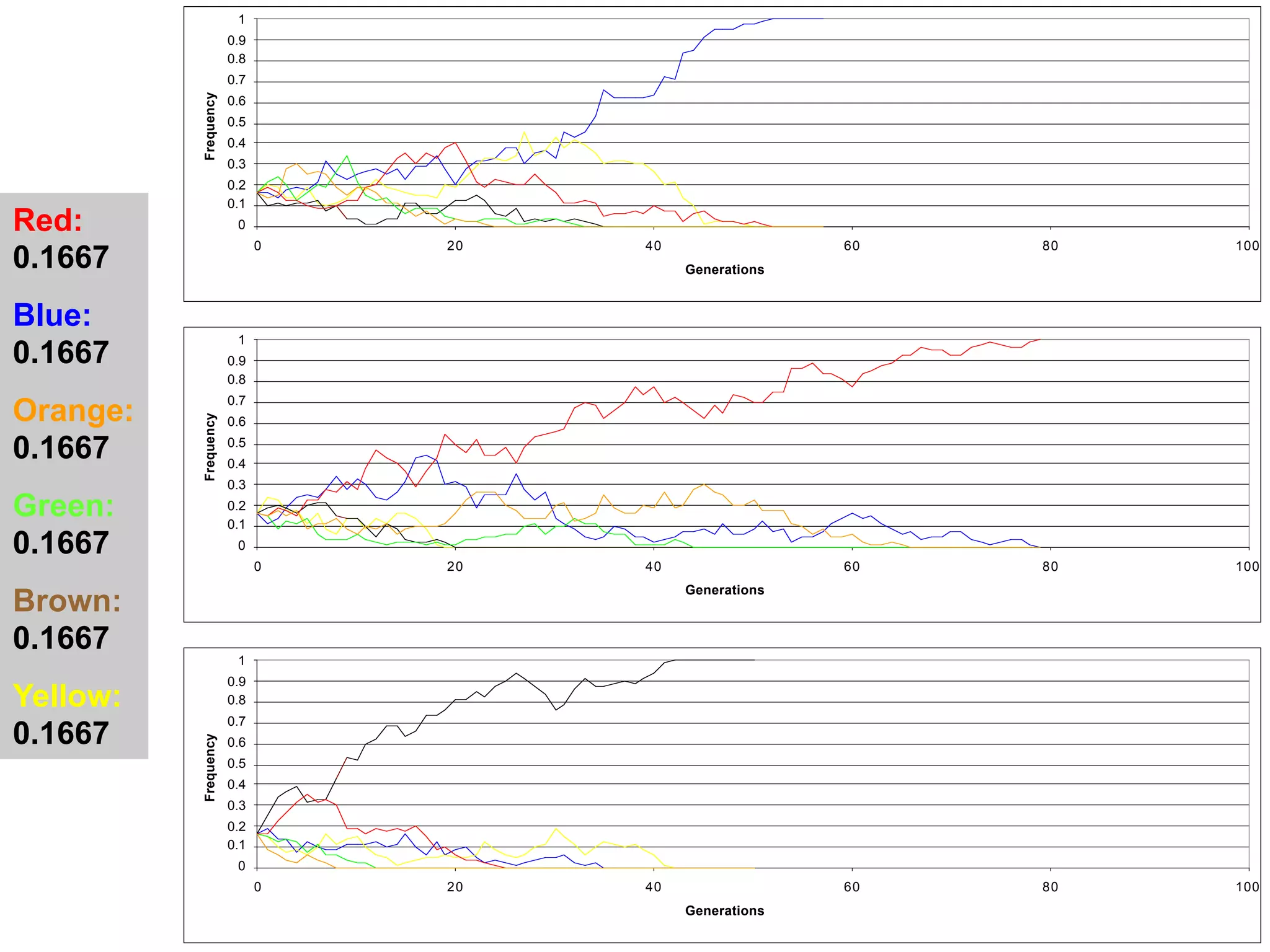
