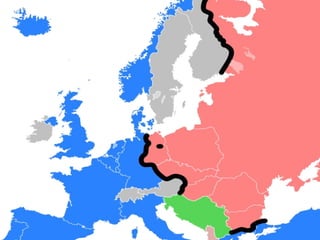
The Cold War was a state of political and military tension between Western powers led by the US and Eastern powers led by the Soviet Union from 1945-1989. It arose due to ideological differences that divided Europe into Western and Eastern blocs, with the Iron Curtain symbolizing efforts by the Soviet Union to isolate itself and its satellite states. Though direct war was avoided due to nuclear deterrence, the conflict played out through regional proxy wars like in Korea and Vietnam, and crises like the Berlin Blockade increased tensions between the two superpowers.