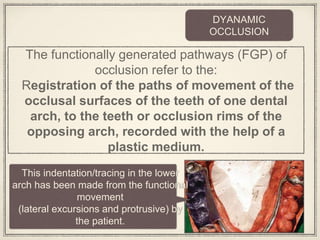
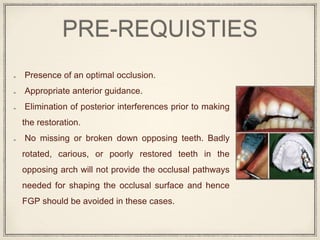
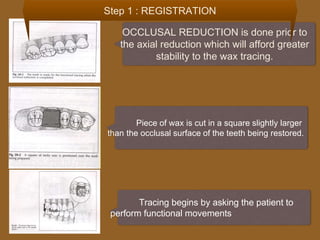
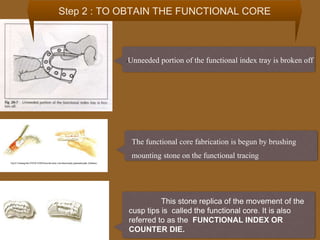
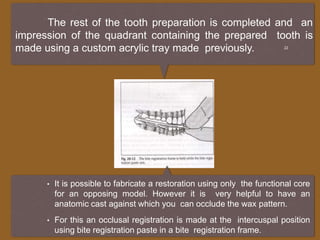
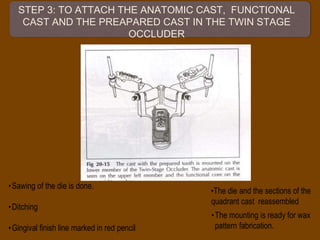
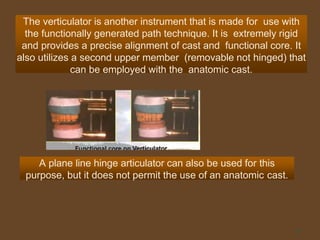
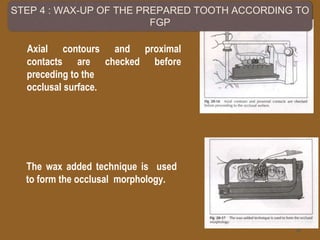
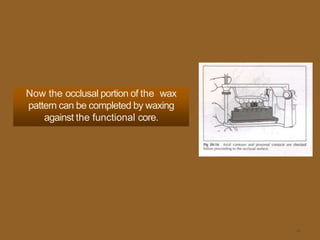
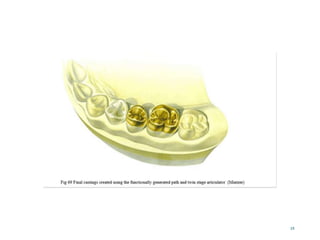
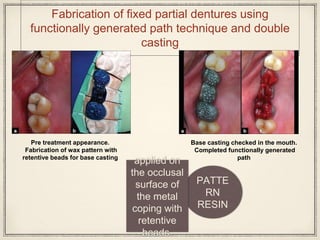
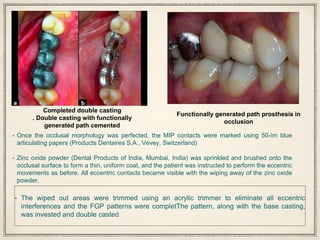
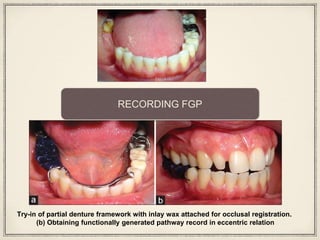
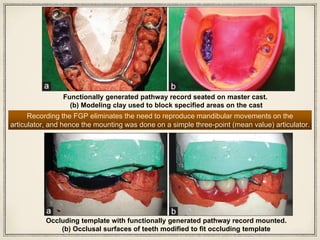
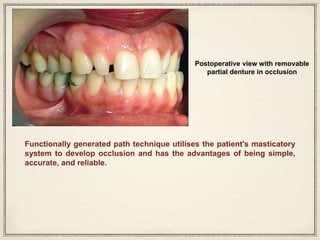
1. The functionally generated pathway technique involves recording the paths of tooth movement during excursive jaw motions using wax or other materials.
2. This recording is used to develop the occlusal morphology for dental restorations like crowns, ensuring optimal occlusion during all jaw motions.
3. Studies have found that the functionally generated pathway technique results in restorations with better functional articulation compared to conventional single casting techniques, with less adjustment needed and higher patient satisfaction.