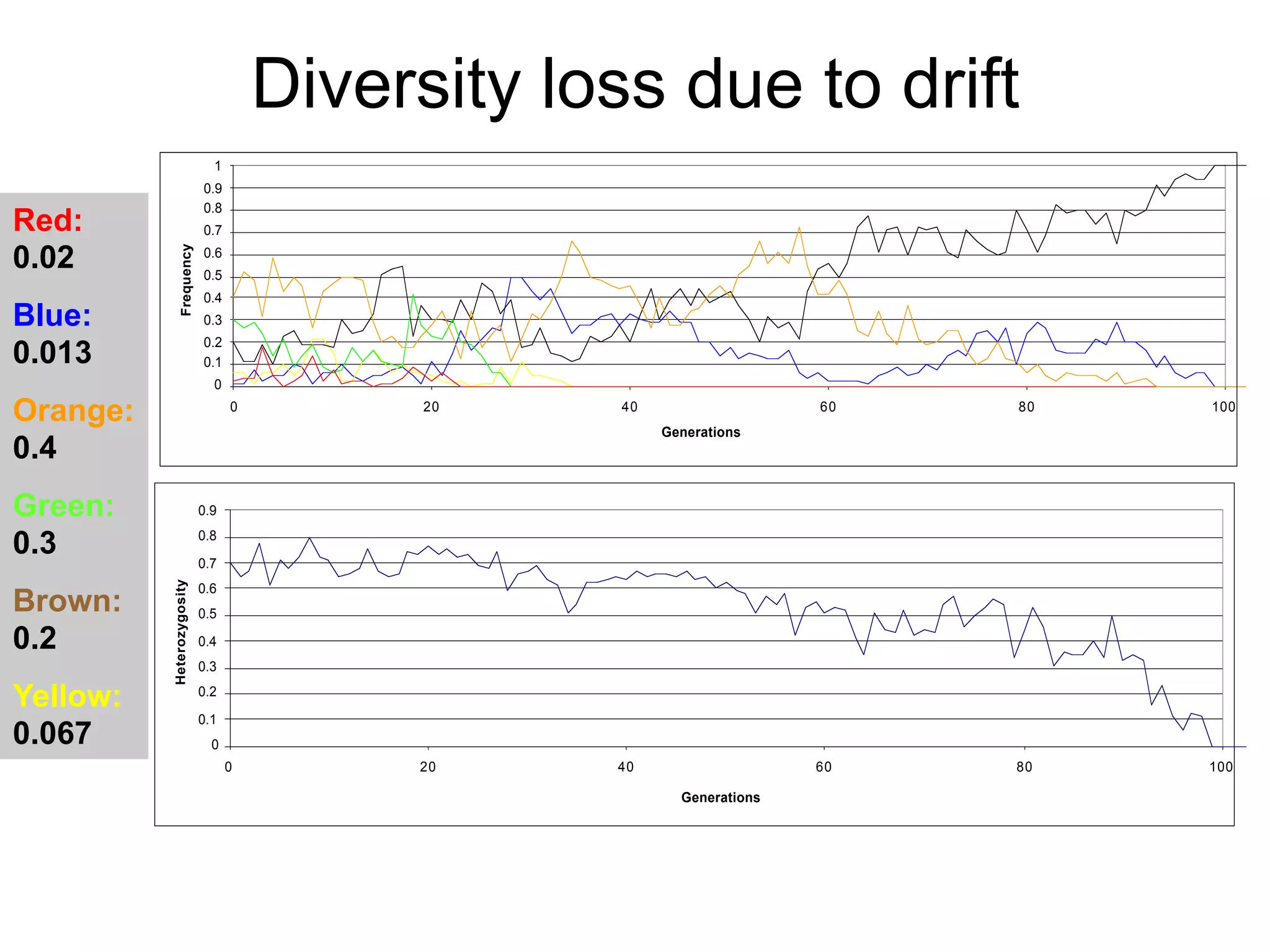
