Embed presentation
Download to read offline






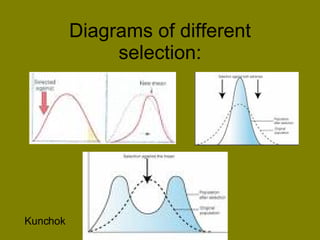
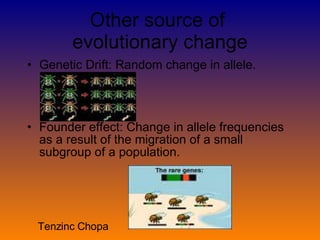


The document discusses genetic variation and evolution. It defines key terms like gene pool, relative frequency, and sources of genetic variation such as mutation and gene shuffling. It also describes how natural selection can affect single-gene and polygenic traits through changing allele frequencies or affecting phenotype distributions in directional, stabilizing, or disruptive ways. Other topics covered include types of selection, diagrams of selection, genetic drift, founder effects, the process of speciation, and an example of speciation in Darwin's finches.









