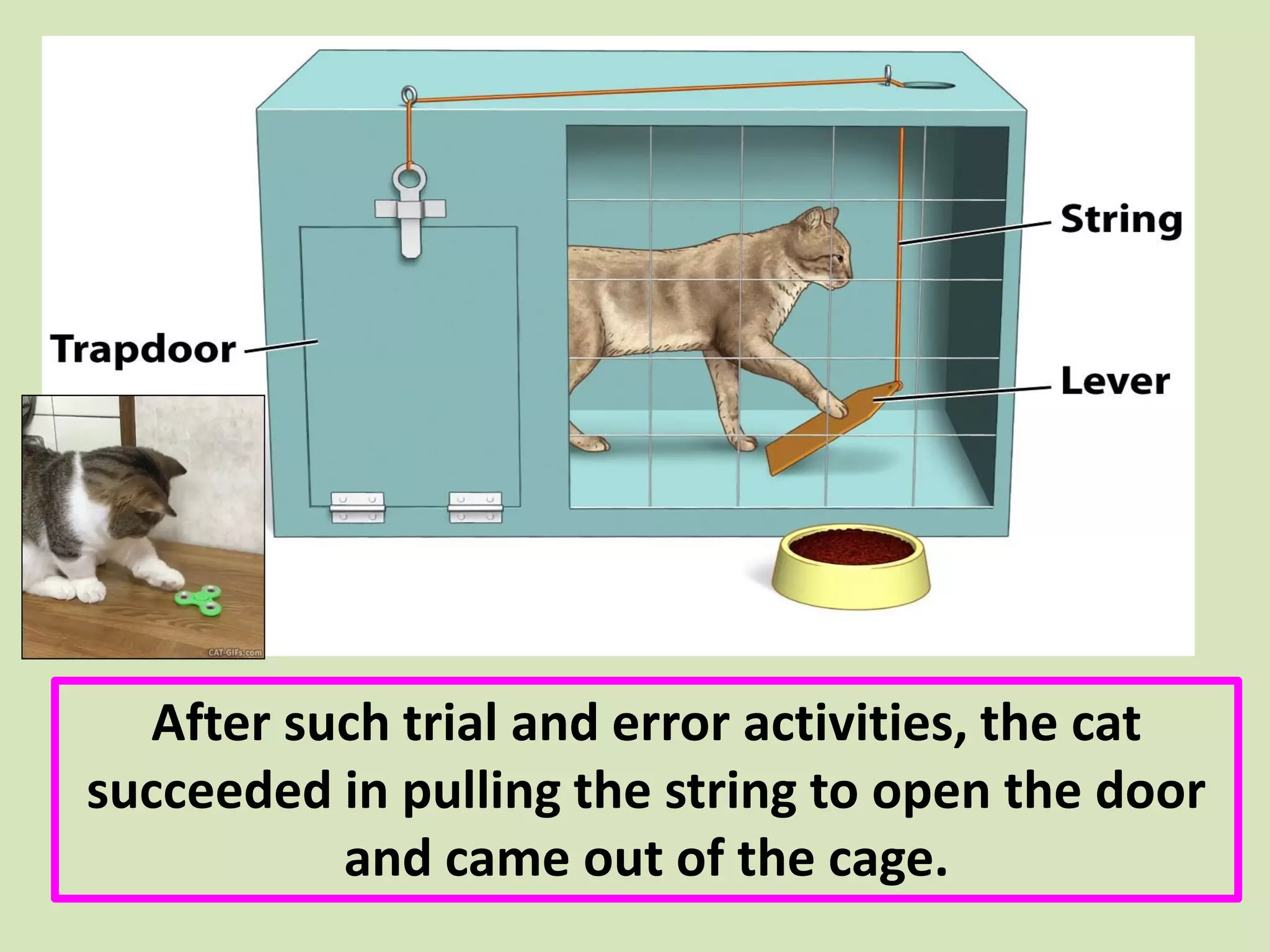
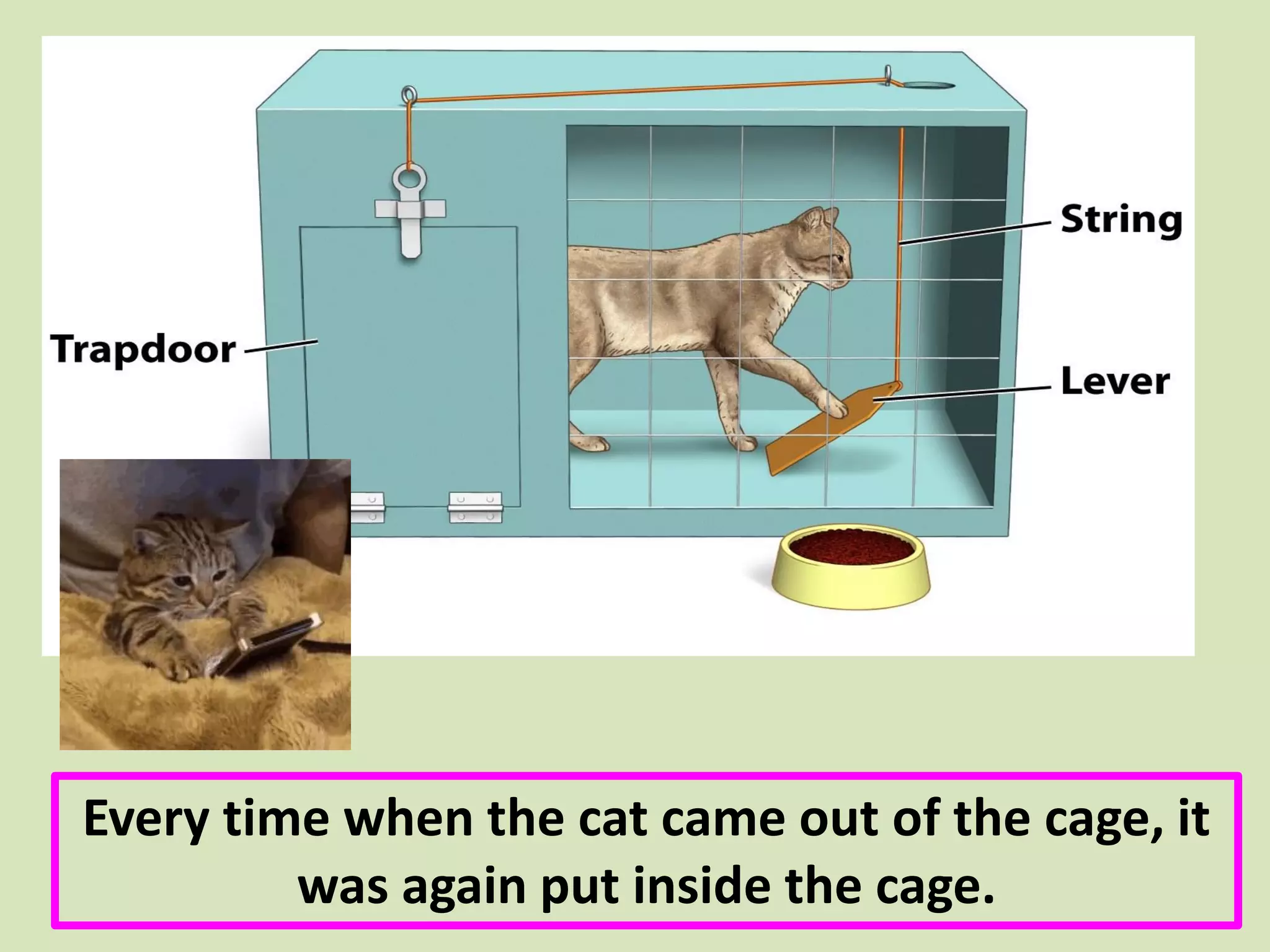
