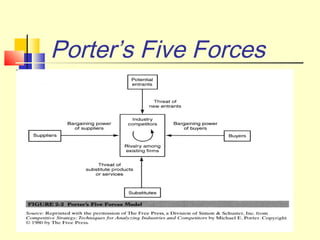
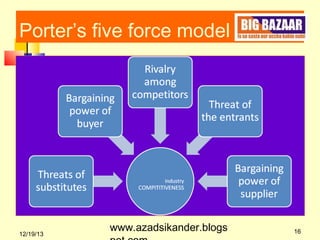
Michael Porter's Five Forces Model analyzes the competitive dynamics within an industry, emphasizing that profit potential is influenced by competitive rivalry and various structural factors. The model includes five forces: the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors, each affecting industry profitability. A case study in the retail sector highlights how these forces manifest, particularly focusing on supplier power and consumer behavior in India.