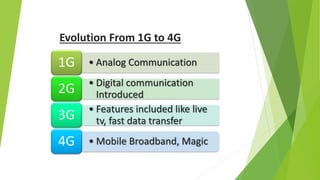
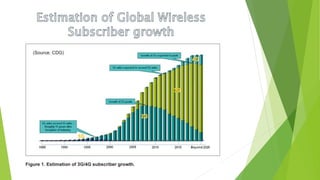
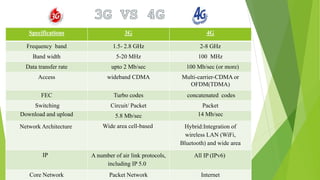
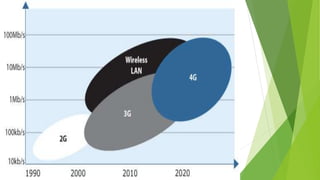
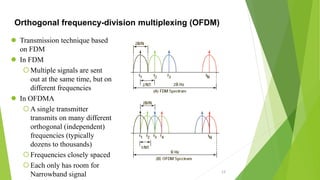
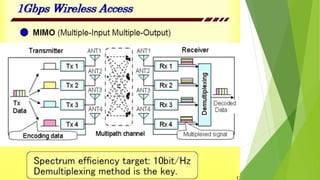
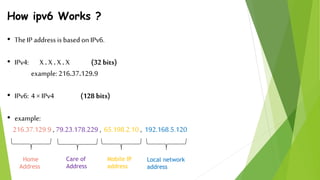
1) Wireless communication has evolved from 1G to 4G networks, with each generation offering faster speeds and new capabilities. 2) 4G networks provide broadband speeds up to 1Gbps using technologies like OFDMA, MIMO, and an all-IP packet switched network. 3) Key aspects of 4G include mobile broadband access, customized services, and support for multimedia and voice over internet protocol.