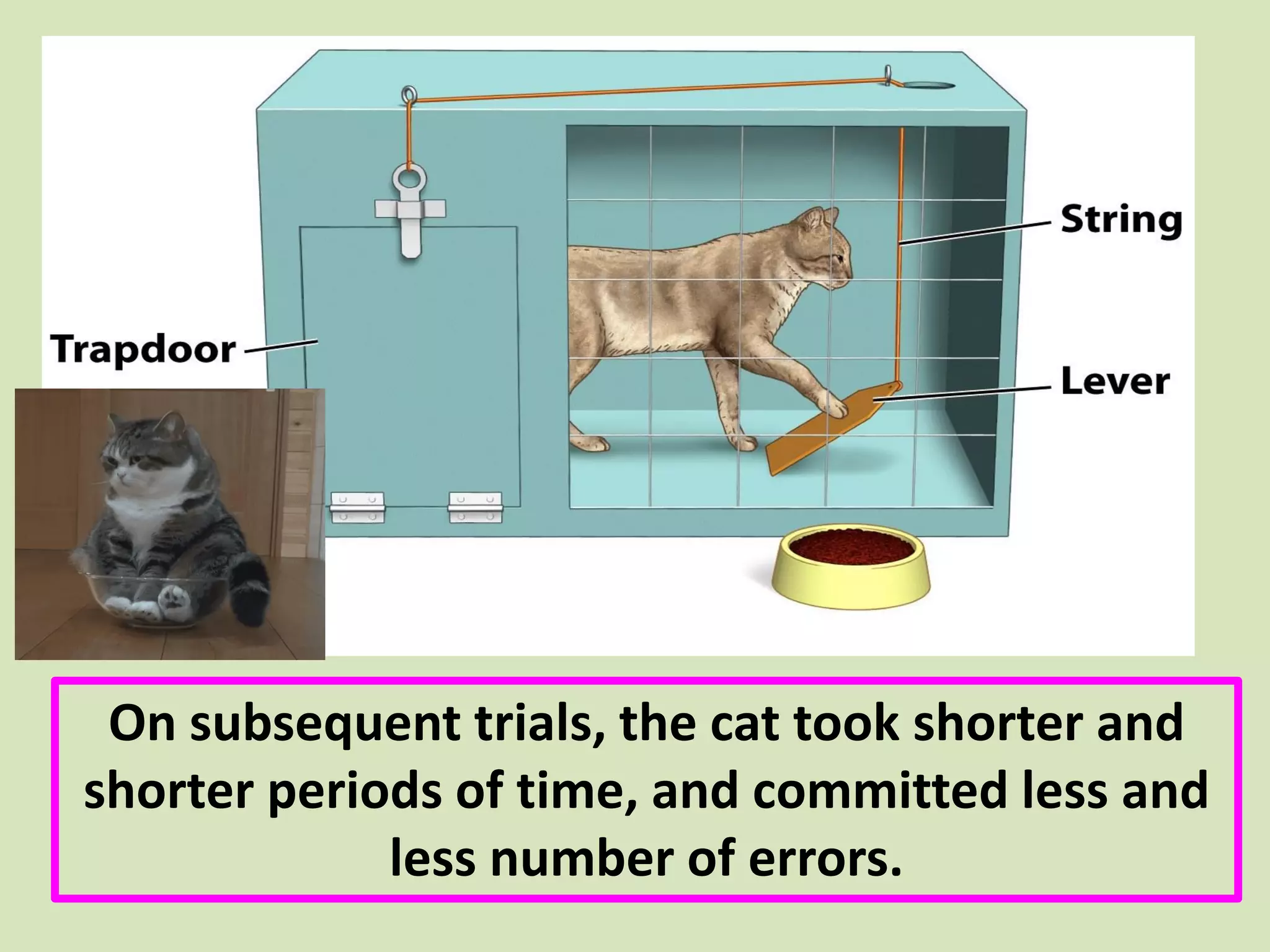
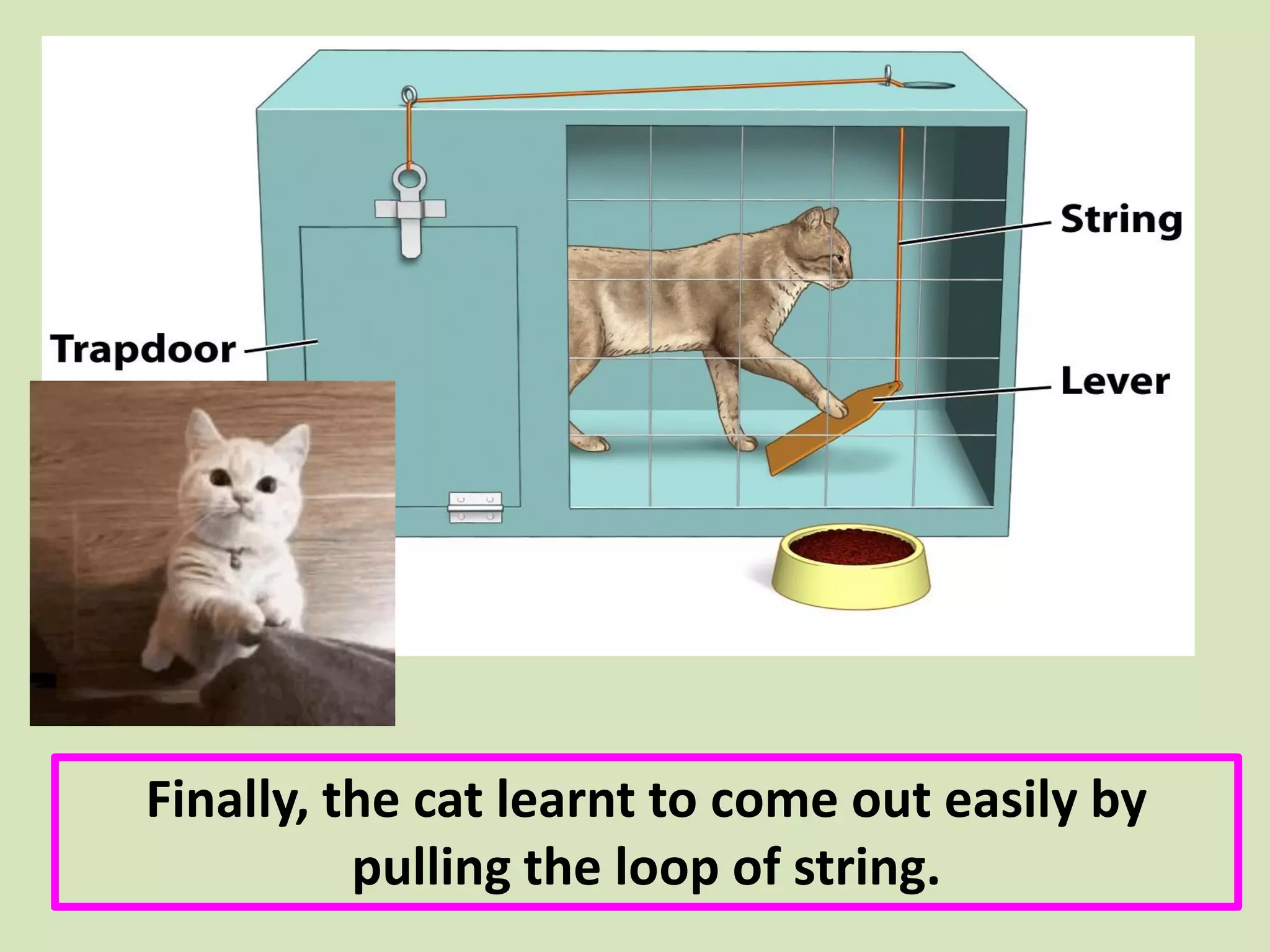
- The document describes a core course on learning and teaching theories with a focus on behavioral theories.
