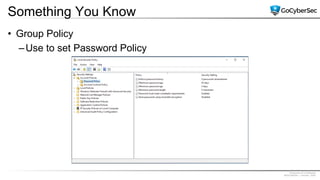
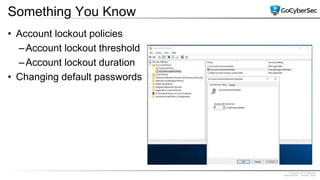
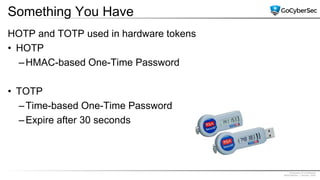
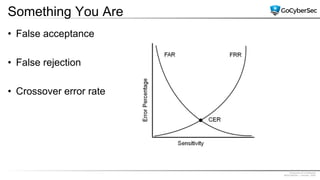
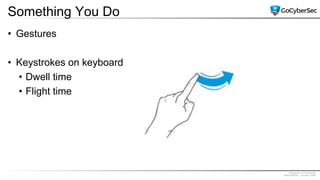
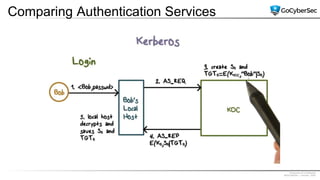
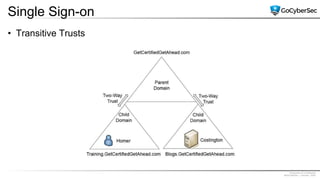
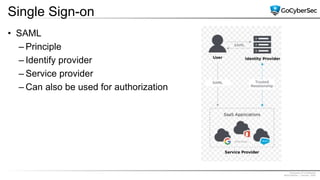
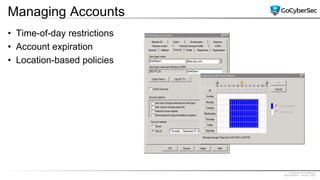
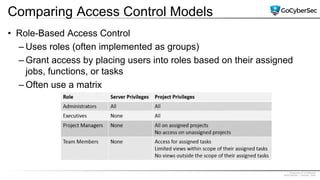
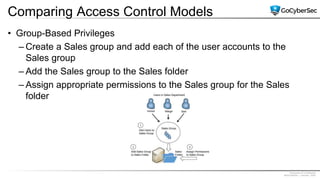
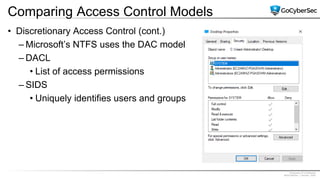
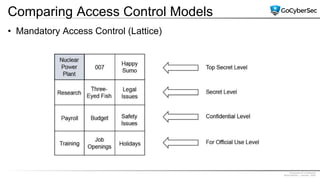
This document discusses identity and access management. It explores authentication concepts like identification, authentication, and authorization. It examines factors of authentication like something you know, have, or are. It also compares authentication services like Kerberos, LDAP, and single sign-on. The document discusses managing user accounts and compares access control models such as role-based access control, discretionary access control, and mandatory access control.