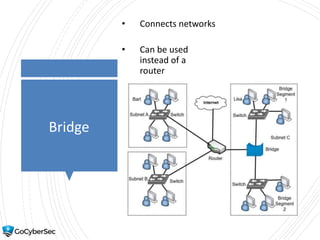
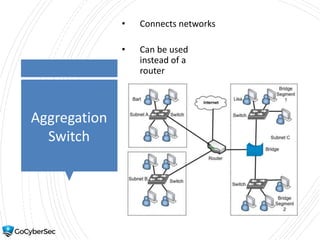
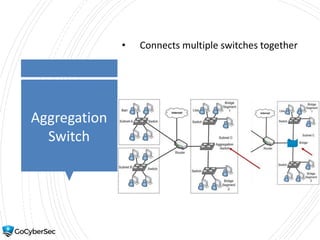
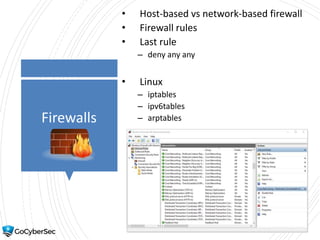
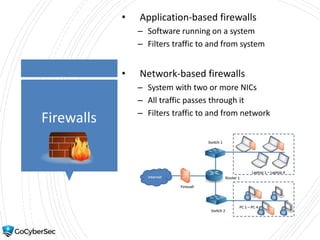
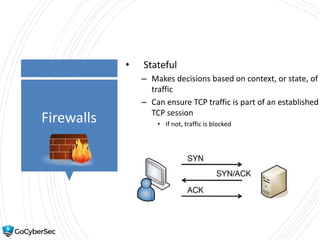
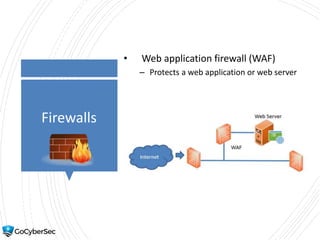
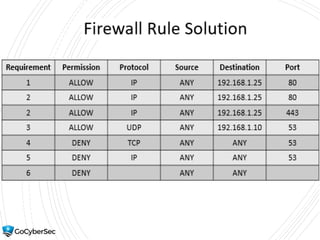
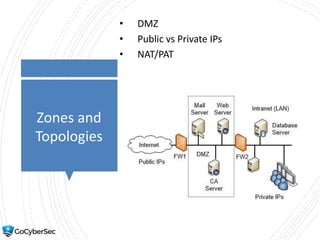
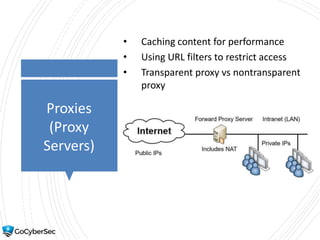
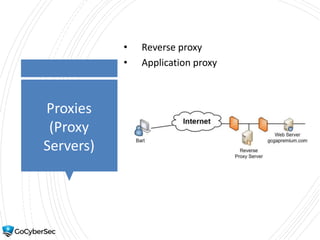
This chapter reviews basic networking concepts like protocols, ports, and network devices. It discusses how switches prevent flooding attacks and use protocols like STP. Routers are covered, including how they route traffic and use ACLs to filter traffic. Firewalls are also summarized, including the differences between stateful and stateless configurations and how firewall rules work. Network segmentation methods like DMZs, proxies, and VLANs are also introduced.