This document discusses the evolution of wireless communication technologies from 0G to 4G. It provides an overview of each generation including key features and standards. The main points covered are:
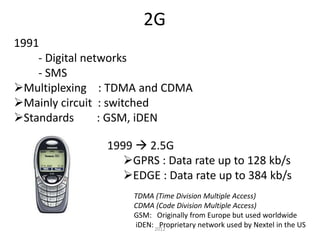
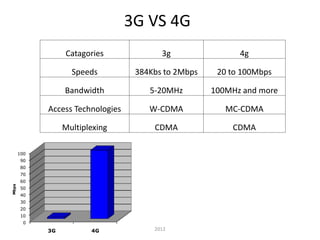
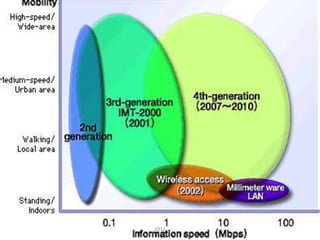
- 0G began with analog radio technology. 1G introduced the first analog cell phone networks. 2G brought digital networks and SMS. 3G added IP-based services like video calling.
- 4G is defined as providing speeds up to 100 Mbps for mobile use and 1 Gbps when stationary, using wide bandwidths of 100MHz and above. It will combine with IP services.
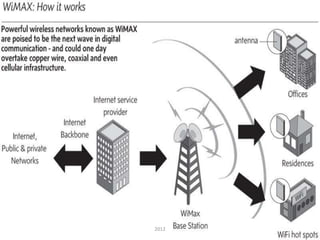
- Applications of 4G include virtual presence, telemedicine, tele-education and high quality video. The document also introduces WiMAX as