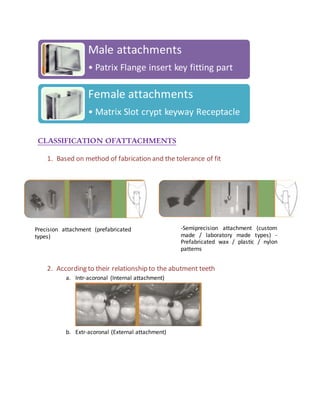
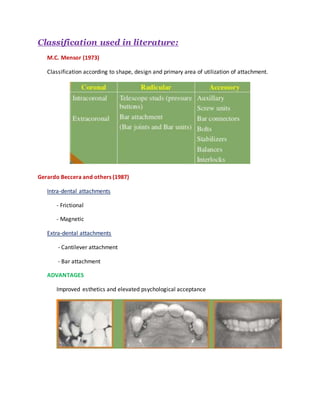
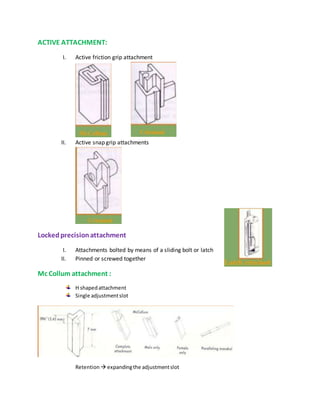
This document discusses the history and classification of precision dental attachments. It begins by outlining some of the early developments in attachment designs from the 19th century. It then classifies attachments based on their fabrication method, relationship to abutment teeth, stiffness, and geometric configuration. The advantages and disadvantages of attachments are provided. Key factors in selecting abutment teeth are identified. Requirements for ideal abutment teeth are outlined. Contraindications and the role of attachments in different types of prosthodontic treatments are summarized.