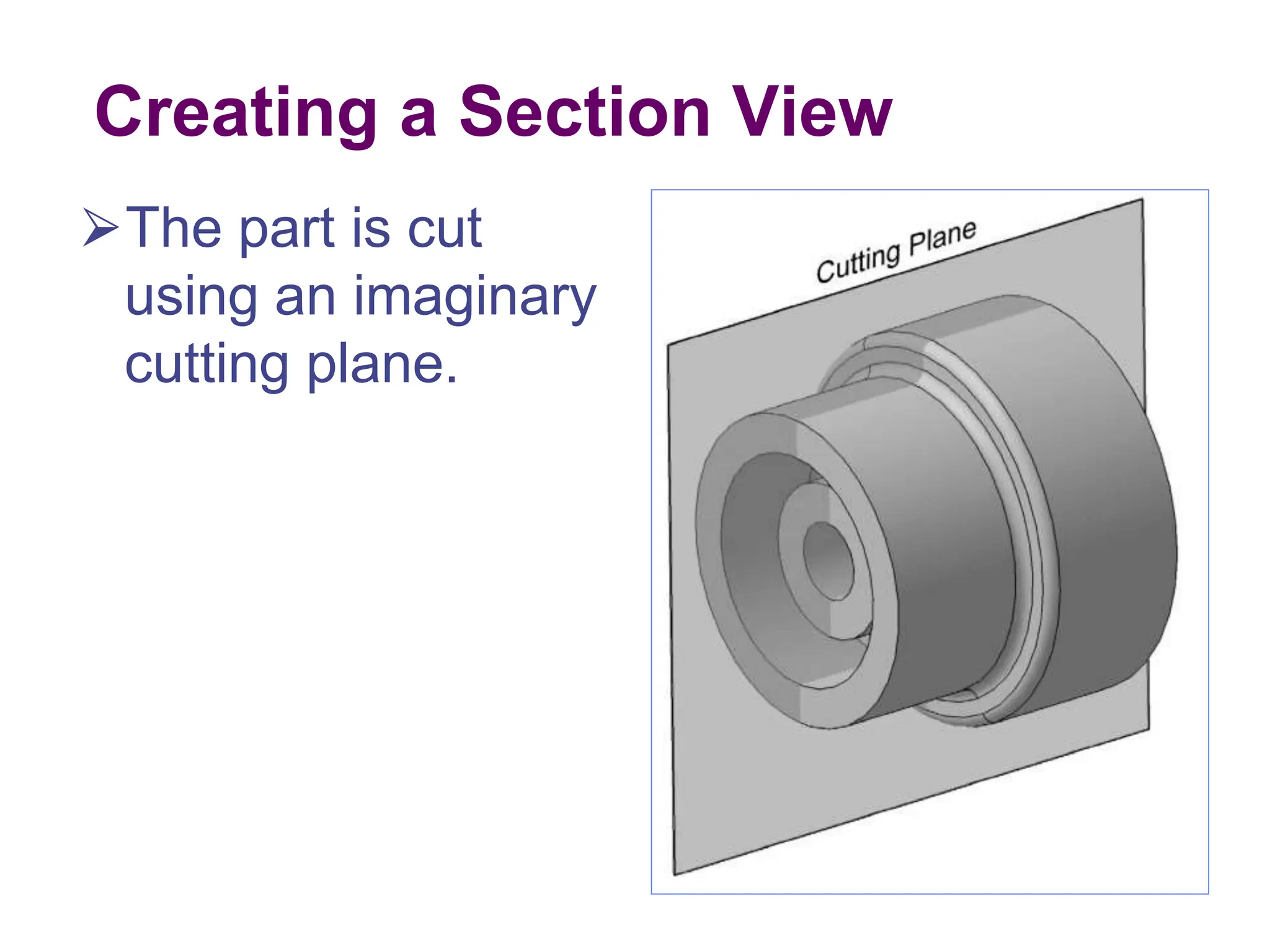
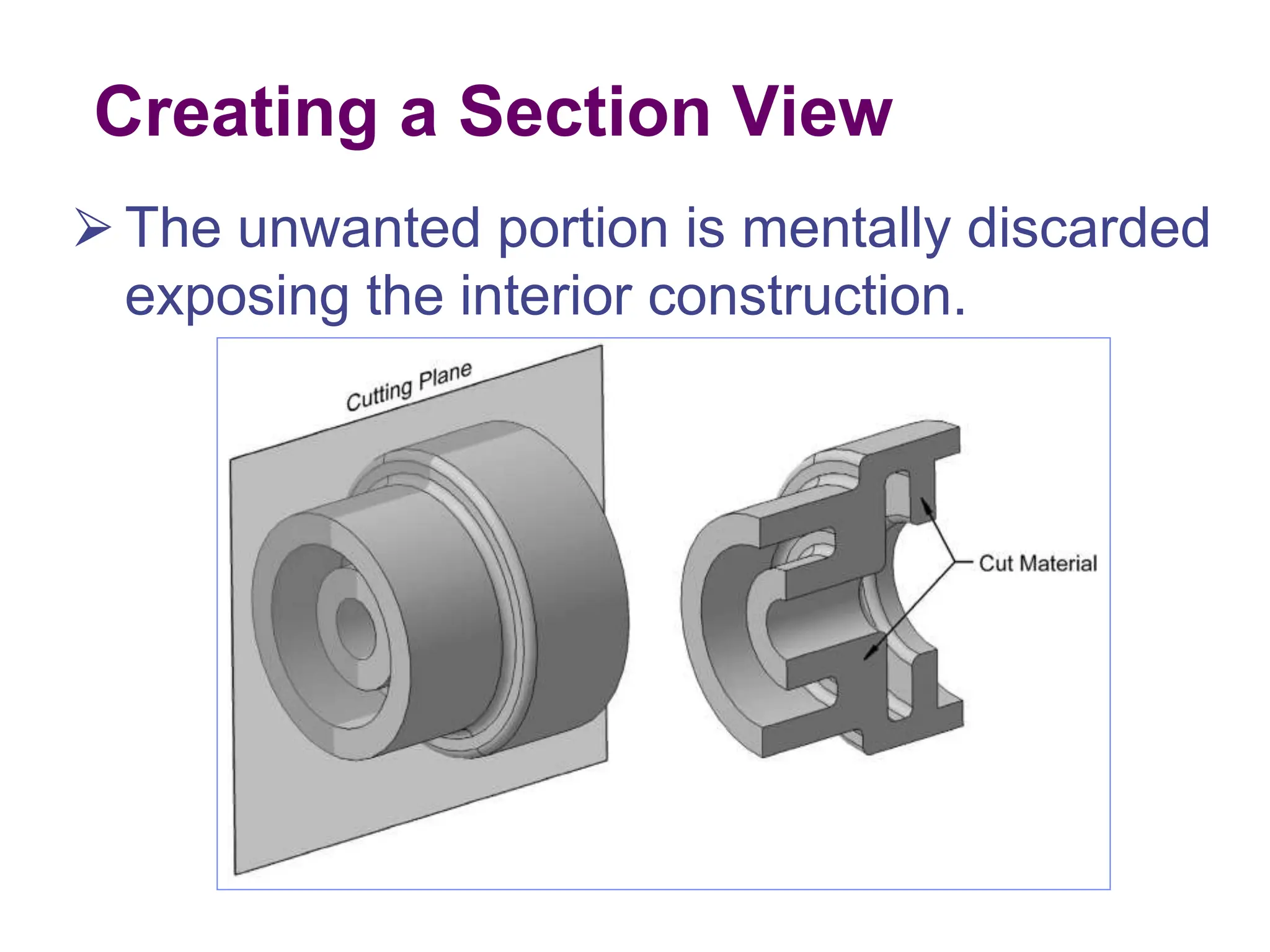
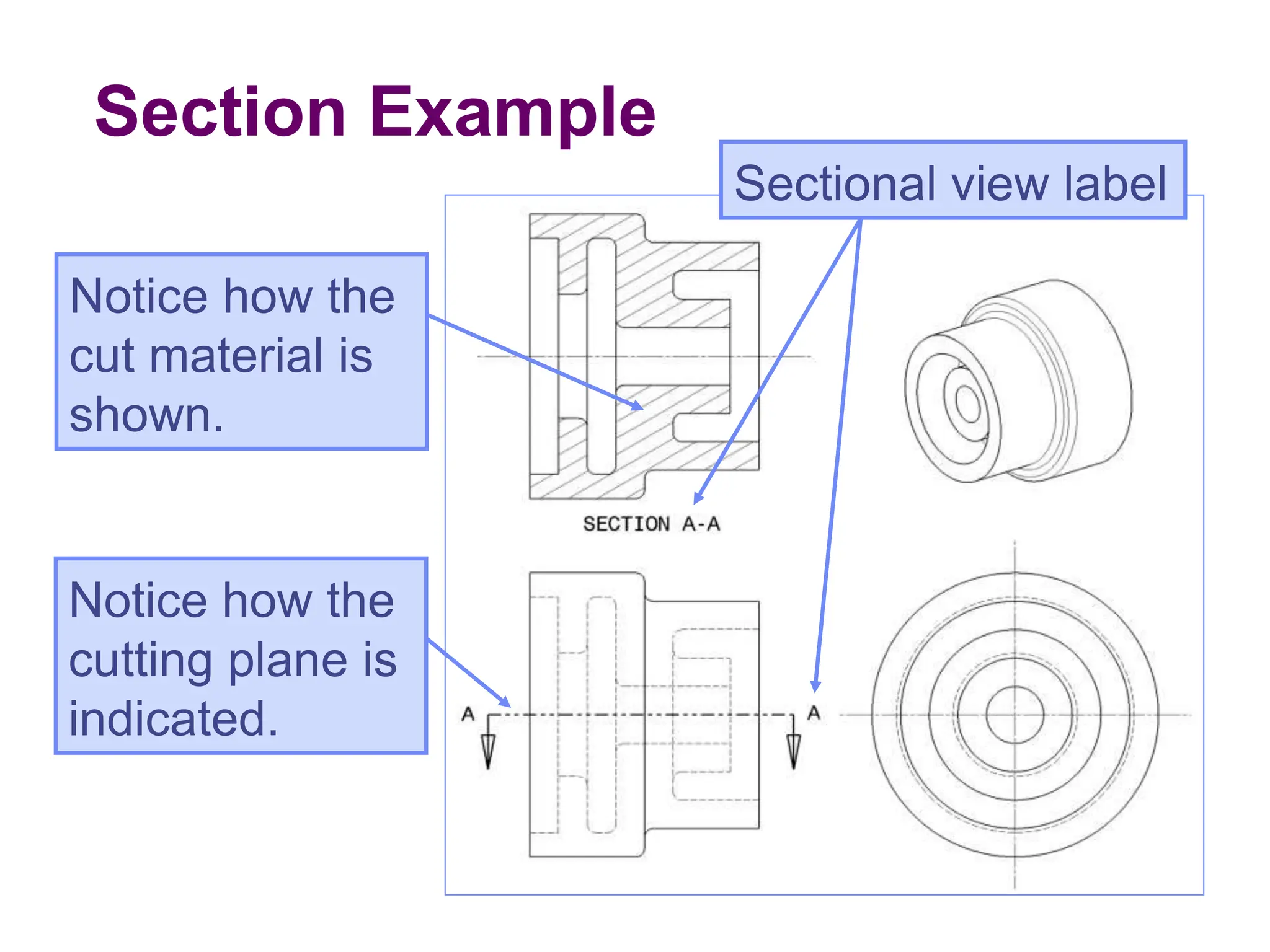
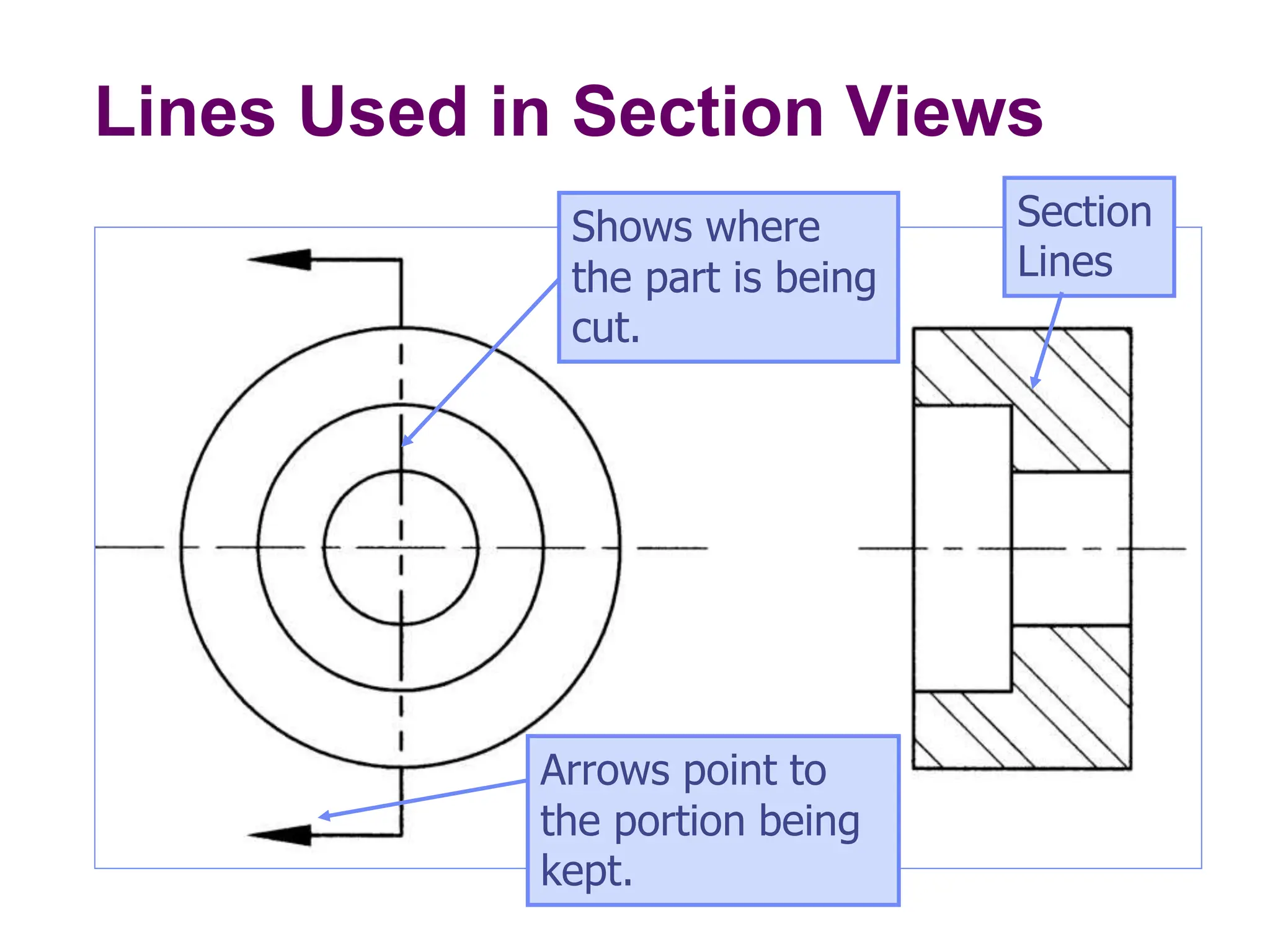
