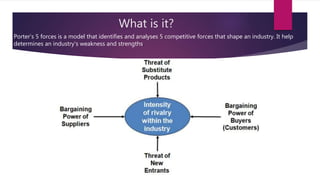
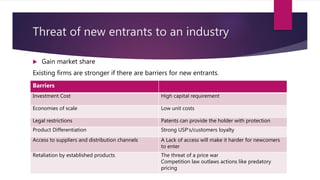
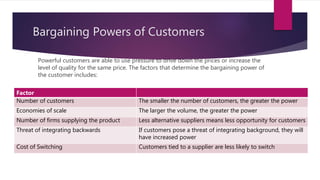
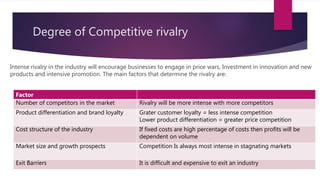
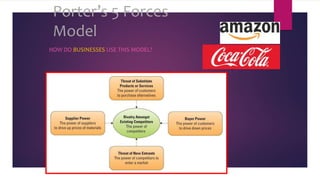
Porters 5 Forces Model identifies 5 competitive forces that shape an industry: (1) threat of new entrants, (2) bargaining power of suppliers, (3) bargaining power of customers, (4) threat of substitute products, and (5) competitive rivalry. This model helps analyze an industry's weaknesses and strengths. For IKEA, rivalry is intense but barriers to entry are high. Customer bargaining power is strong while supplier power is low. Substitute threats are also low. For Coca-Cola Enterprises, economies of scale are a barrier to entry while supplier relationships are strong. Customer switching costs are low and competitive rivalry is high.