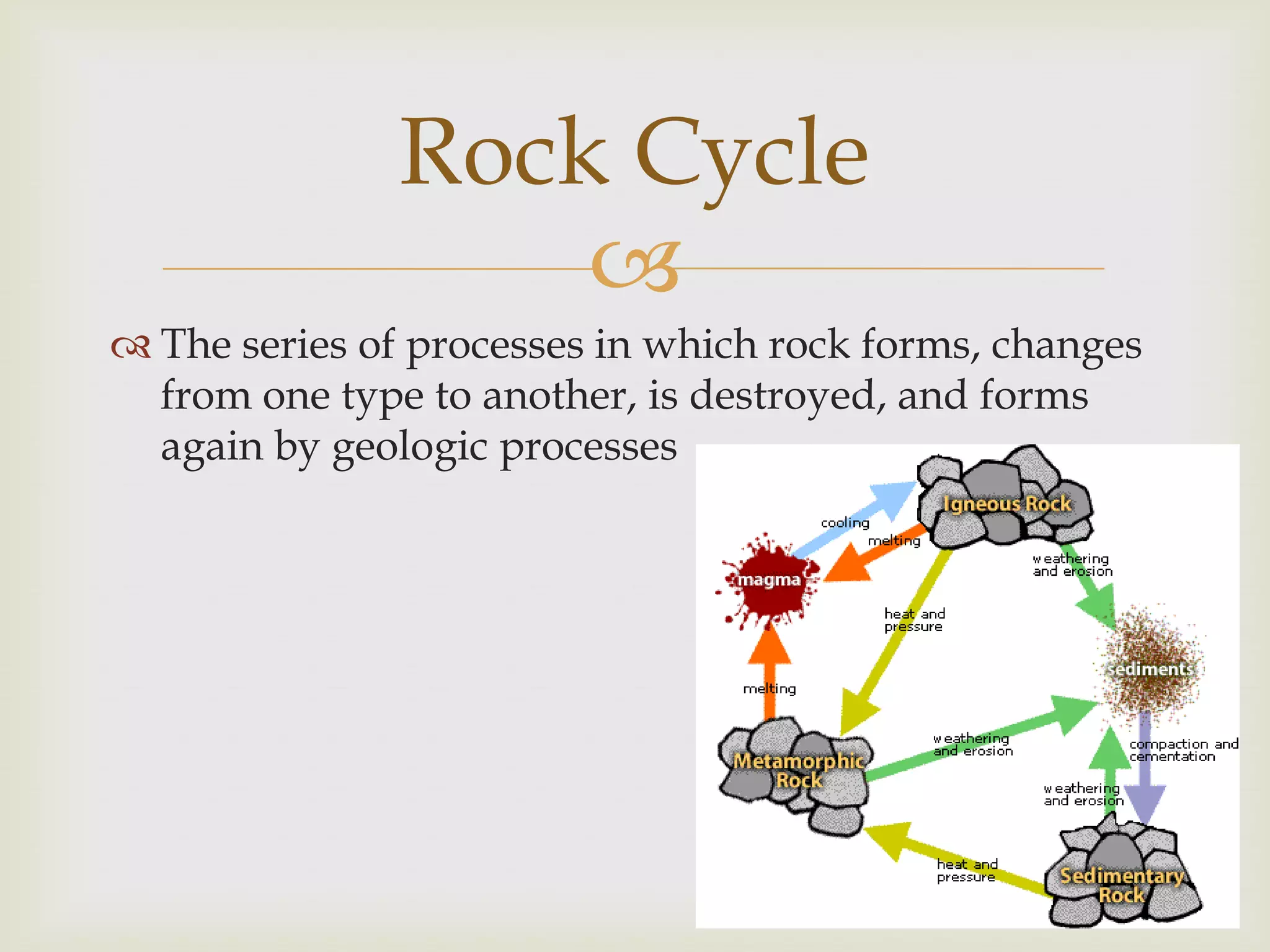
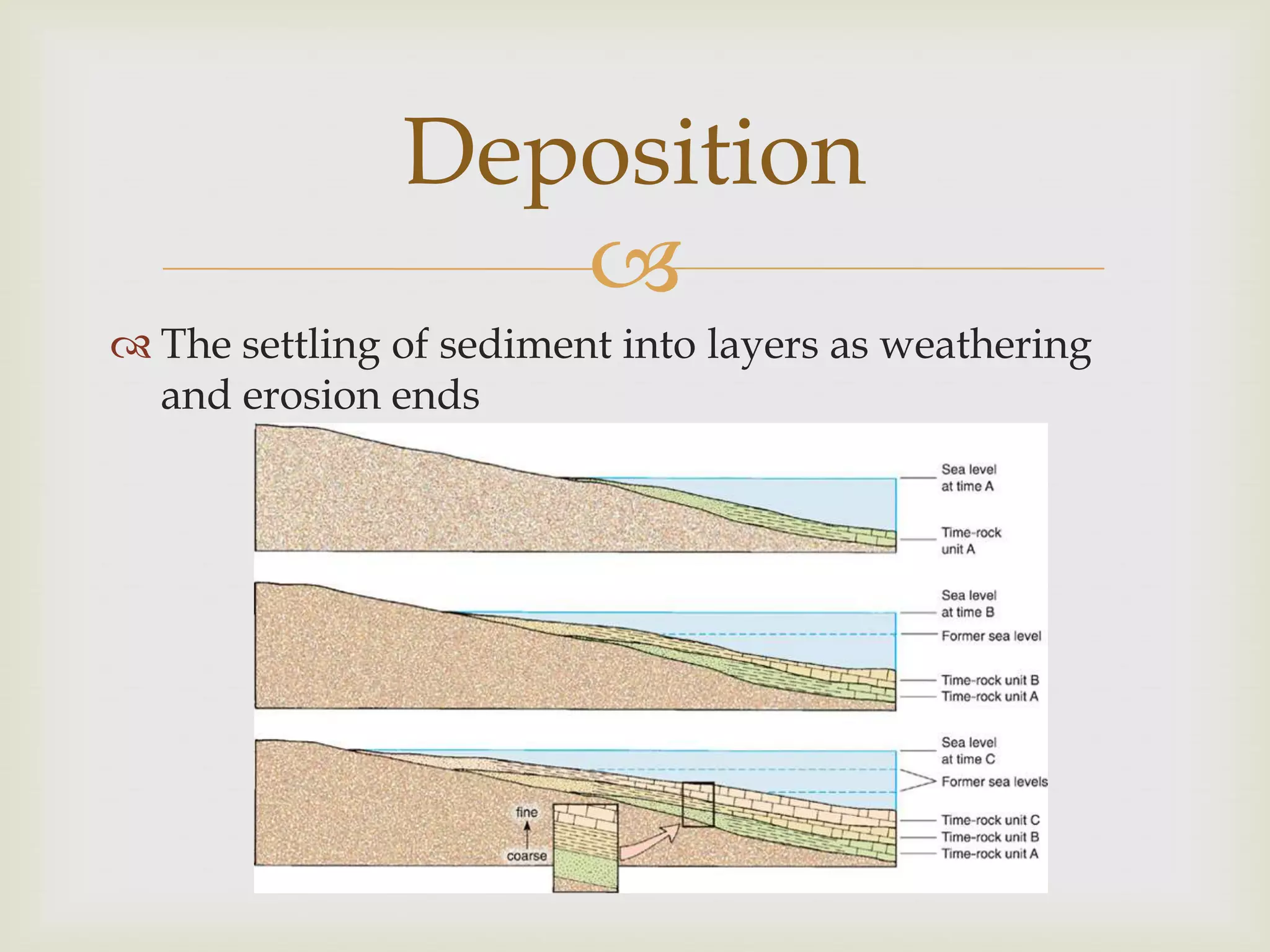
The rock cycle describes how rocks are formed from magma or other existing rocks and changed over time through geological processes. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, metamorphic rocks form under heat and pressure, and sedimentary rocks form through the weathering of other rocks and deposition of sediments. Rocks are constantly changing between these three types as they move through the rock cycle.