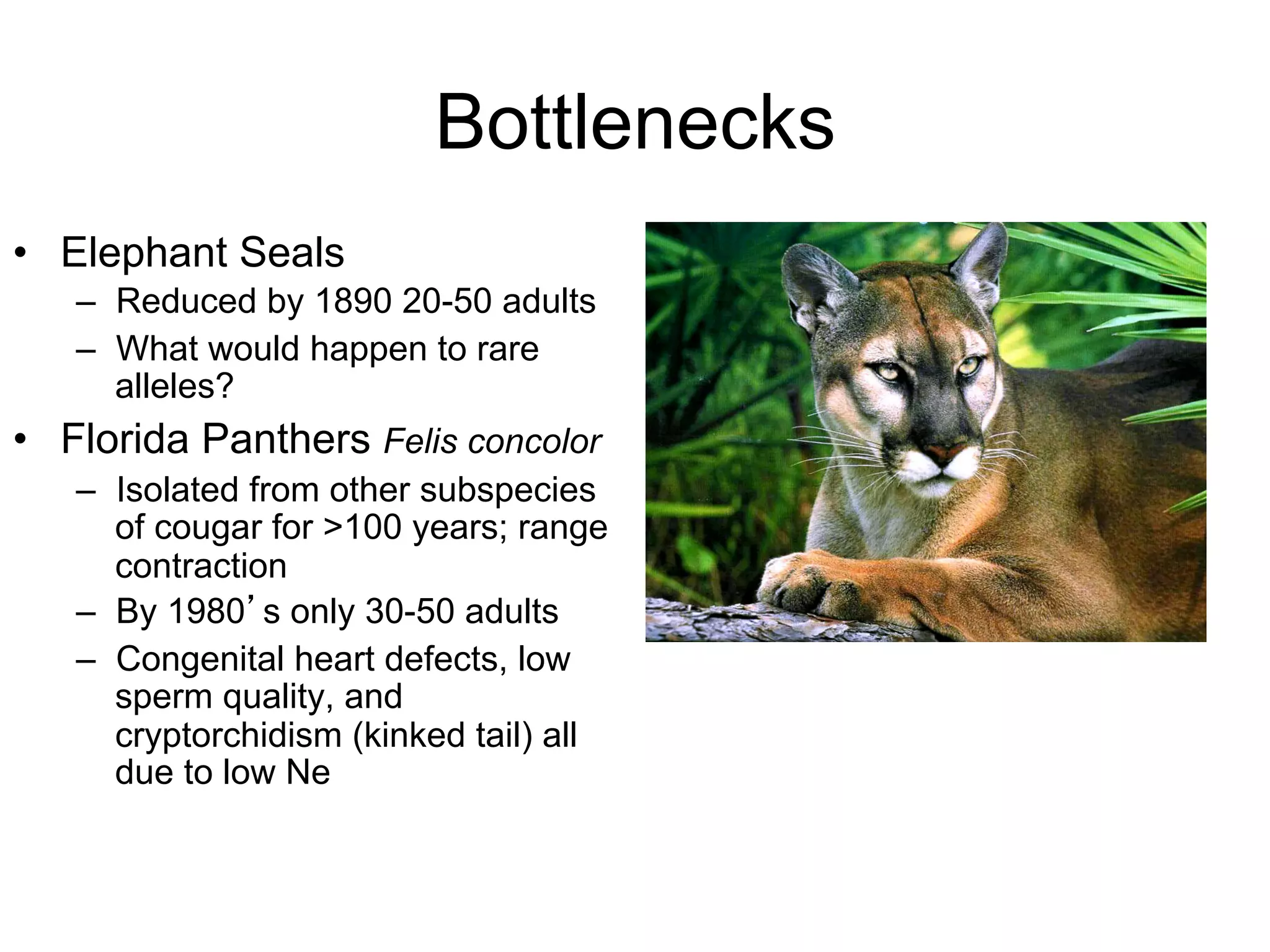