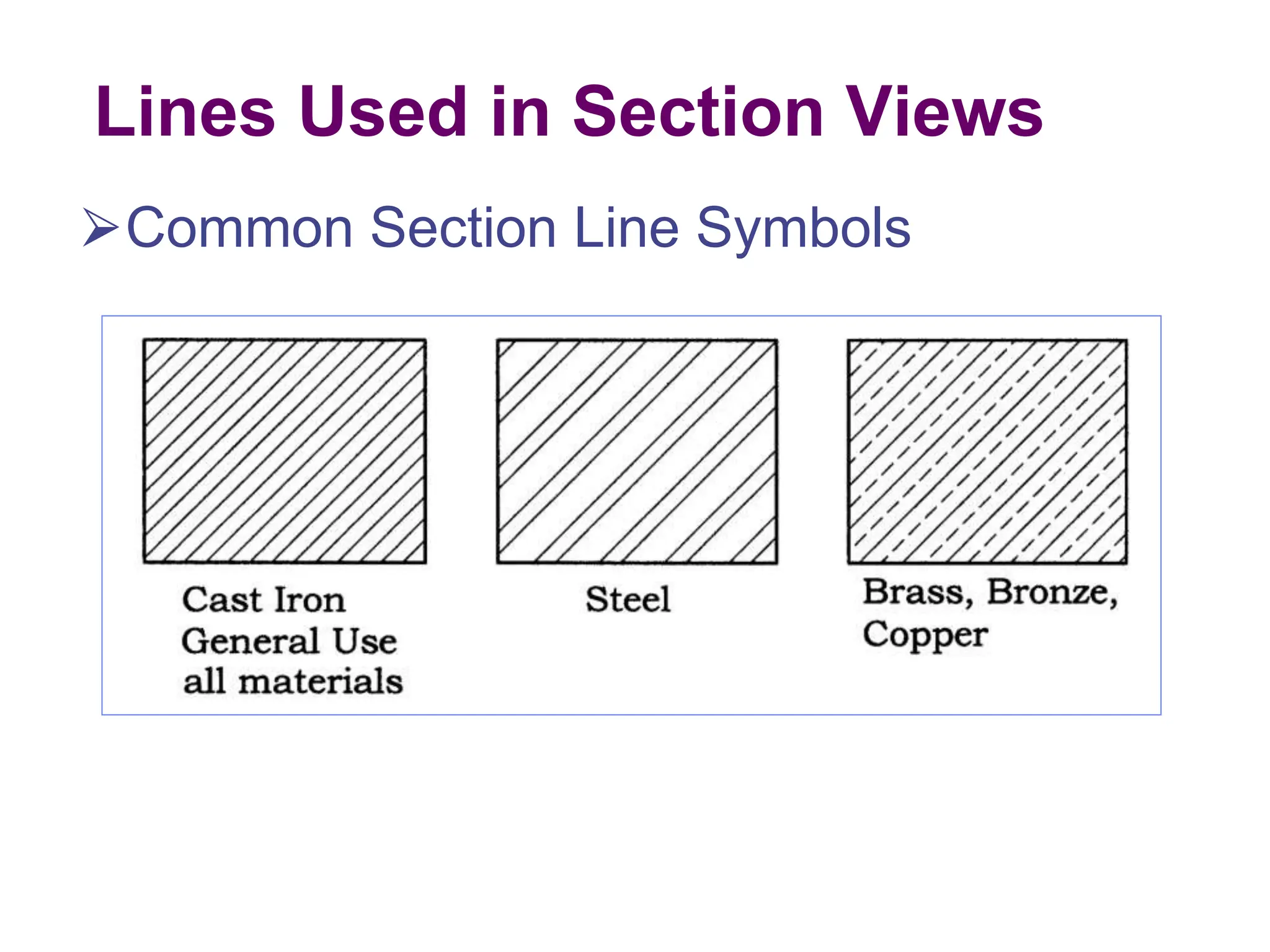
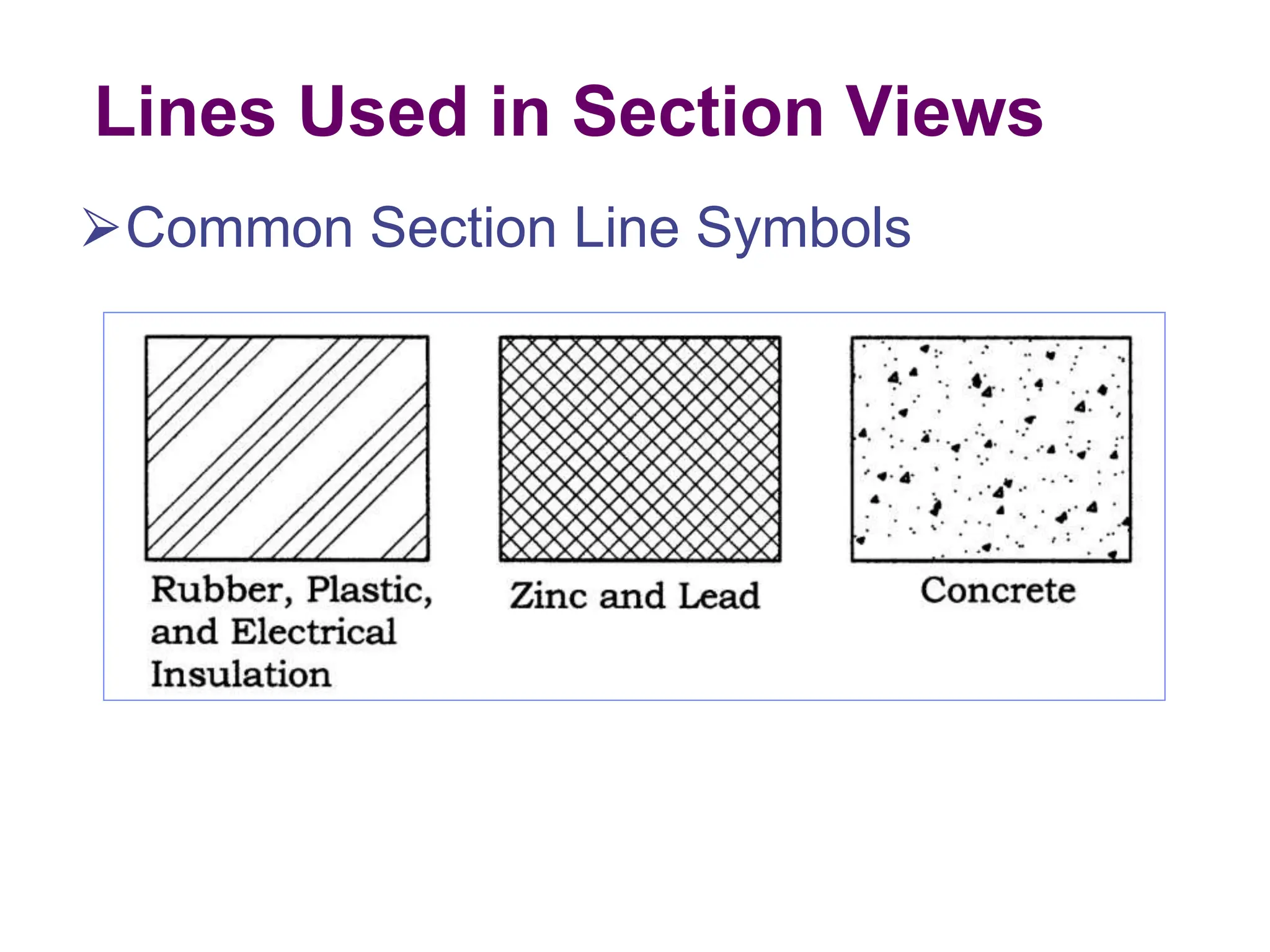
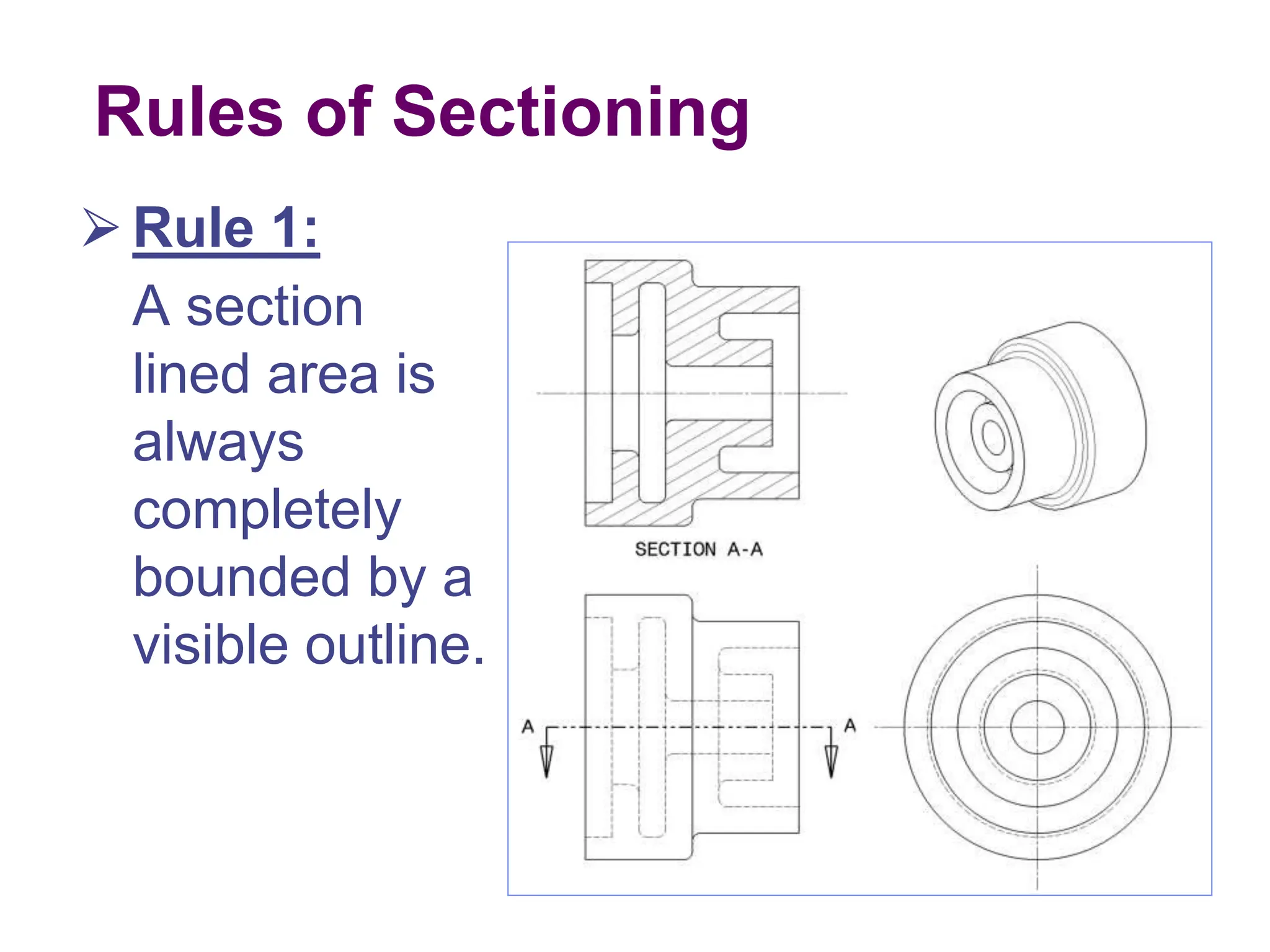
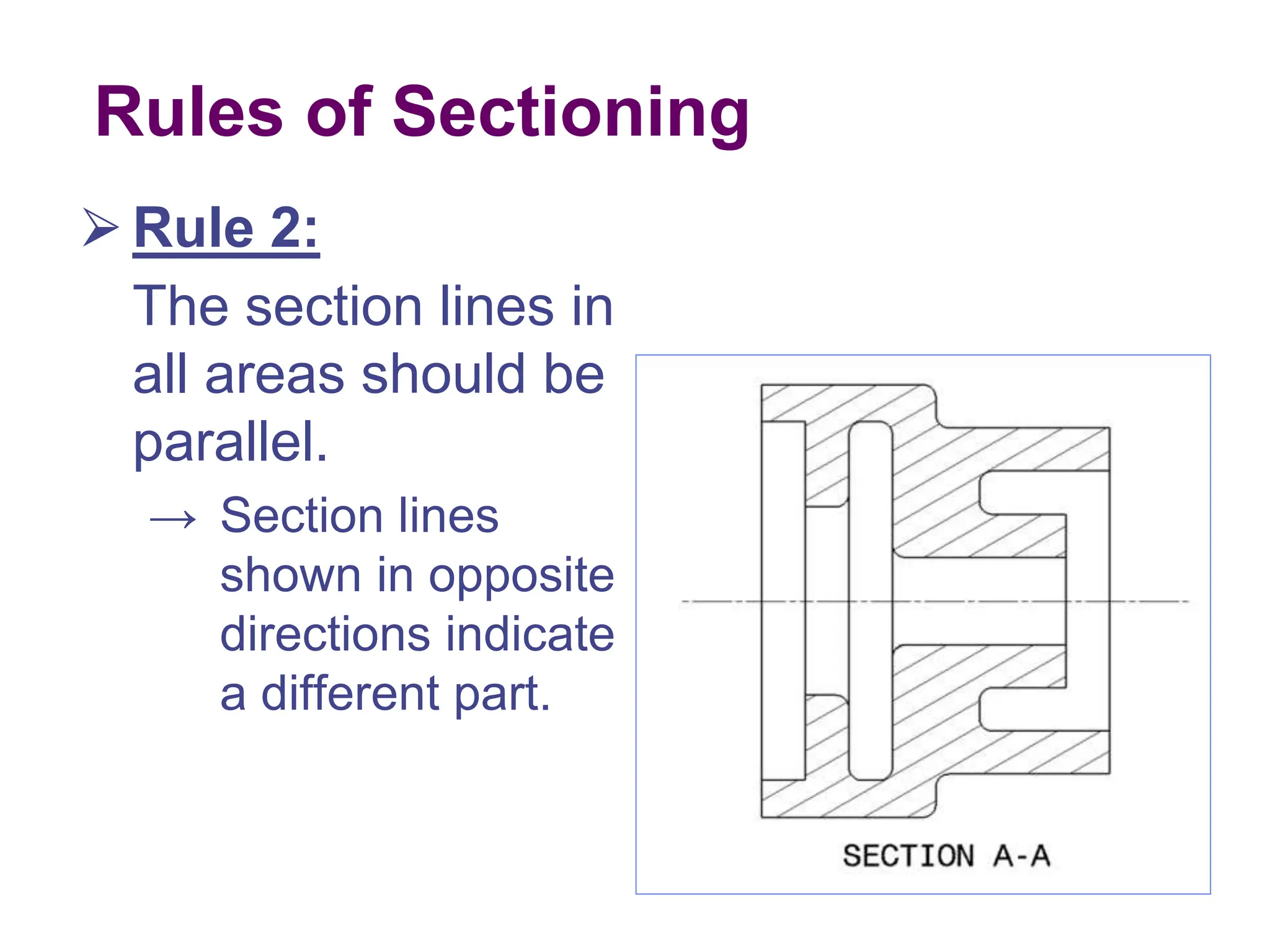
