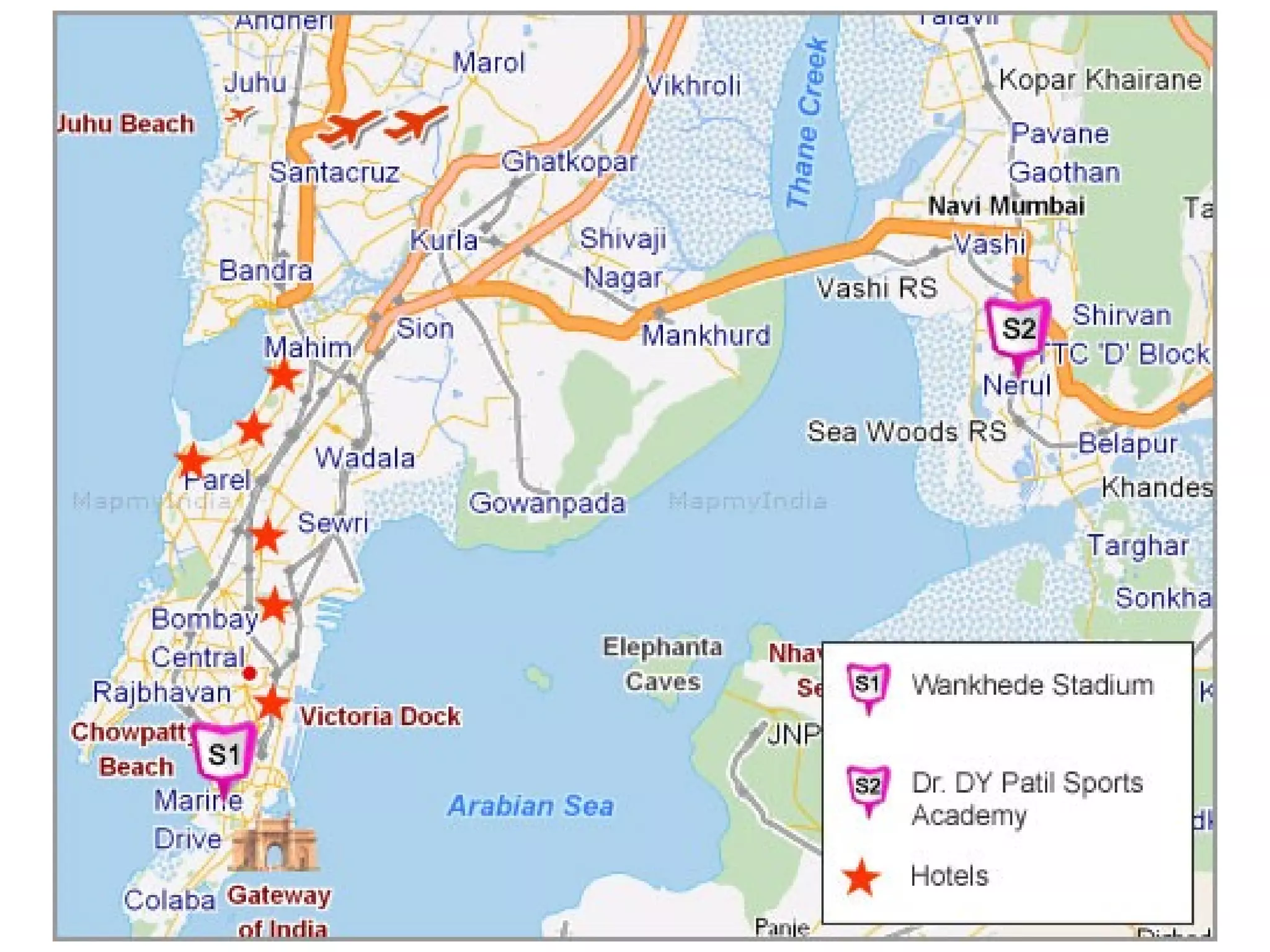
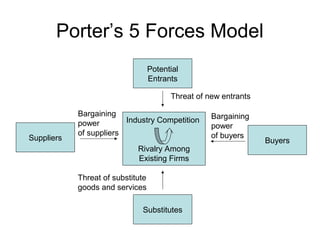
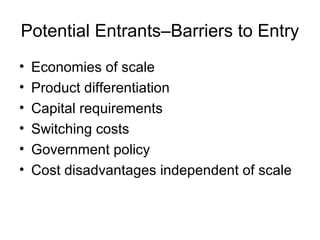
Porter's 5 Forces model analyzes competitive forces in an industry including the threat of new entrants, power of suppliers and buyers, and threat of substitute products. The model outlines factors that influence barriers to entry like economies of scale, product differentiation, and capital requirements. It also describes how concentrated and high-volume buying groups gain bargaining power over sellers, and how connected suppliers of important inputs gain power if substitutes are unavailable.