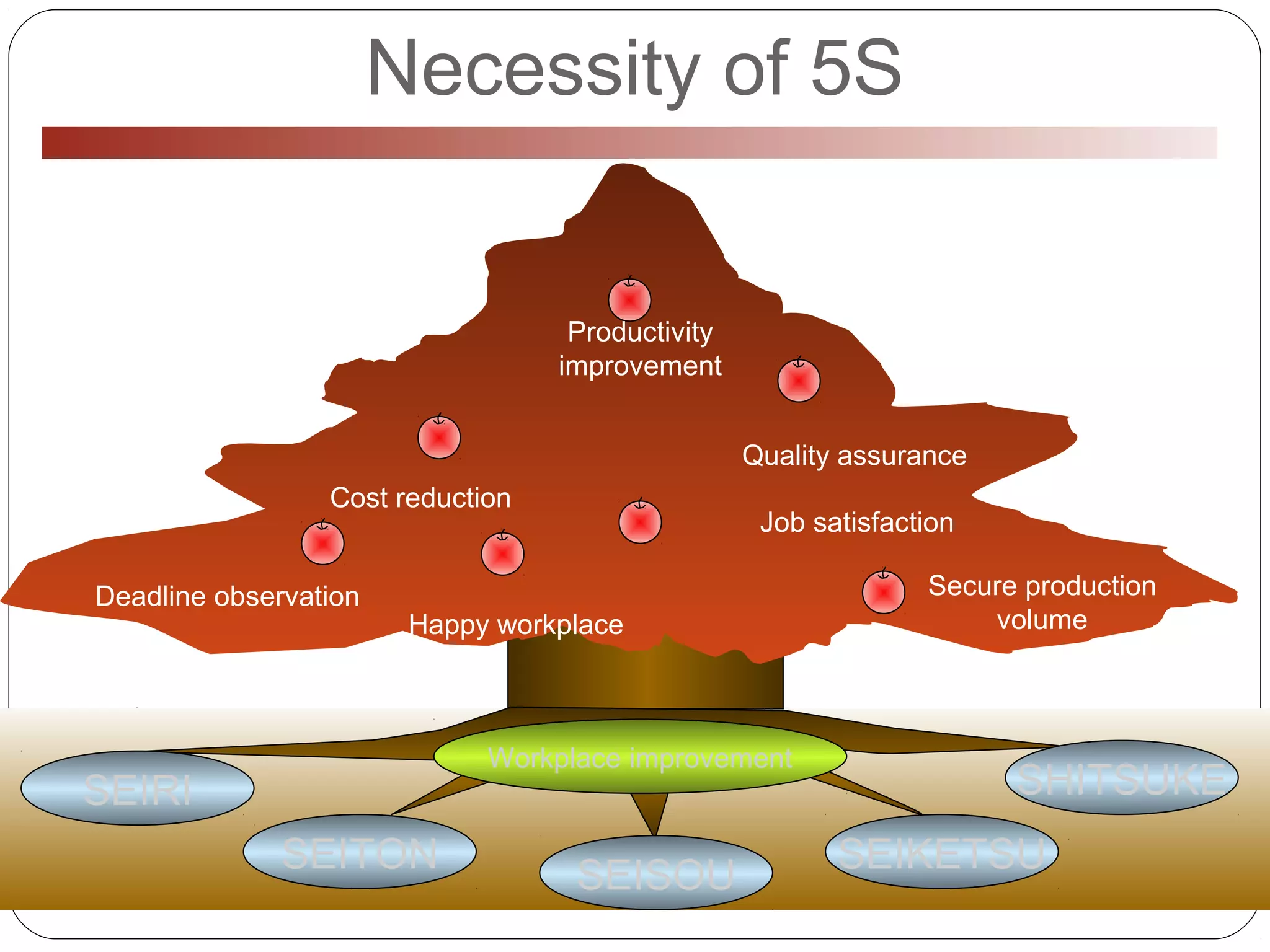
The document outlines the 5S methodology, consisting of five key components: Seiri (Sort), Seiton (Set in Order), Seisou (Shine), Seiketsu (Standardize), and Shitsuke (Sustain), aimed at improving workplace productivity and maintaining a clean and organized environment. It discusses the importance of self-discipline in successfully implementing 5S and provides practical steps for each component to enhance workspace efficiency and ensure adherence to standards. Additionally, it includes examples and tools for achieving effective organization and cleanliness within the workplace.