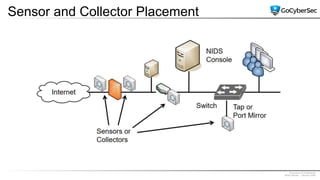
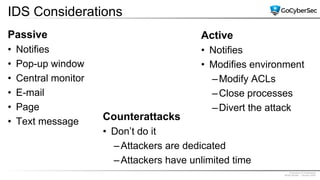
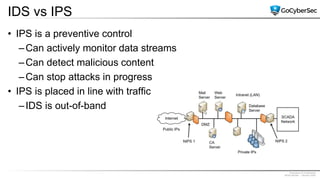
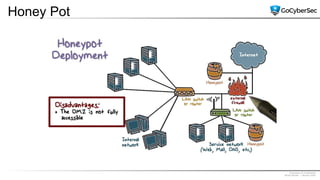
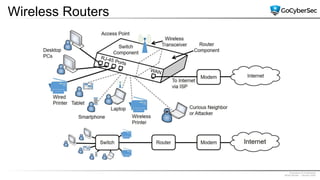
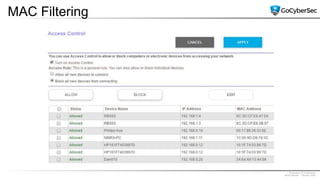
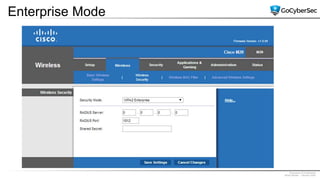
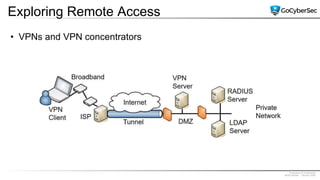
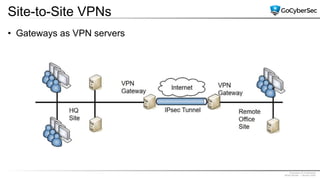
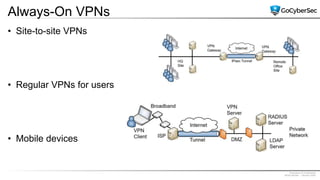
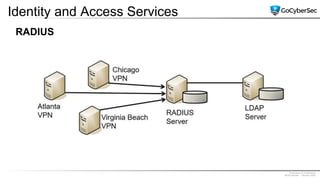
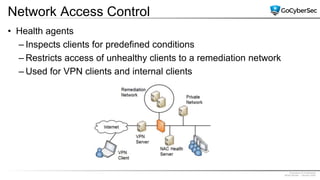
This document discusses securing networks through the use of intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, packet sniffers, firewalls, virtual private networks, and securing wireless networks. It covers topics such as host-based and network-based IDS, sensor placement, detection methods, VPN types, wireless encryption, and common wireless attacks.