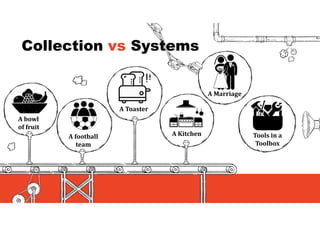
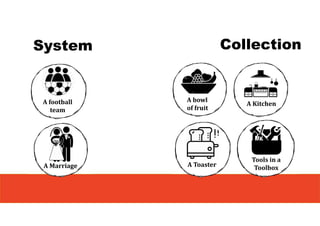
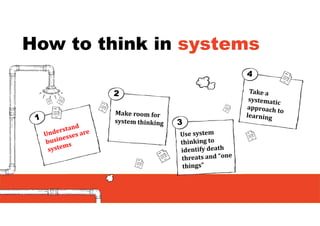
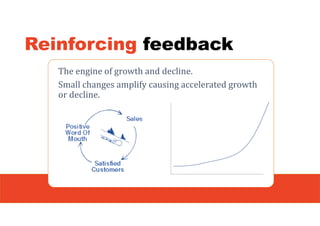
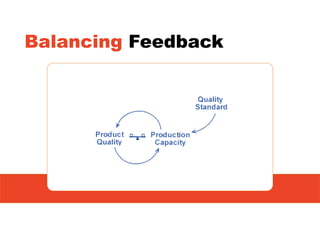
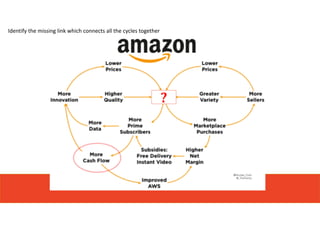
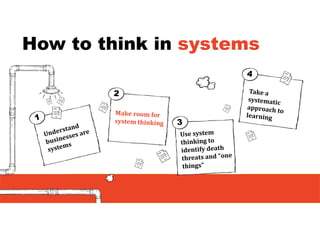
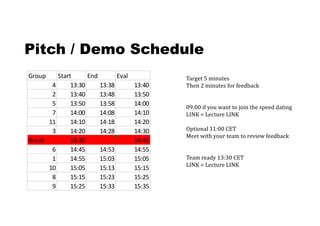
1. The document discusses systems thinking and applying it to business and innovation.
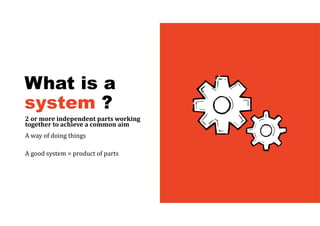
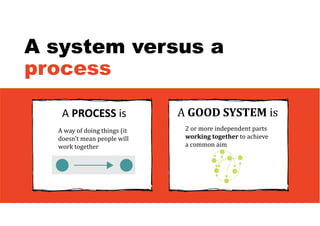
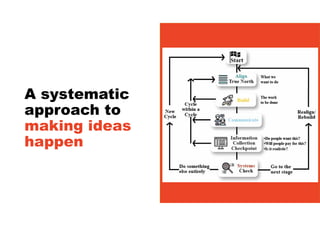
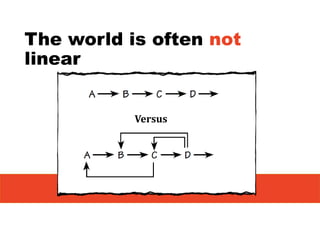
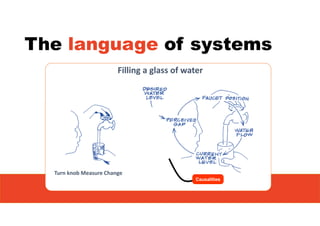
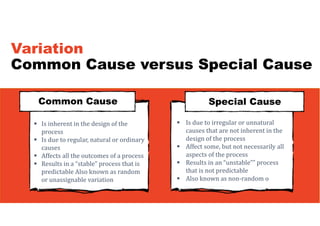
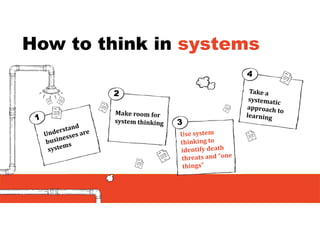
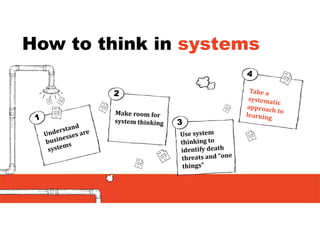
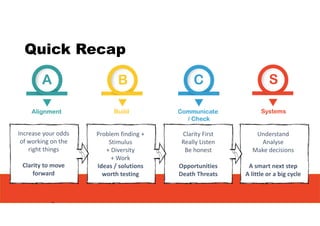
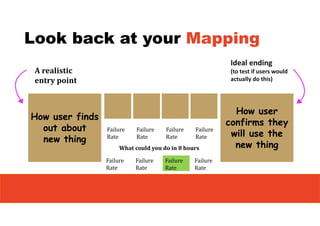
2. It emphasizes understanding how all parts of a system work together and influence each other, as well as identifying high-leverage opportunities to improve the system.