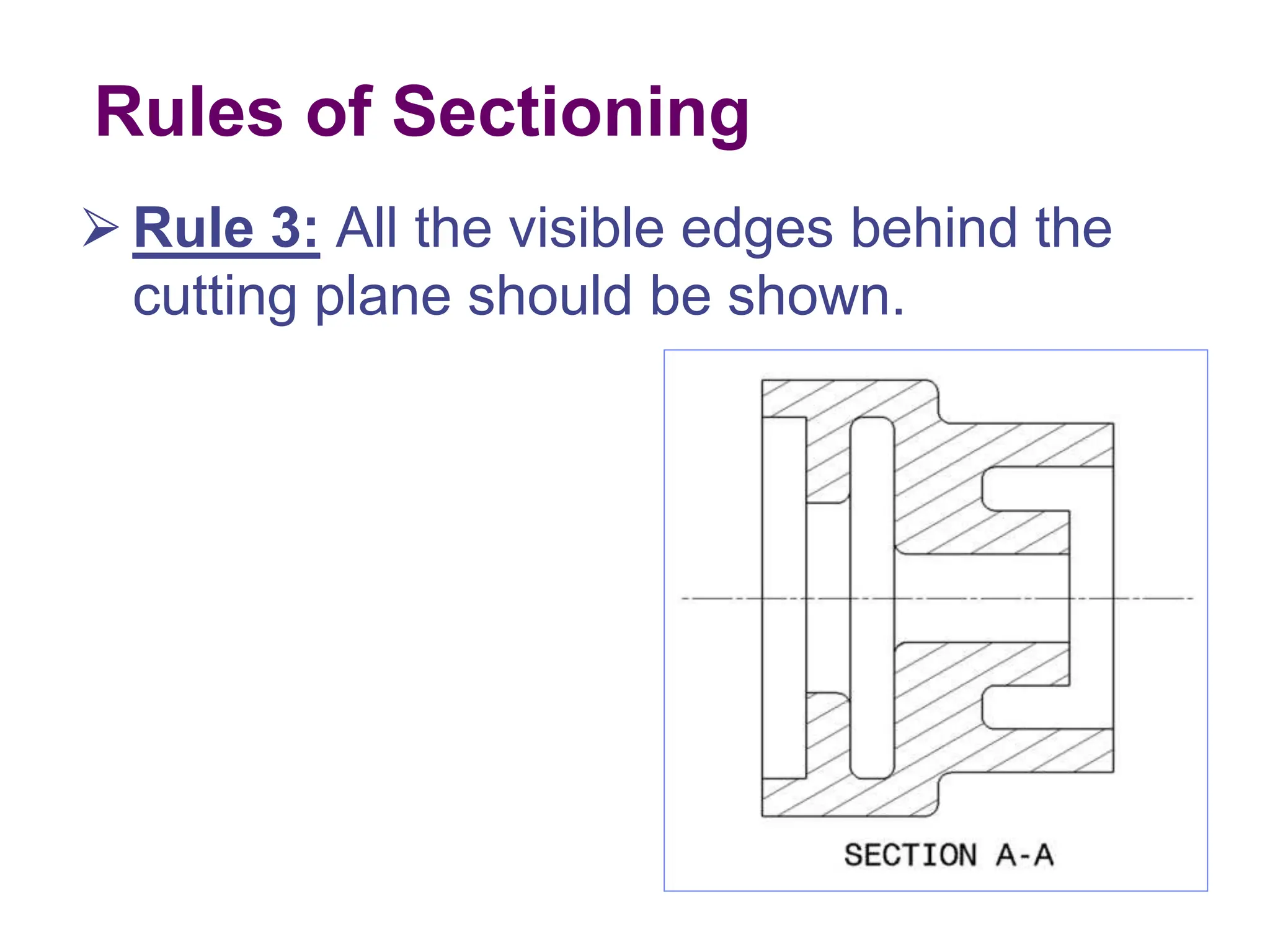
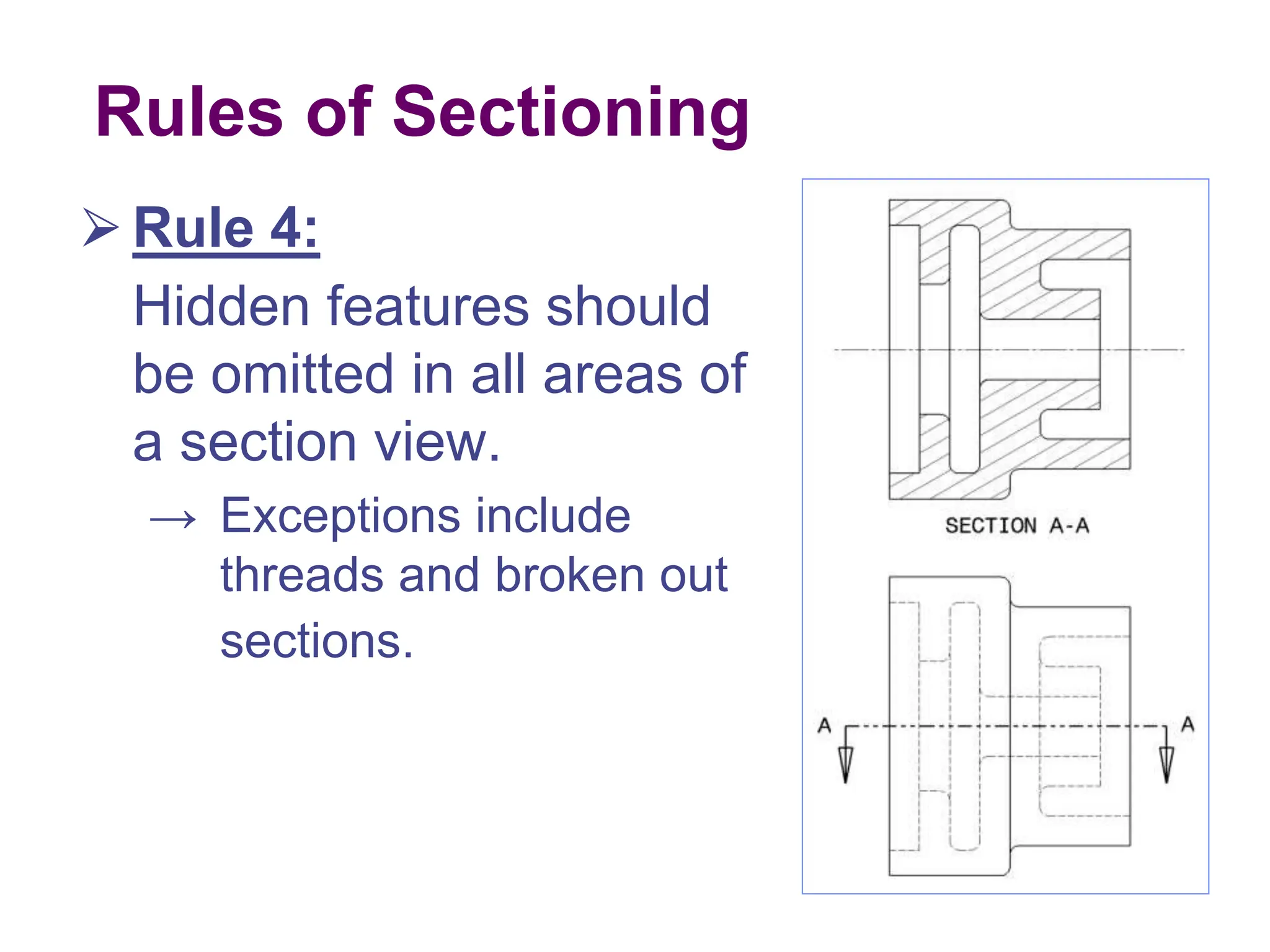
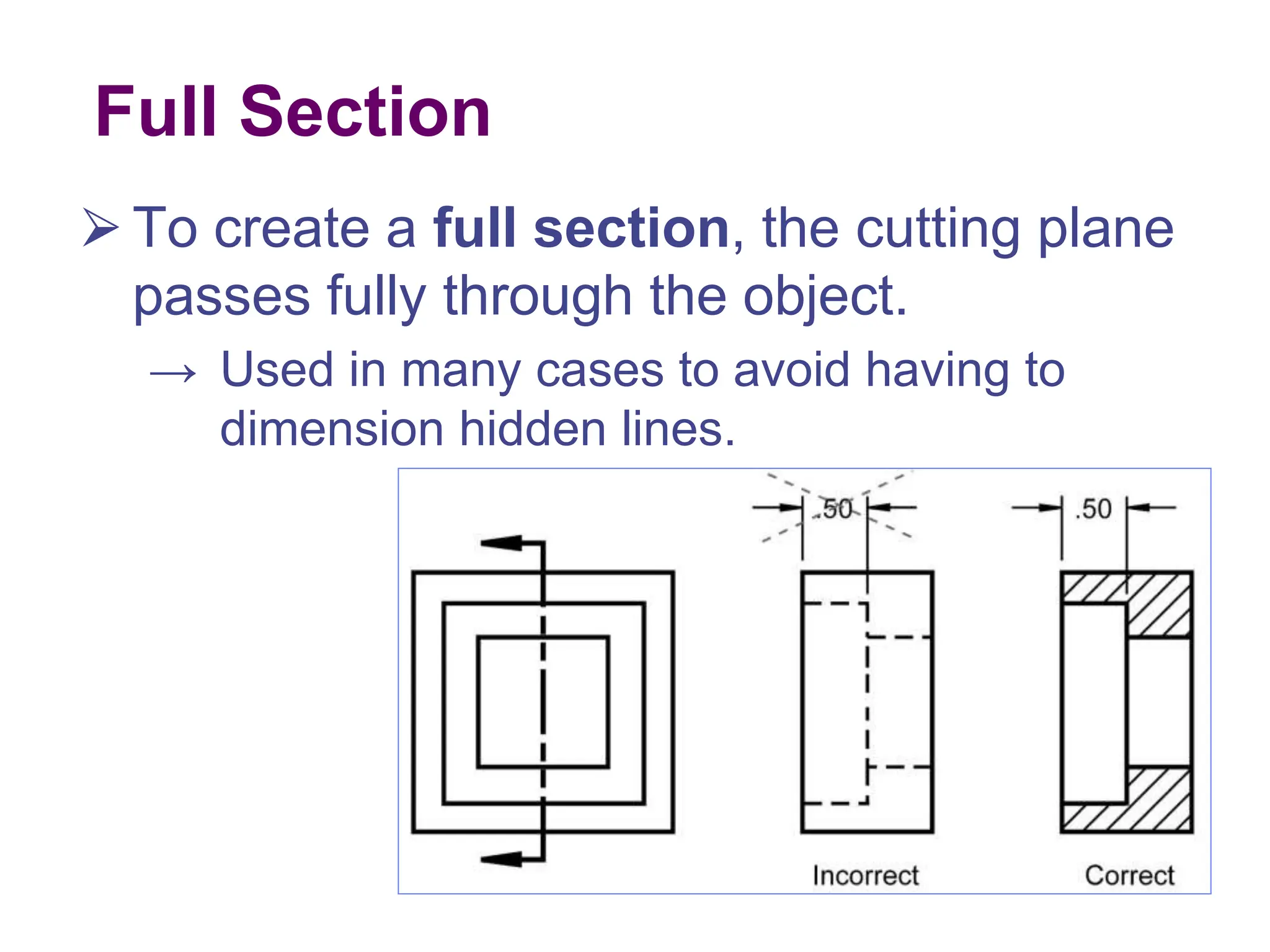
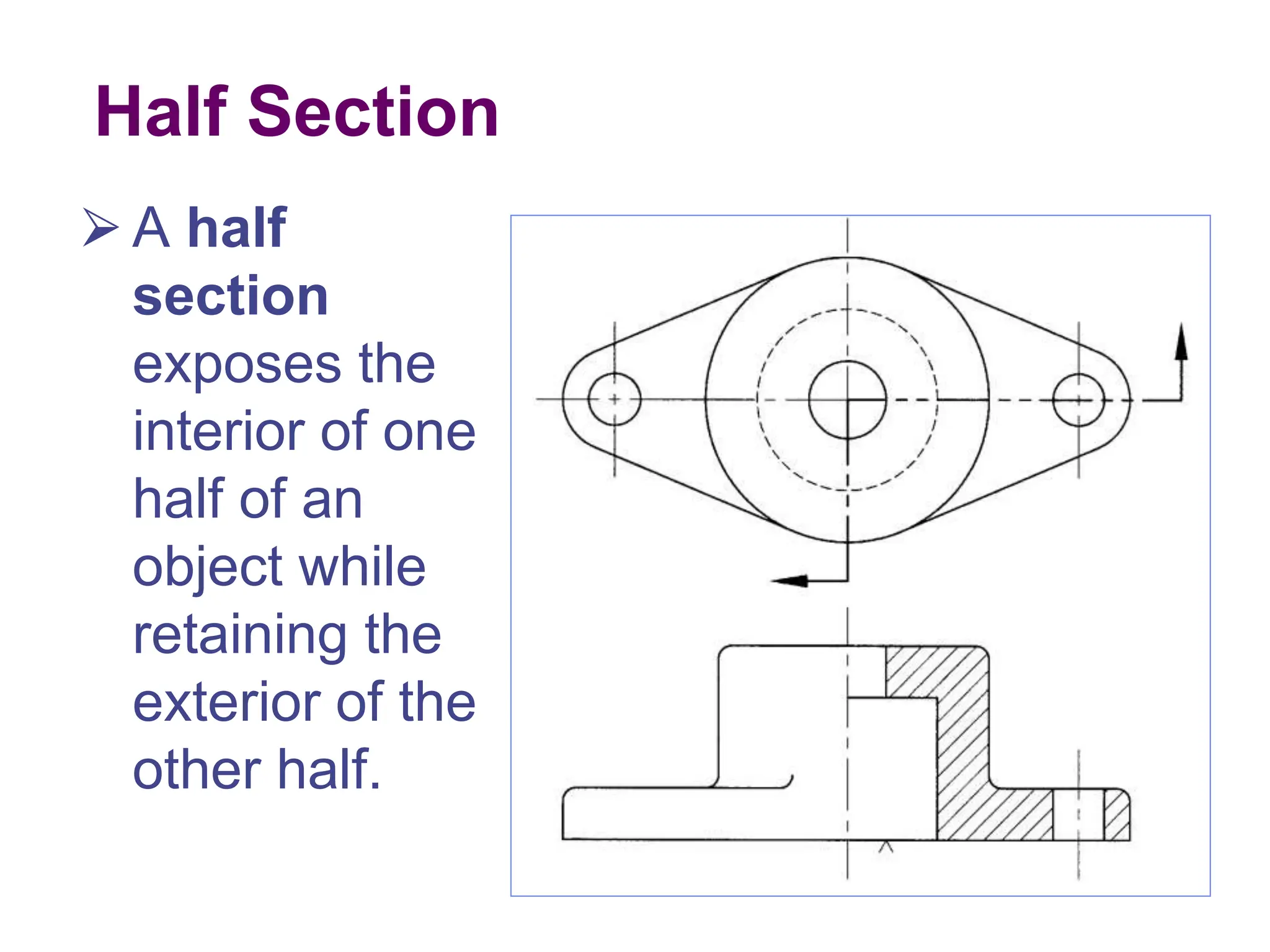