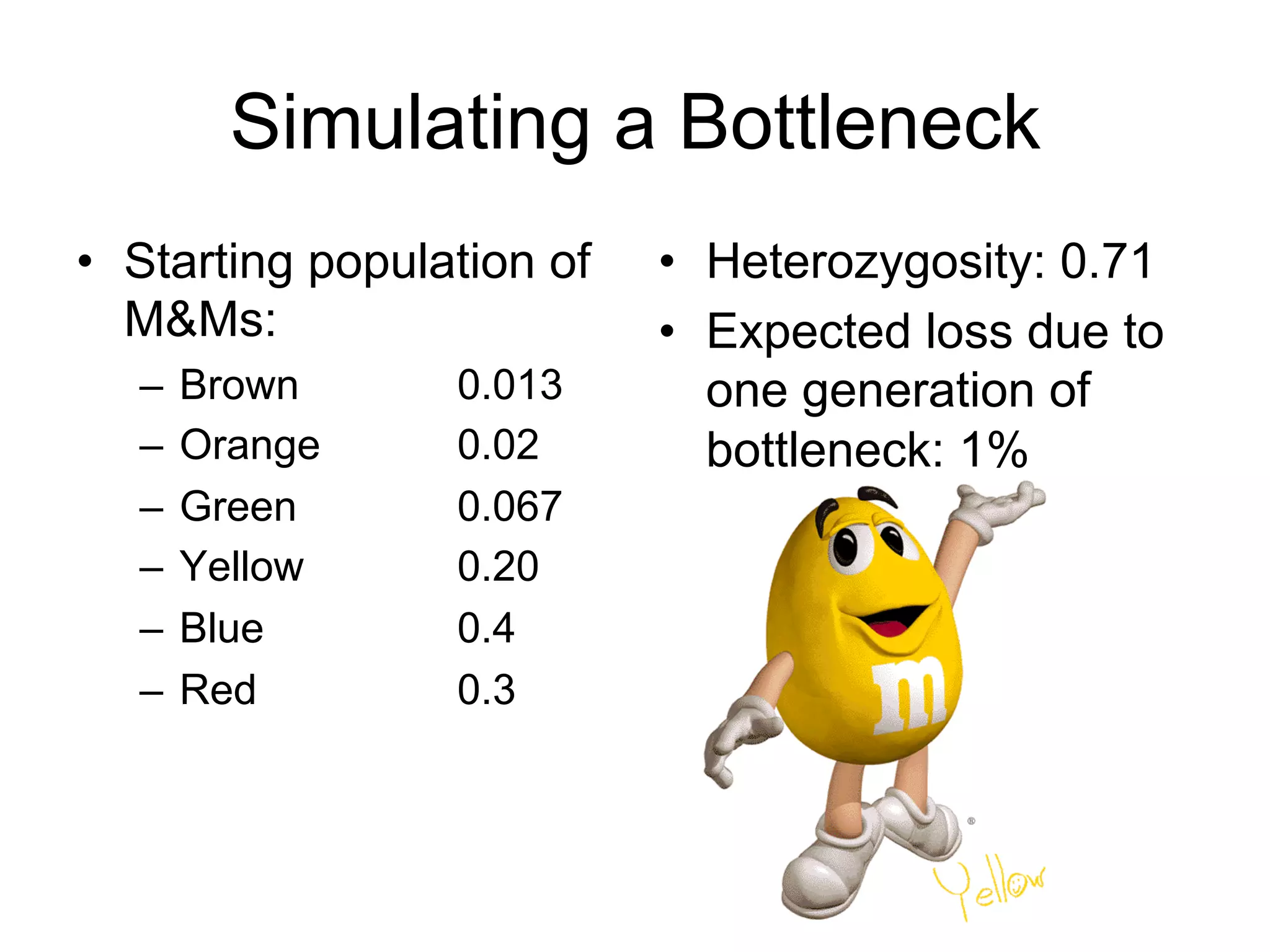