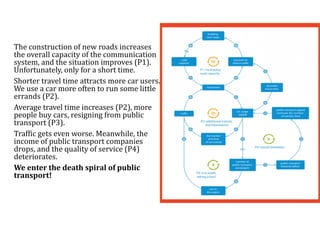
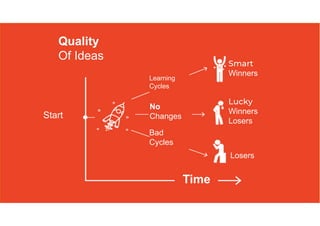
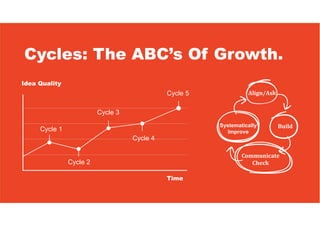
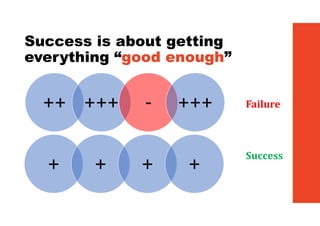
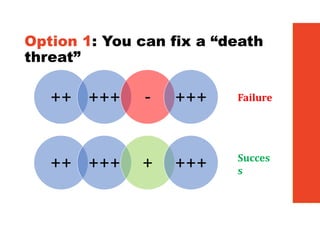
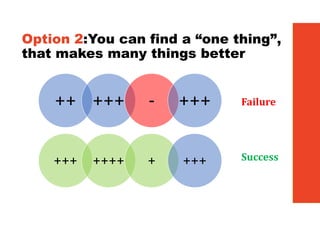
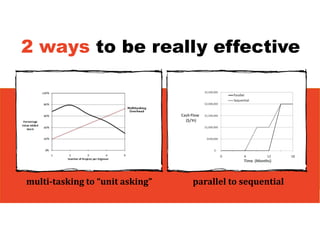
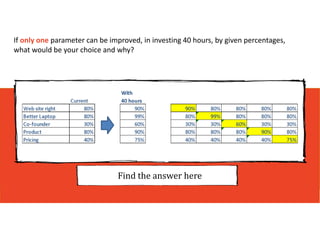
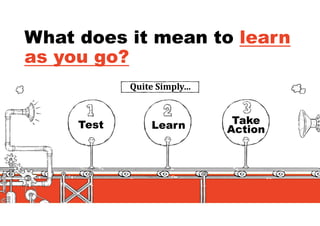
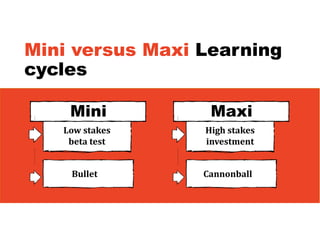
3. The key lessons are to take a holistic view of the system, understand how different elements impact each other through feedback loops, and use an active learning approach of testing ideas in small cycles to drive iterative improvement of the overall system.