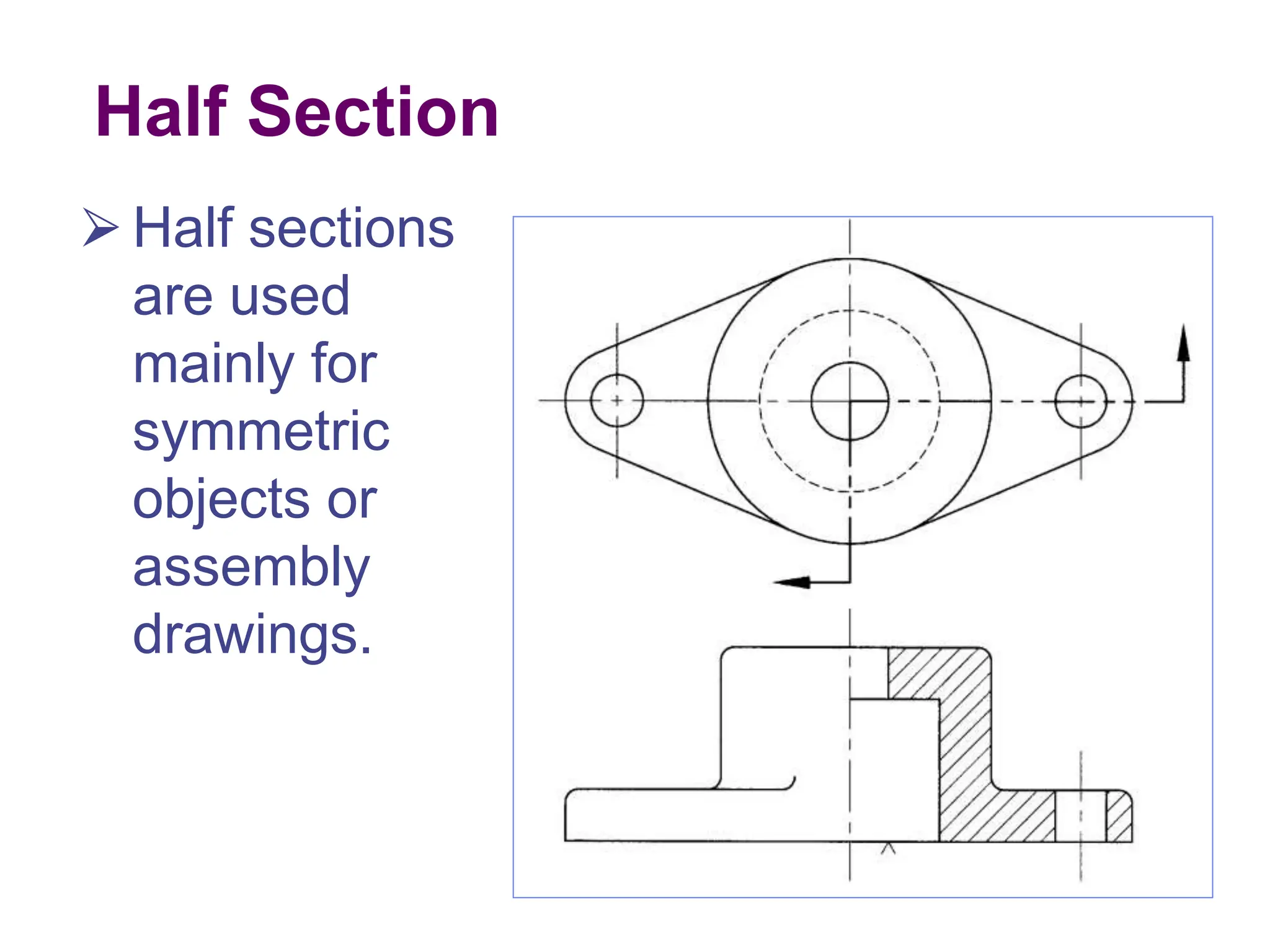
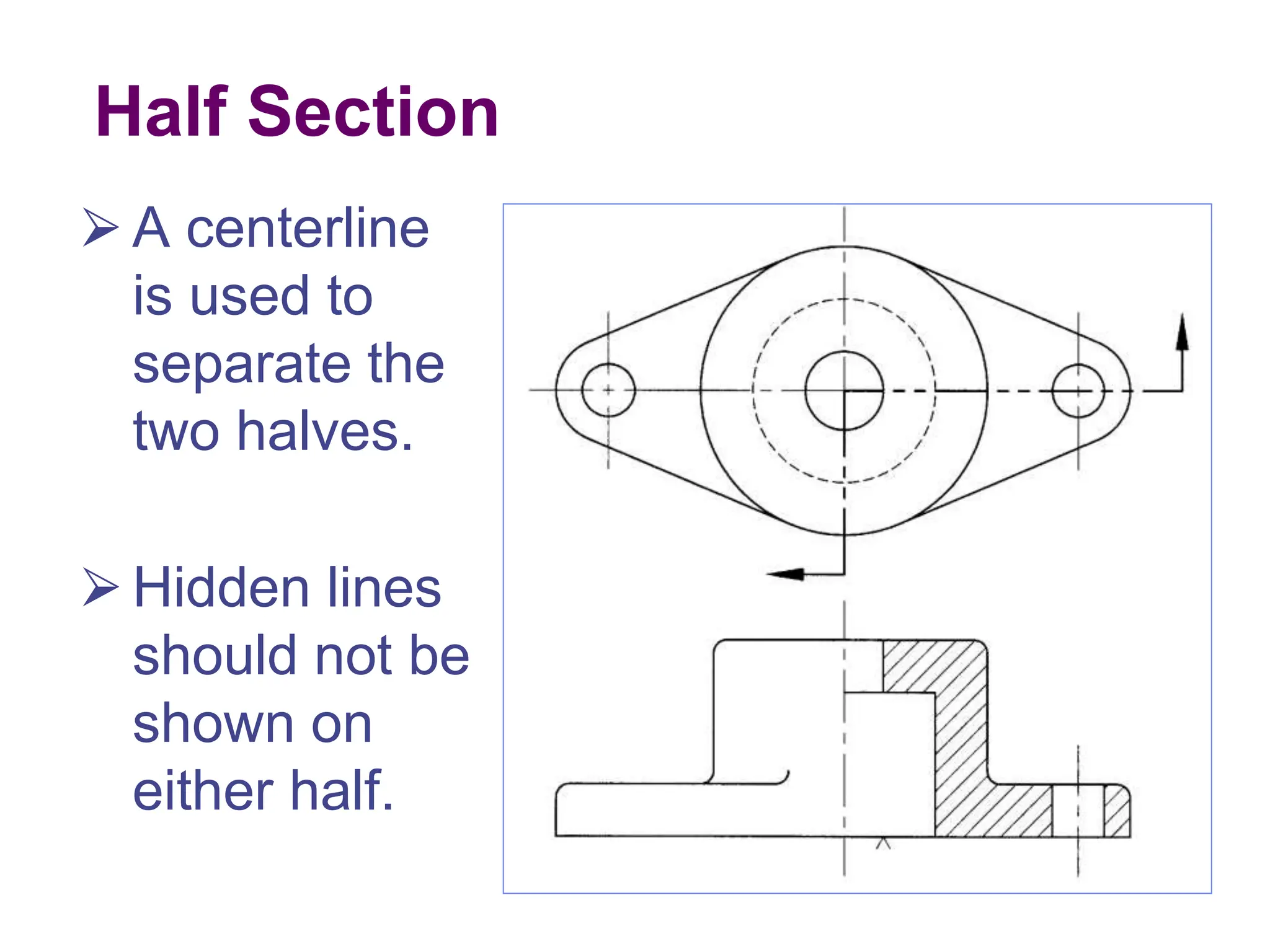
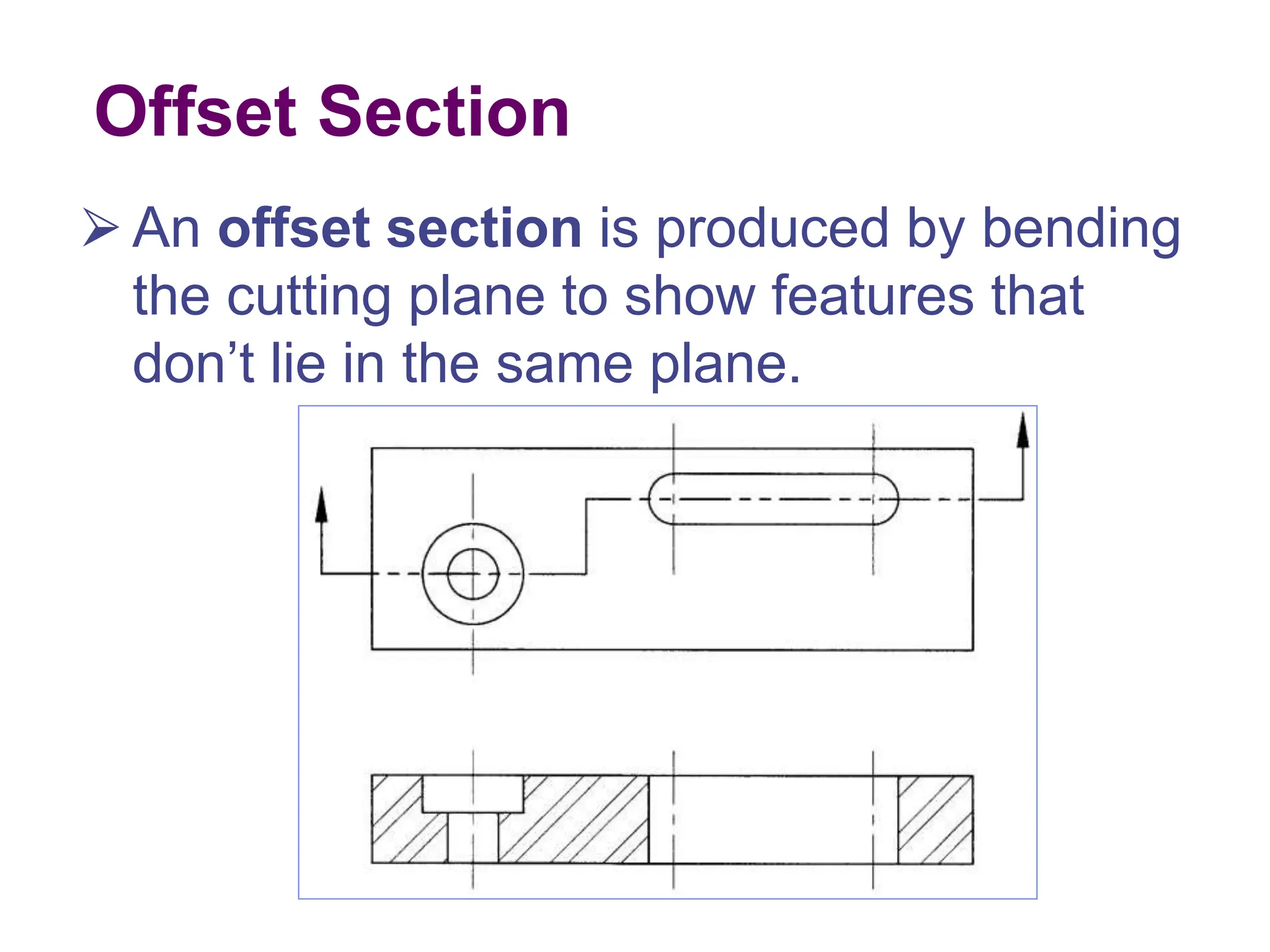
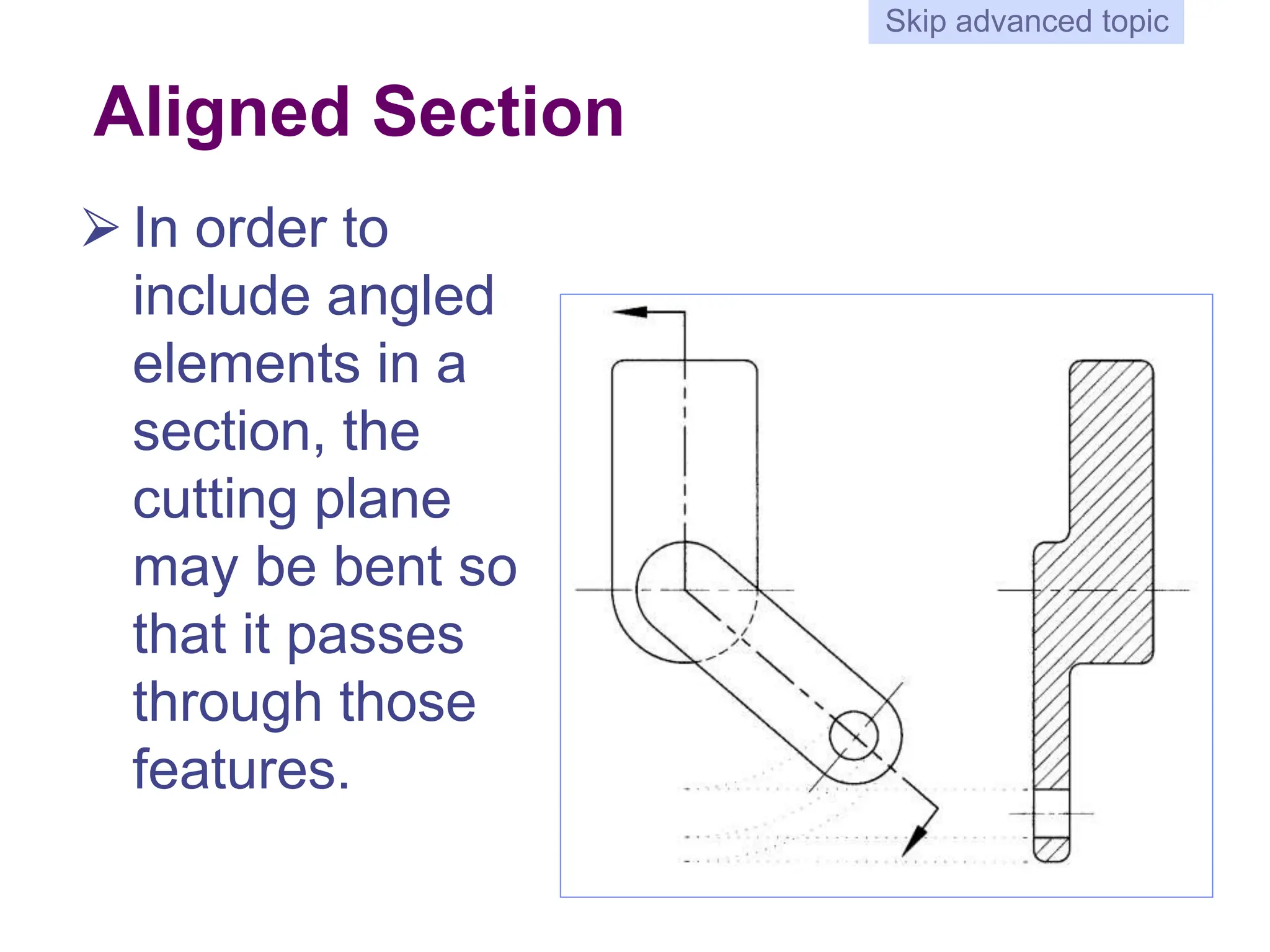