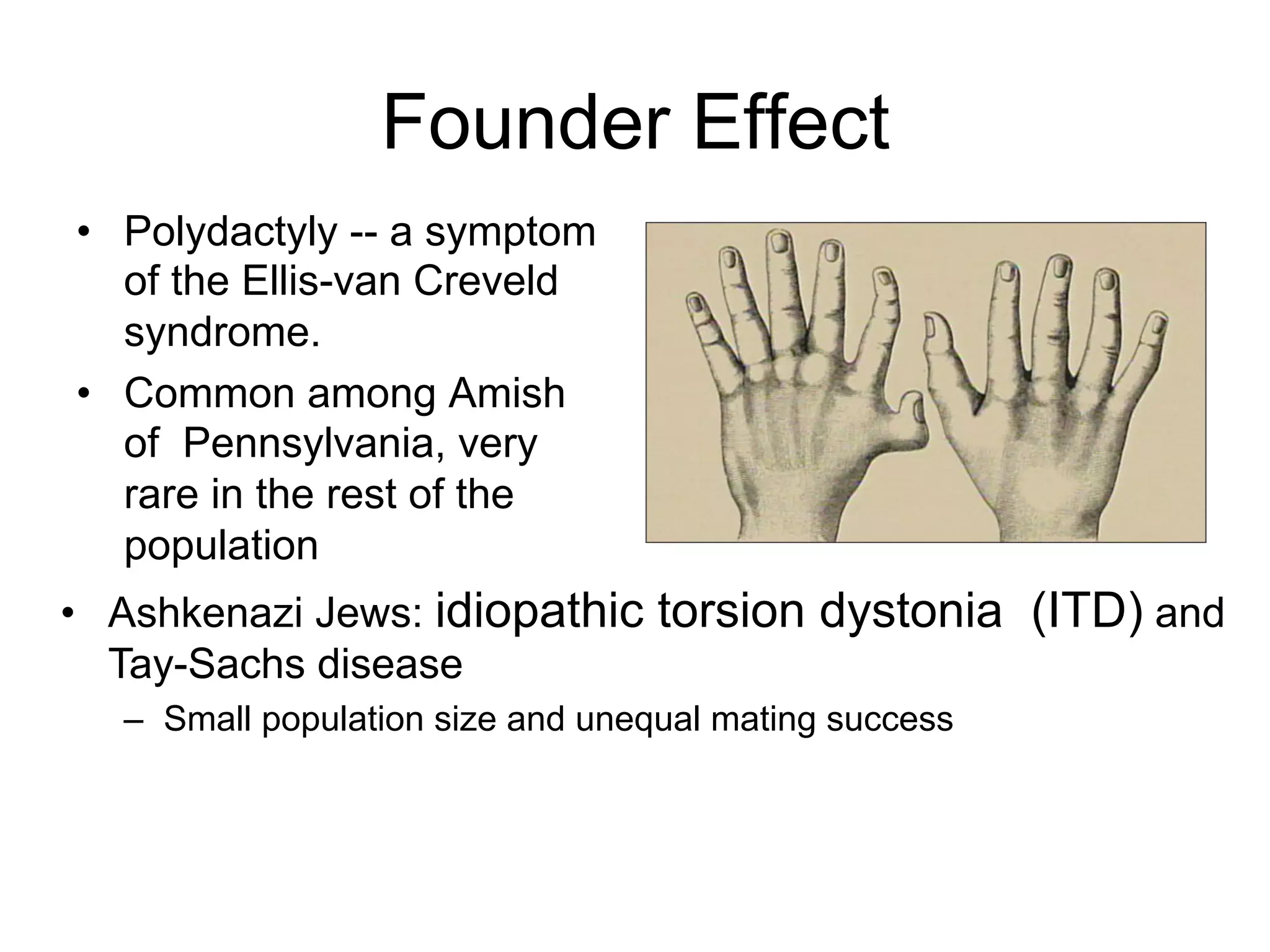
