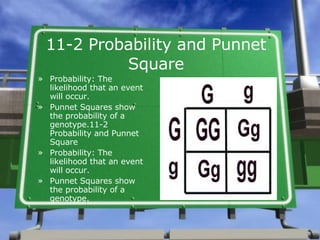
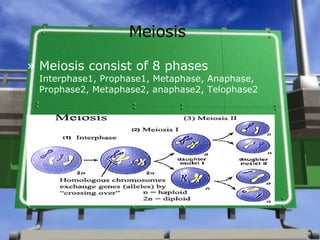
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 11 on genetics. It discusses Gregor Mendel's work with pea plants, the principles of dominance and segregation. It also explains probability and Punnett squares, Mendel's two-factor crosses, his principles of inheritance, meiosis, the differences between mitosis and meiosis, and gene mapping.