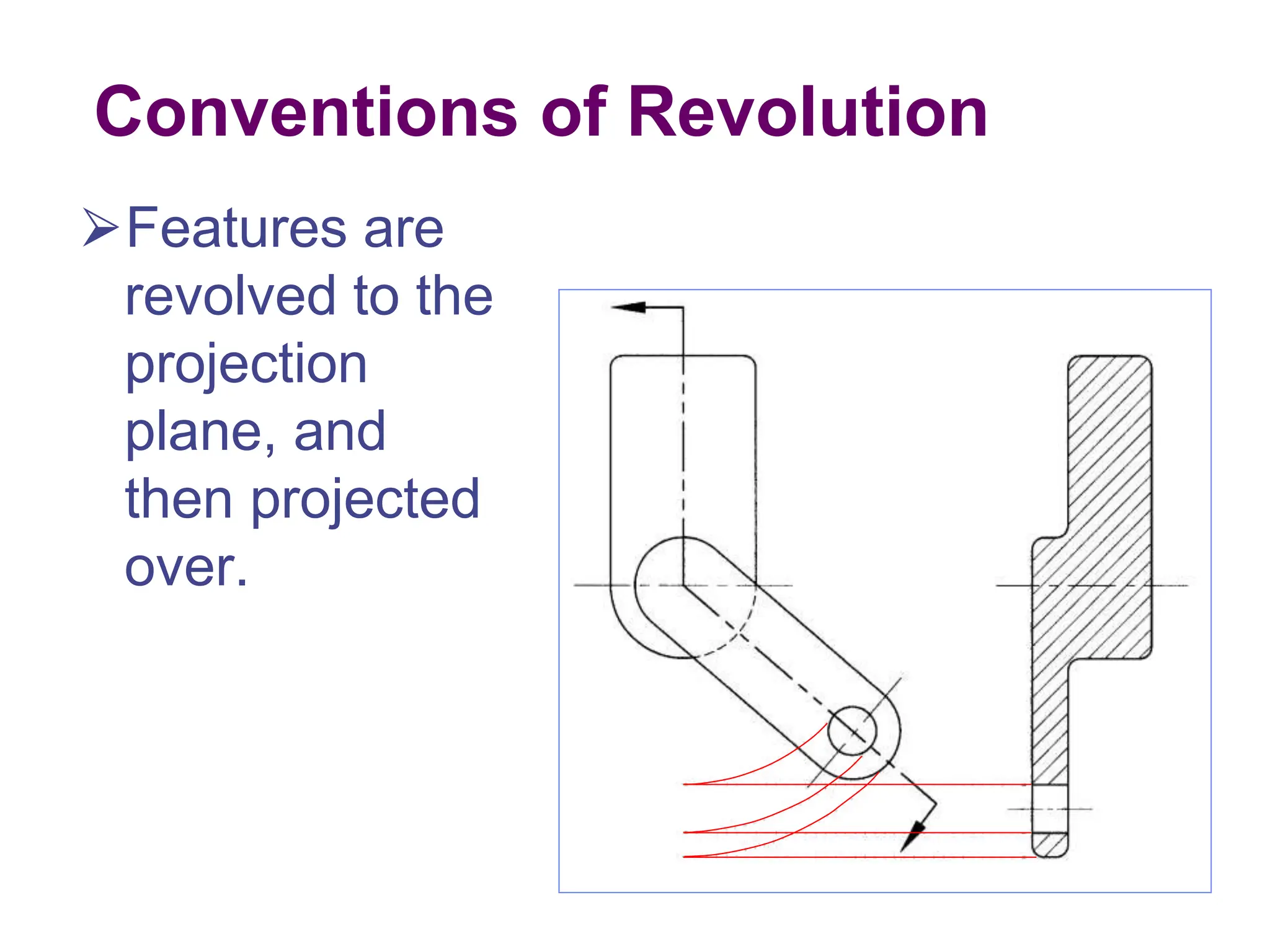
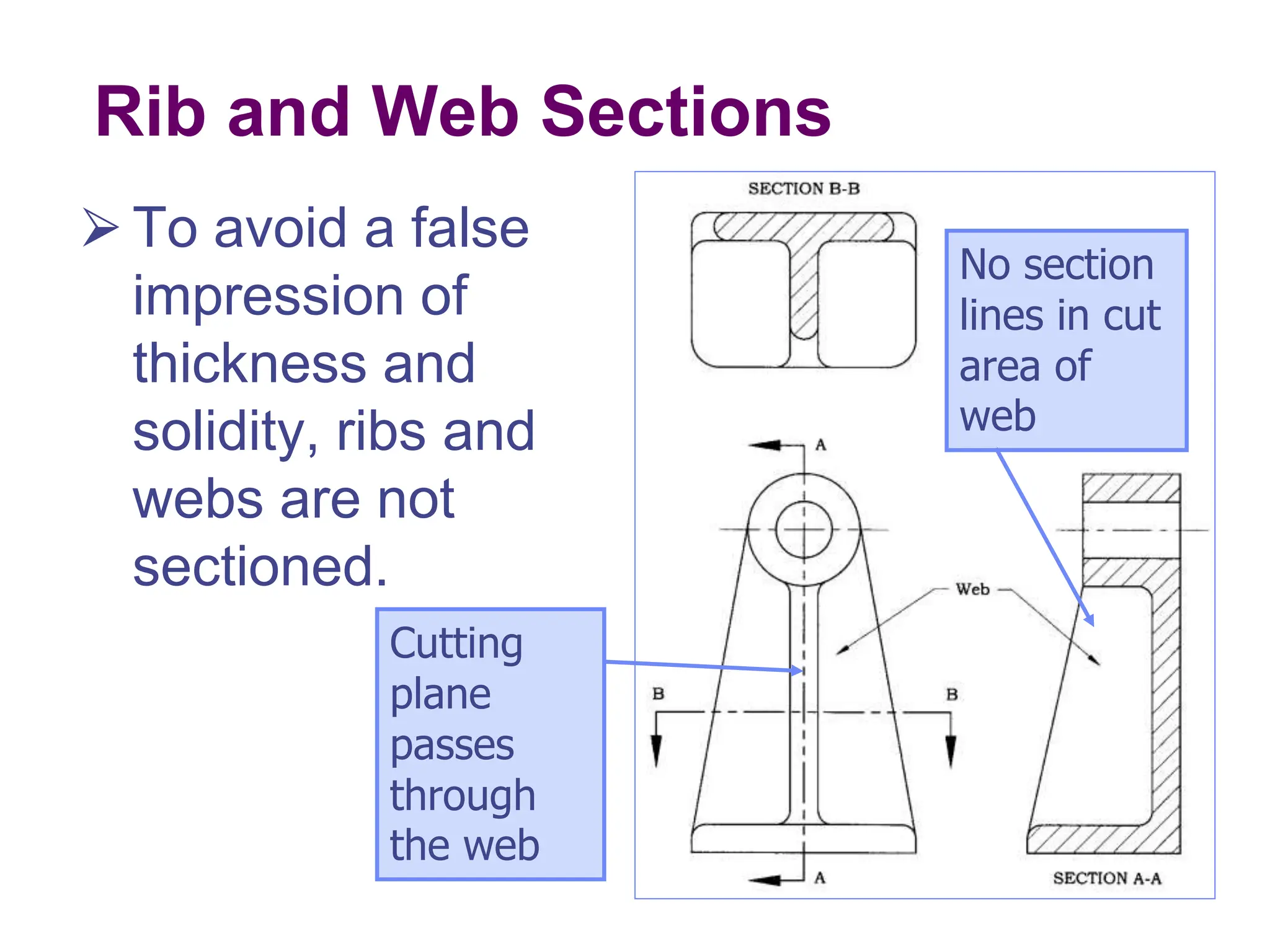
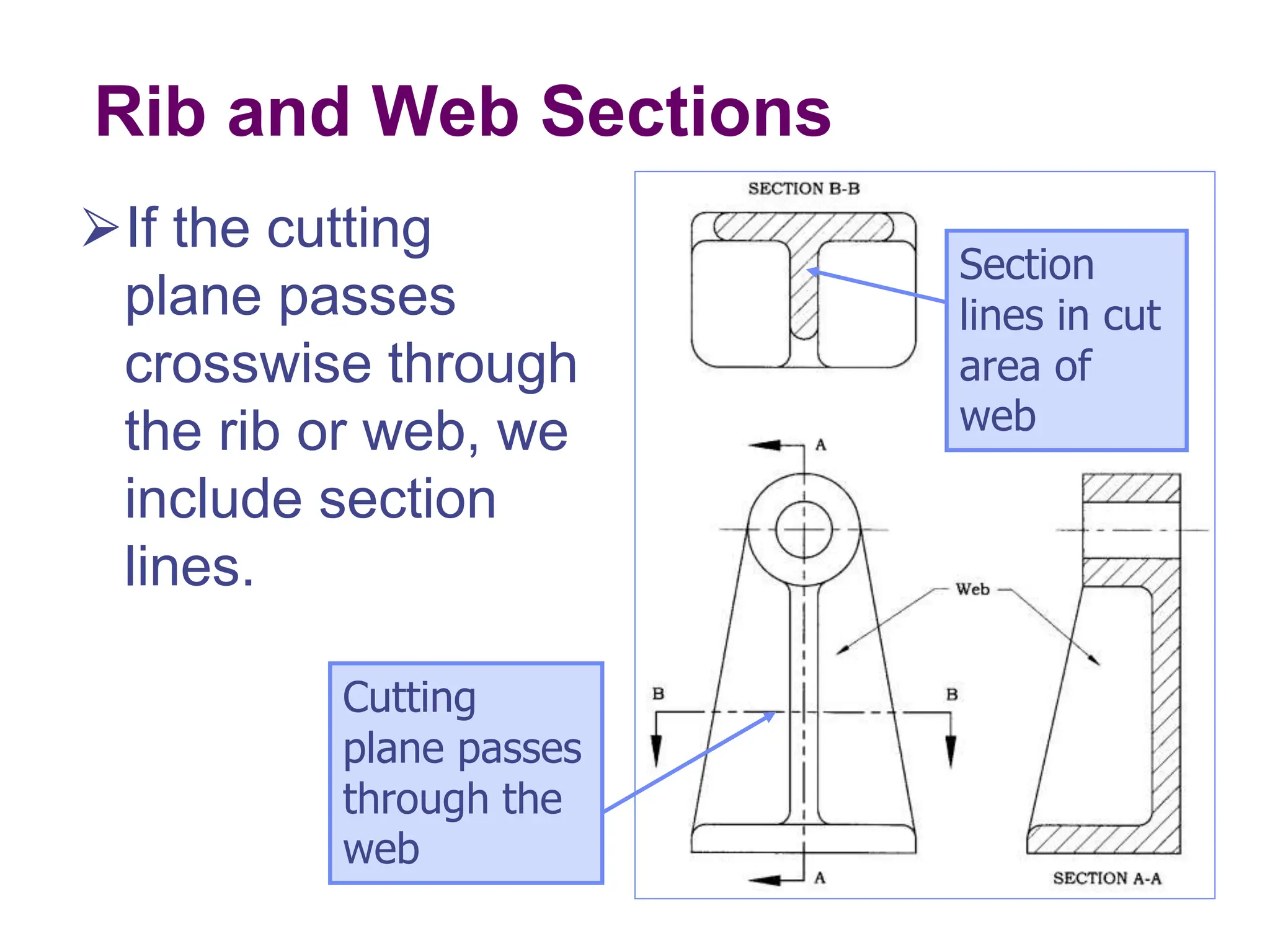
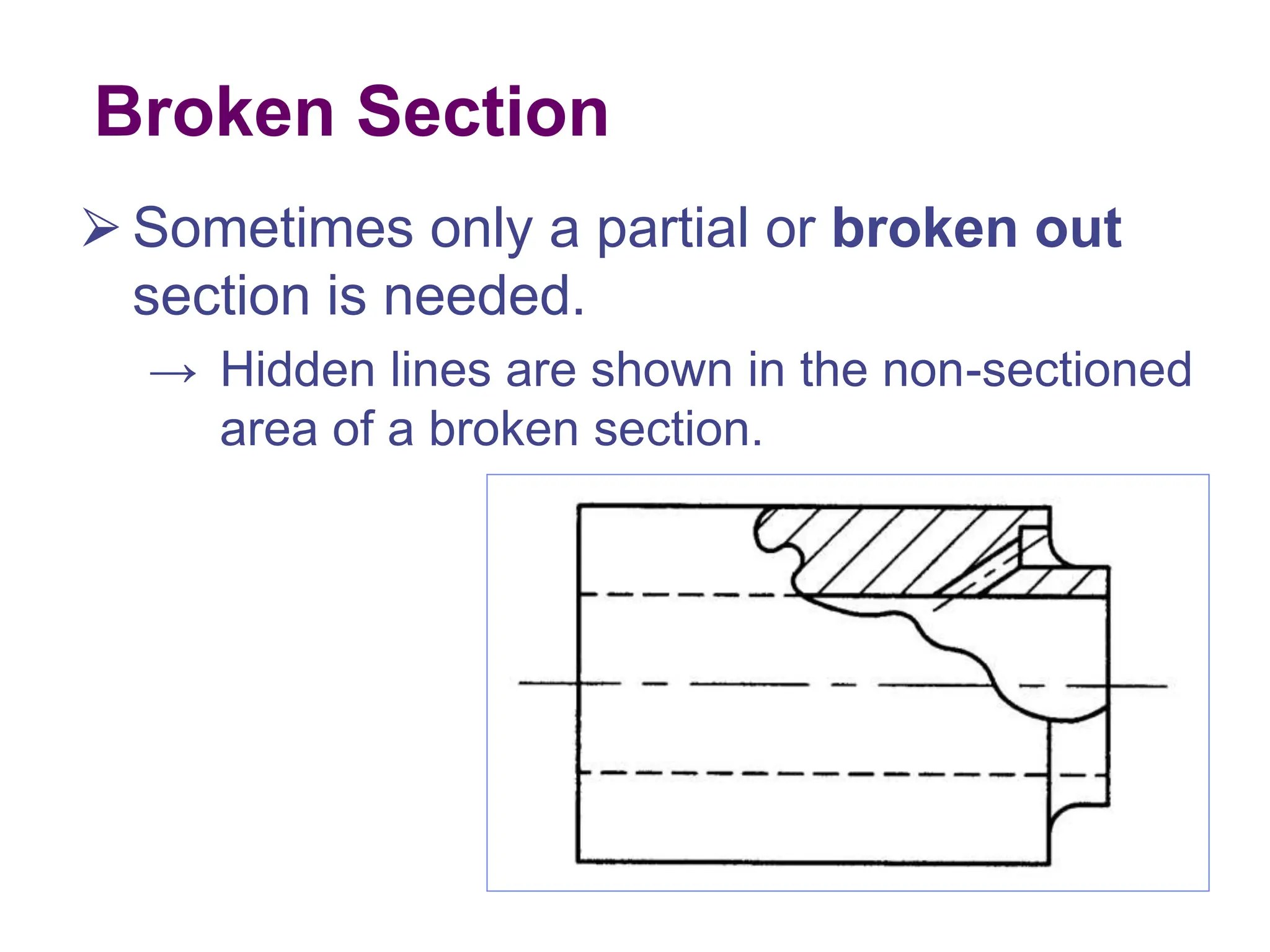