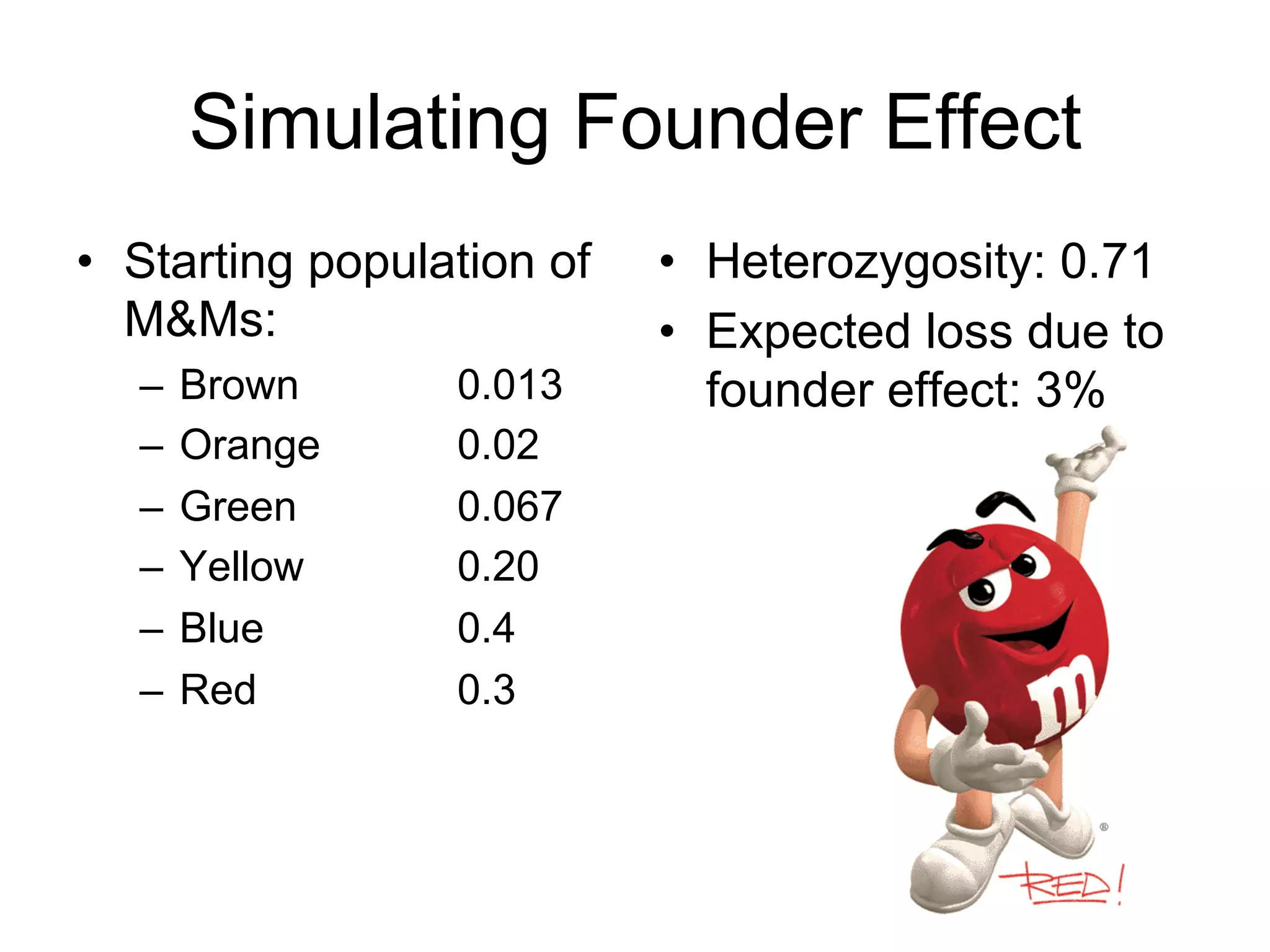