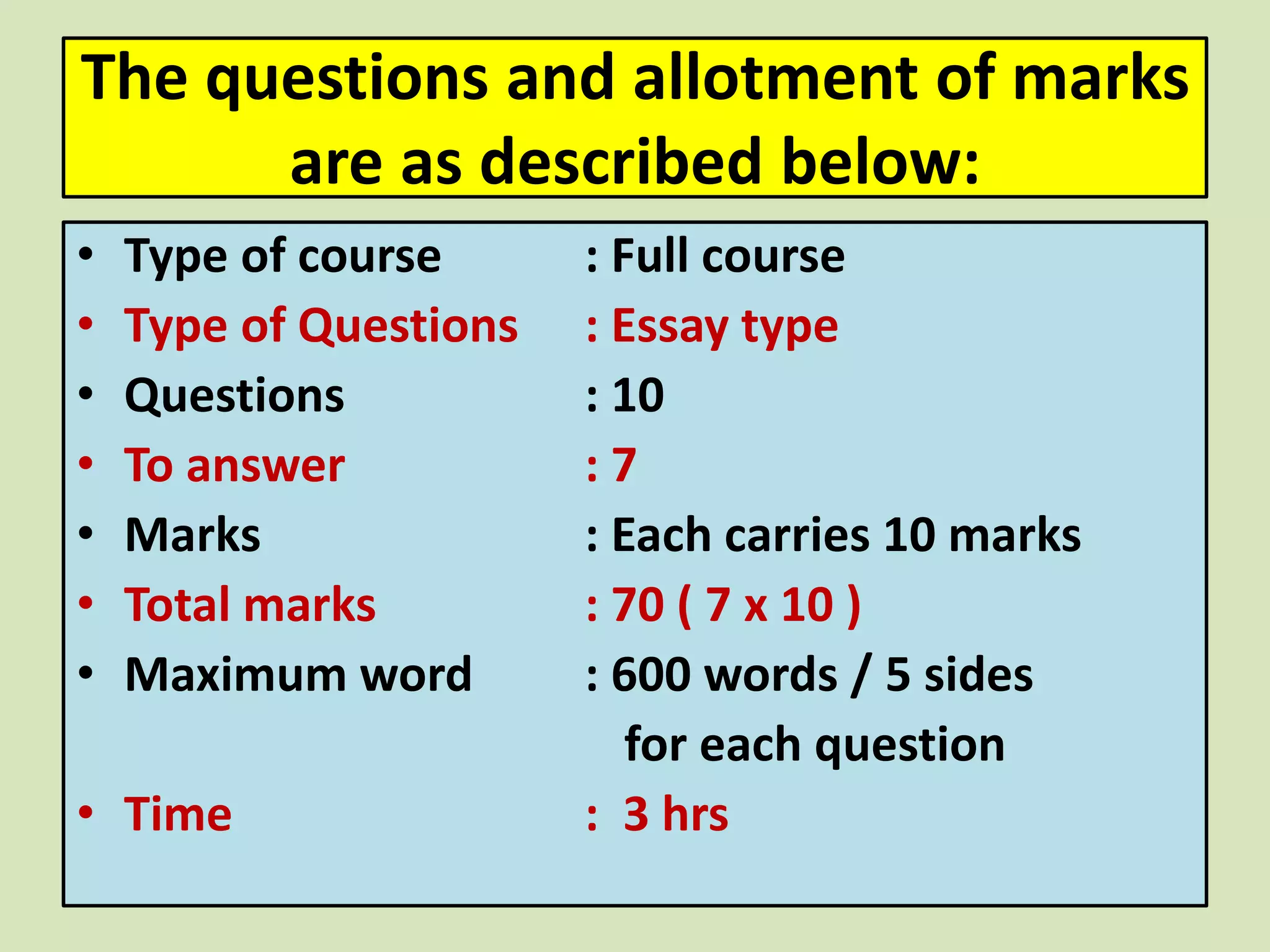
- It includes 10 essay questions to be answered over 3 hours, with each question worth 10 marks and a maximum of 600 words.
