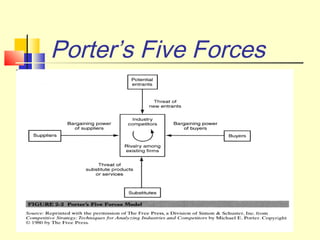
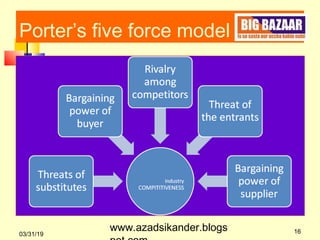
Michael Porter's Five Forces model analyzes competitive rivalry and industry profitability. The model examines five forces: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Porter argued that these five forces determine the ultimate profit potential of an industry. The model provides a framework for analyzing the key factors influencing organizational strategy within an industry.