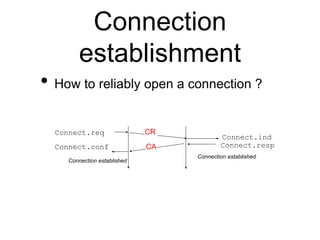
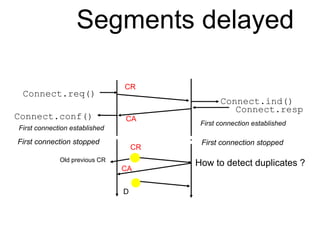
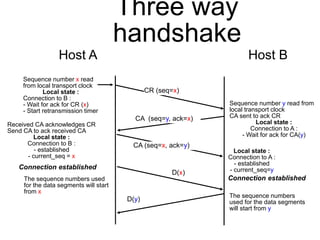
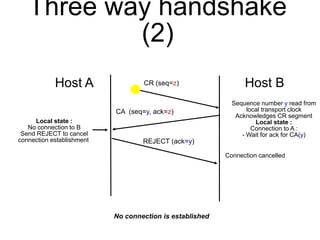
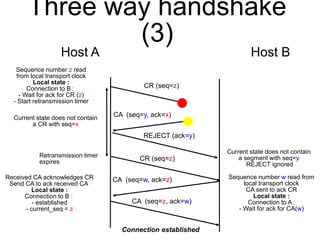
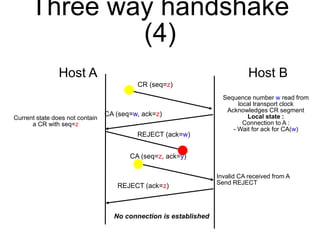
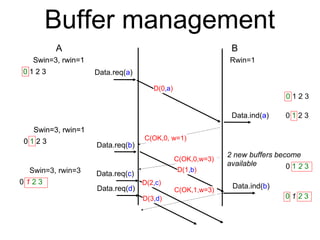
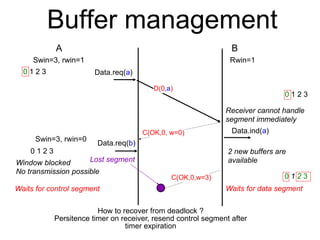
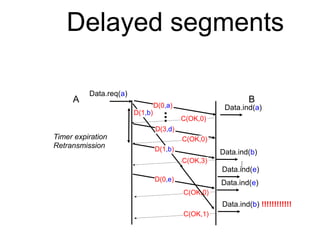
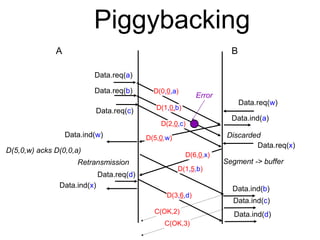
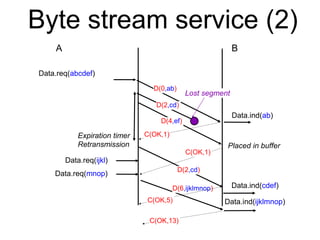
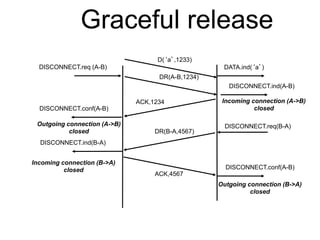
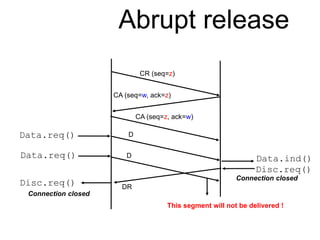
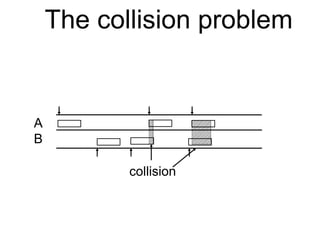
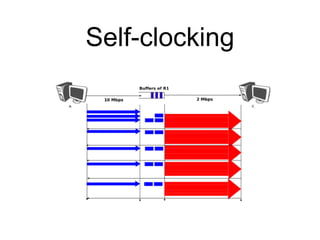
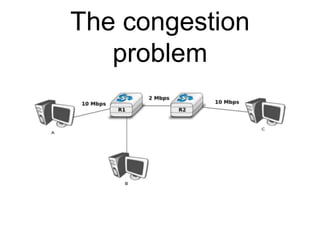
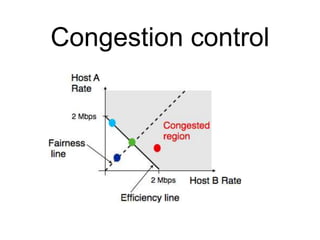
The document discusses reliable transport protocols, focusing on connection establishment, data transfer, and resource sharing, with an emphasis on multiplexing and managing network resources. It covers mechanisms such as the three-way handshake for connections, handling delayed segments, and strategies for reliable data transfer and retransmission policies. Additionally, it addresses methods for managing congestion control and ensuring fair resource allocation across a network.