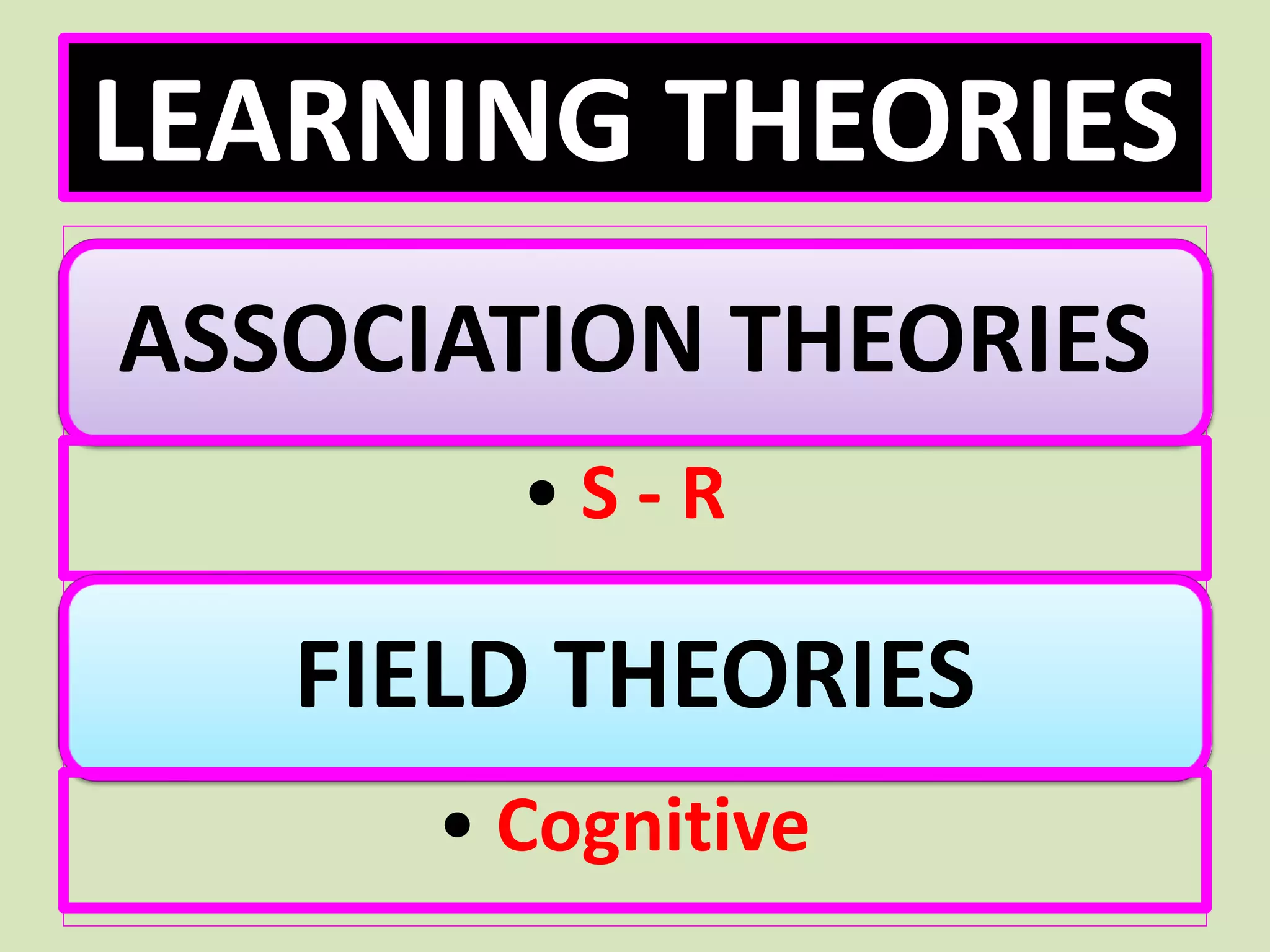
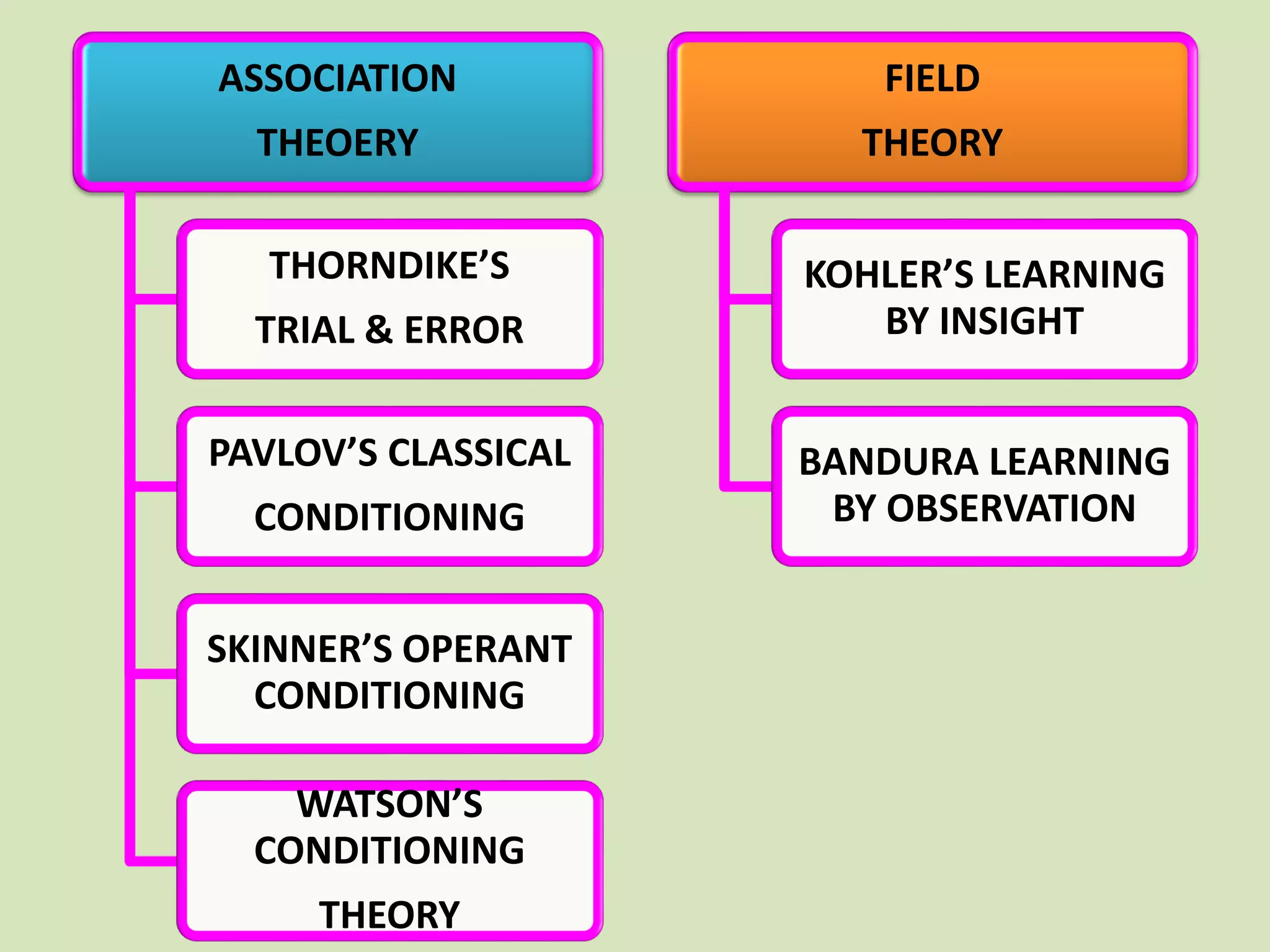
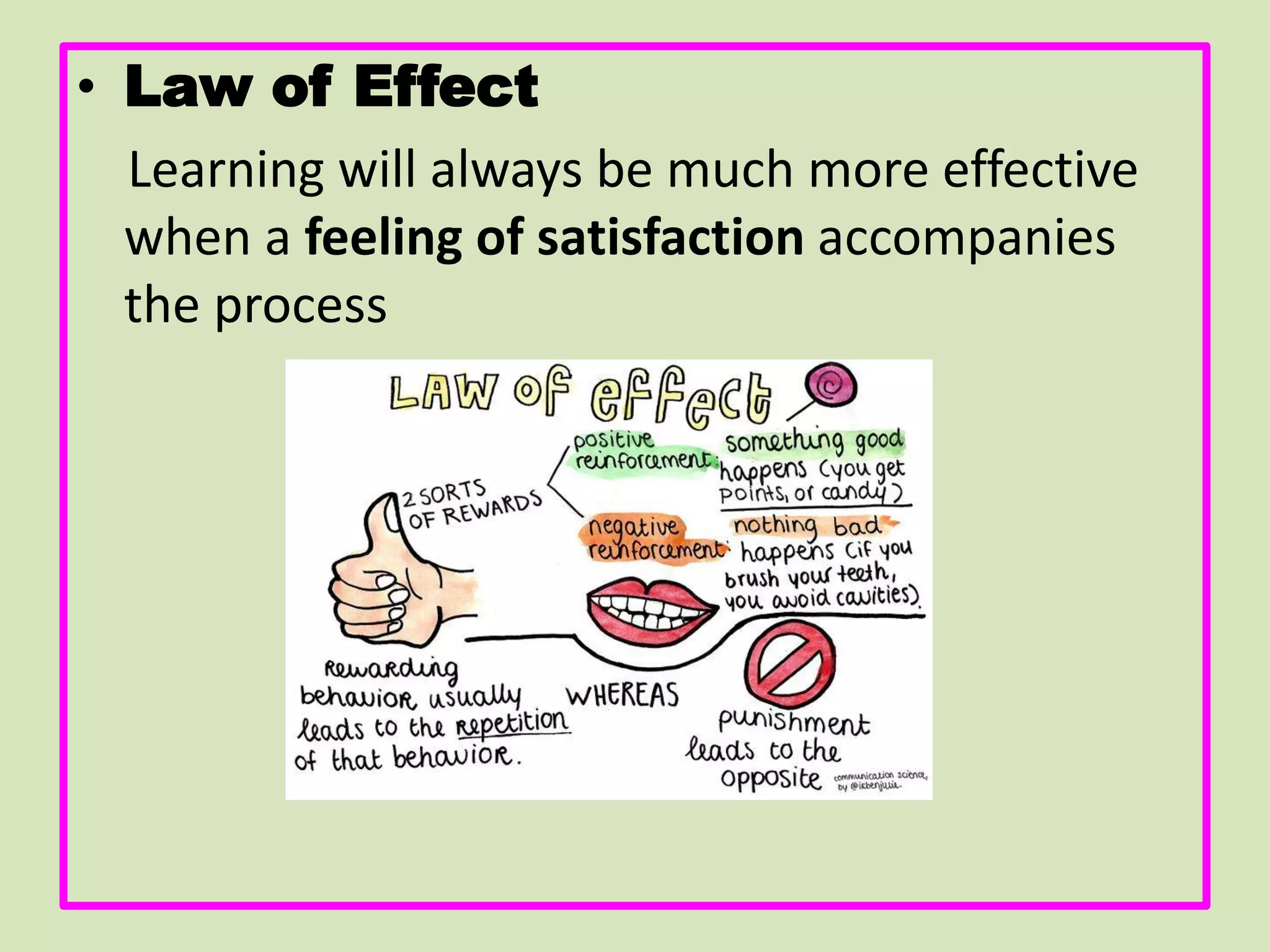
- The key topics covered are the