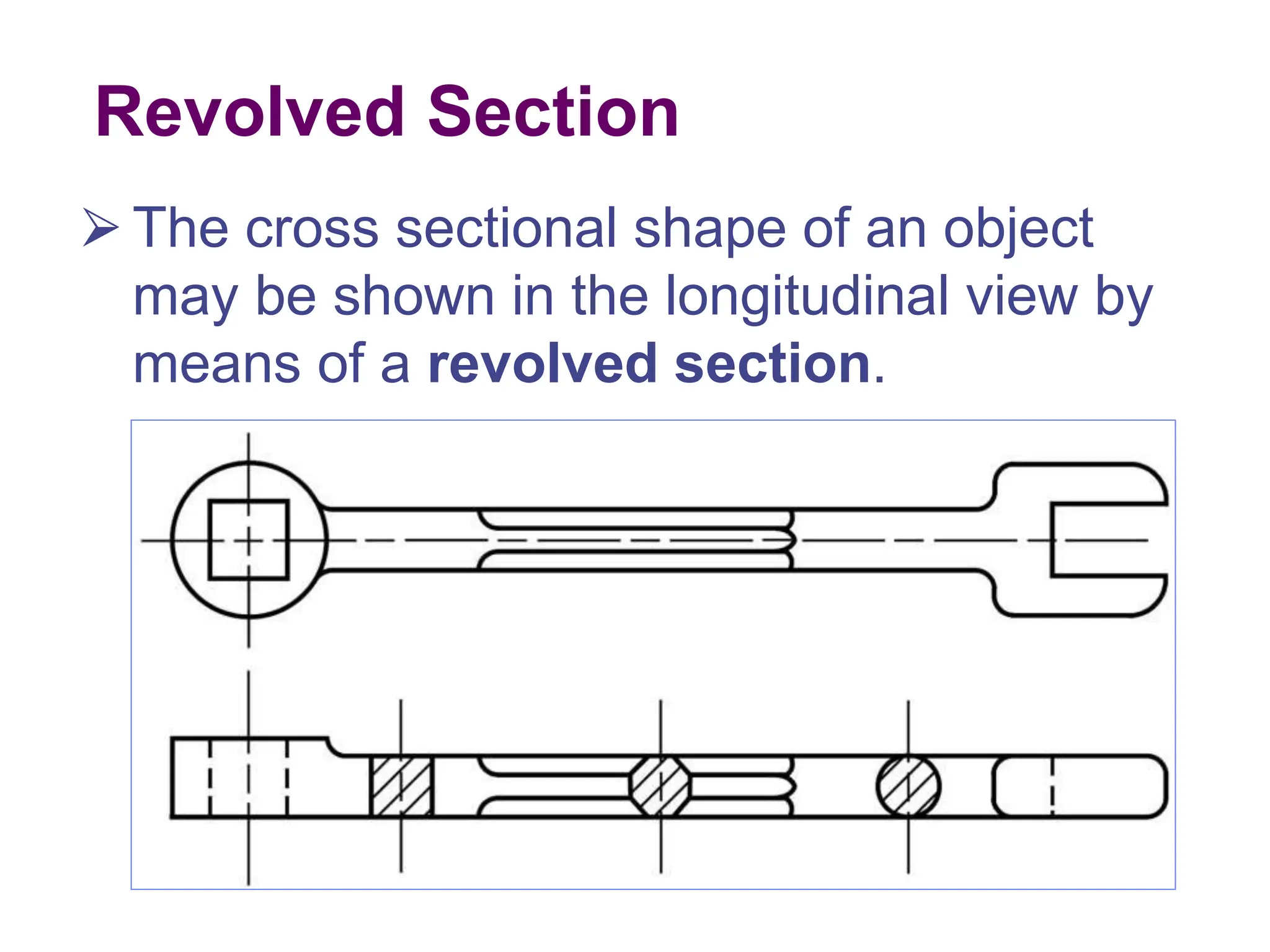
This document discusses different types of section views used in mechanical drawings and CAD models. It describes various sectioning techniques like full sections, half sections, offset sections, and broken sections. Rules for sectioning are provided, along with guidelines for cutting planes, section lines, and conventions for showing cut and uncut portions. Common section line symbols are shown and types of sections are explained for conveying internal features and dimensions.