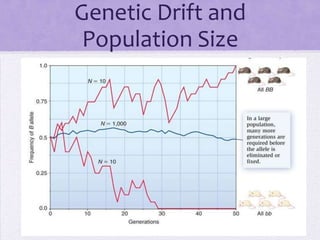
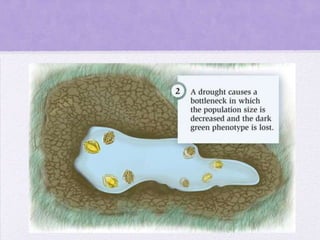
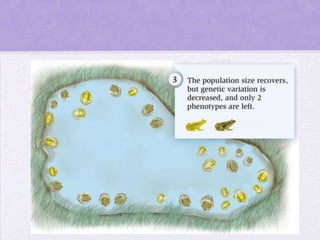
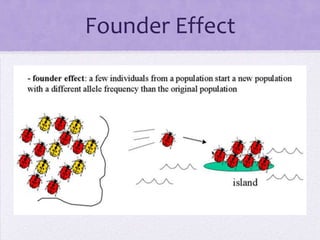
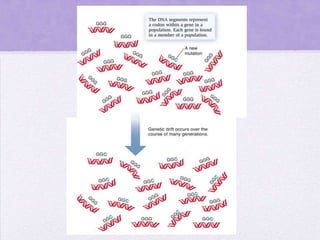
This document discusses genetic drift, which refers to random changes in allele frequencies between generations independent of natural selection. Genetic drift has a greater impact in small populations and can lead to the loss or fixation of alleles. The bottleneck effect and founder effect are examples where genetic drift in small populations causes allele frequency changes compared to the original larger population. The neutral theory of evolution proposes that most genetic variation arises from the accumulation of neutral mutations through genetic drift rather than natural selection.