meaning of learning according to behaviorists, classical conditioning, Thorndike's law of effect, operant conditioning and shaping, social learning, and the basic assumptions and strengths/limitations of behavioral theories.
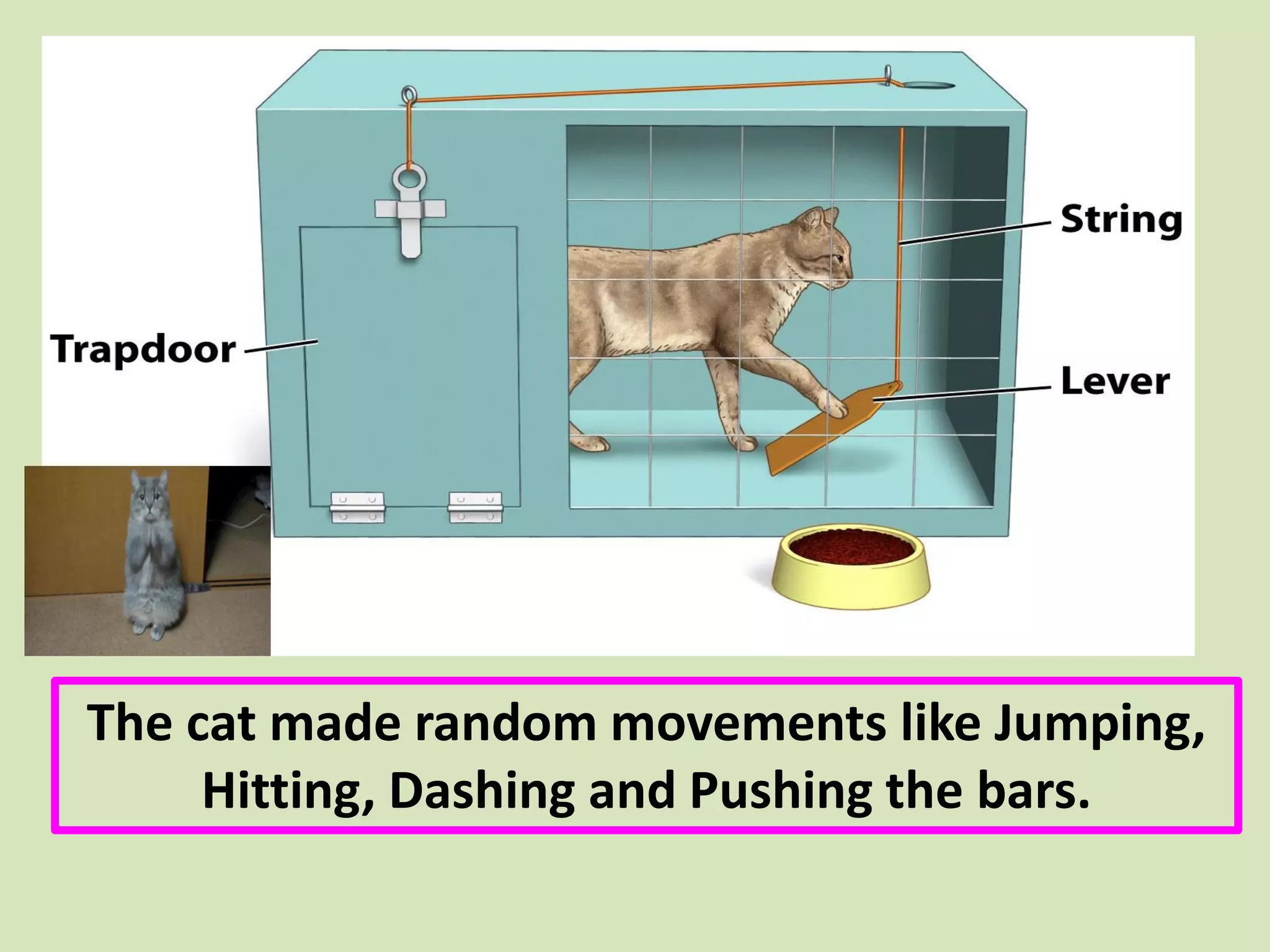
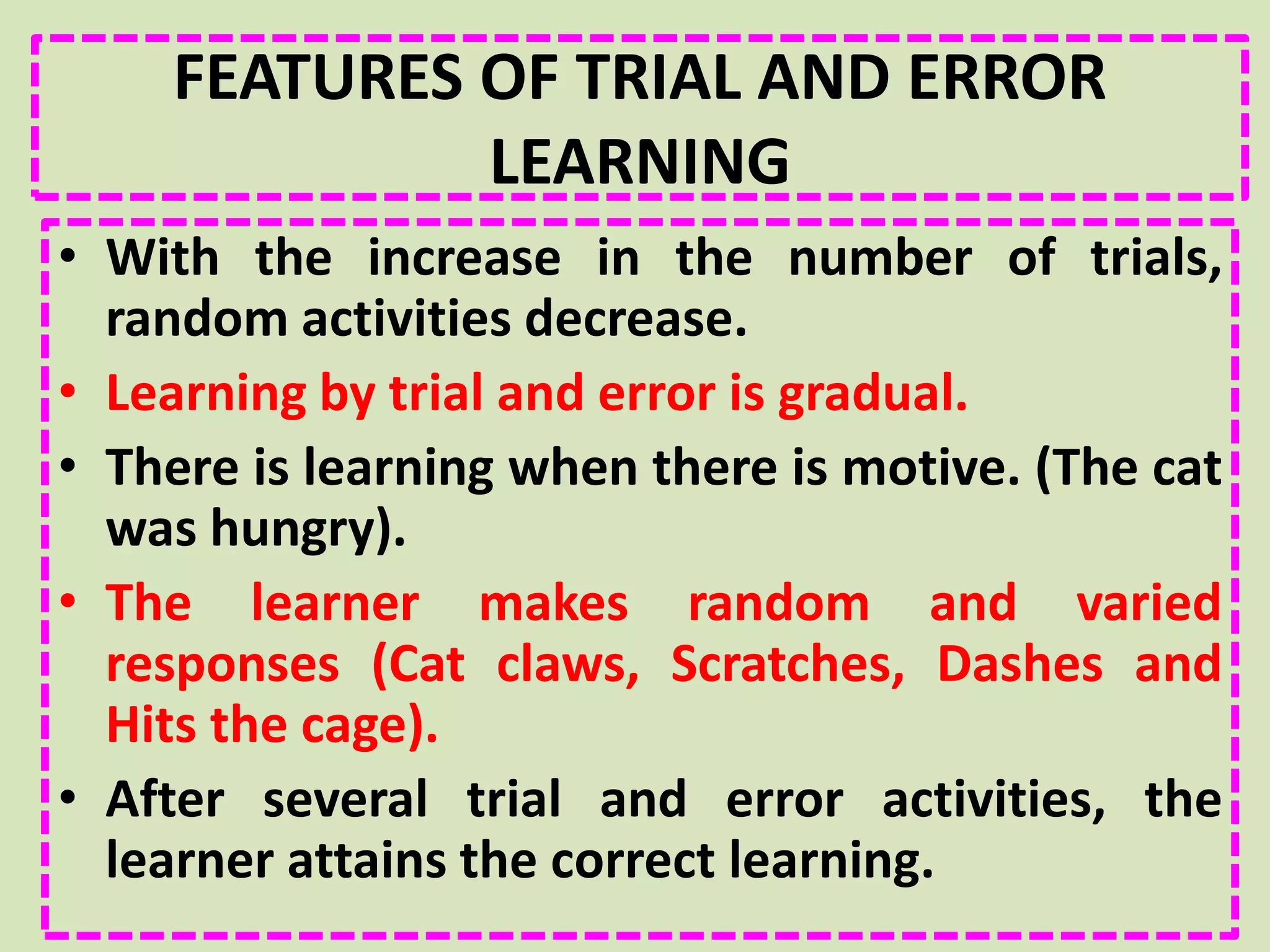
- Thorndike's law of effect and trial-and-error learning are specifically discussed, using the example of a hungry cat learning to escape from a cage to get food.