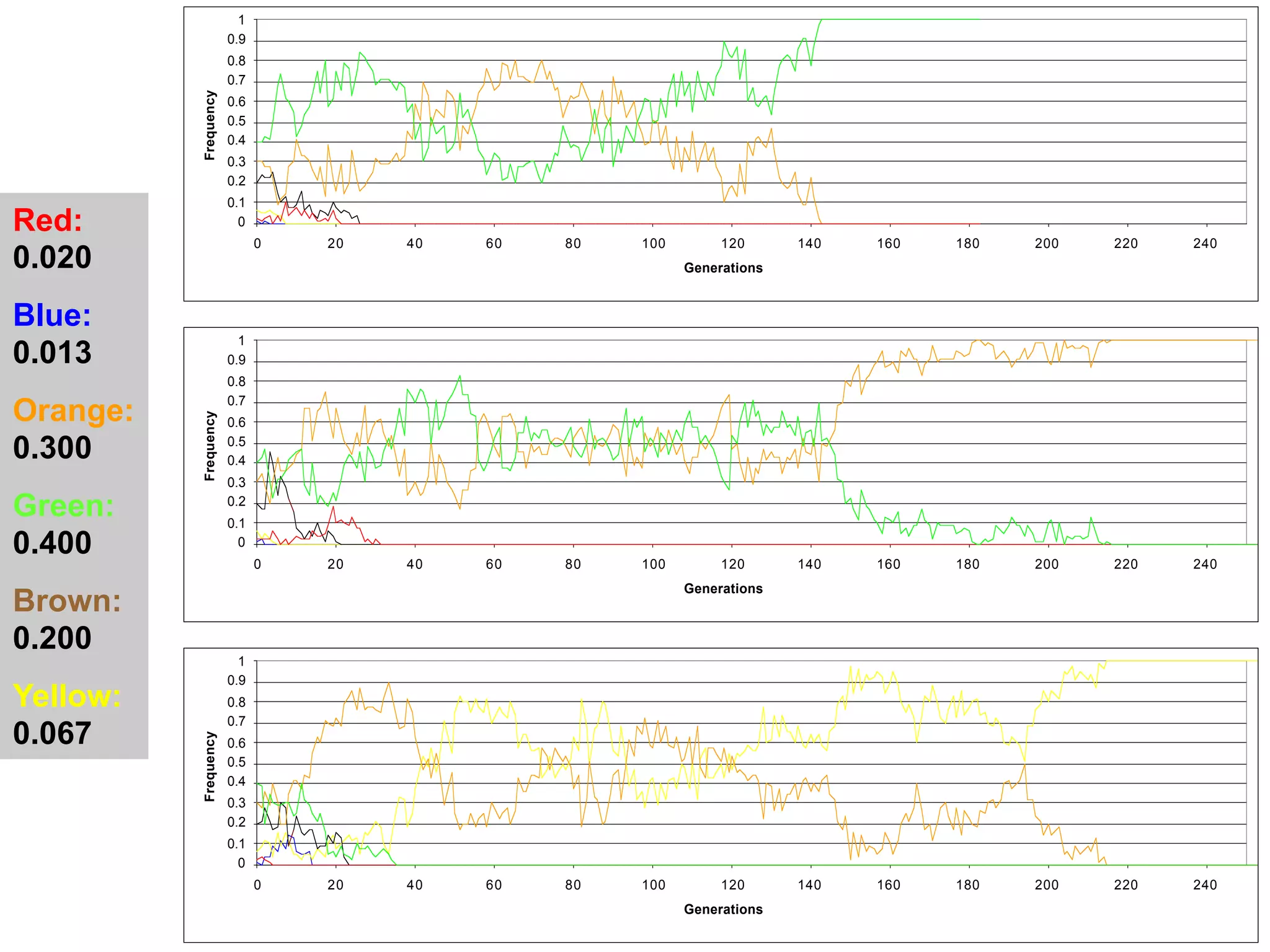
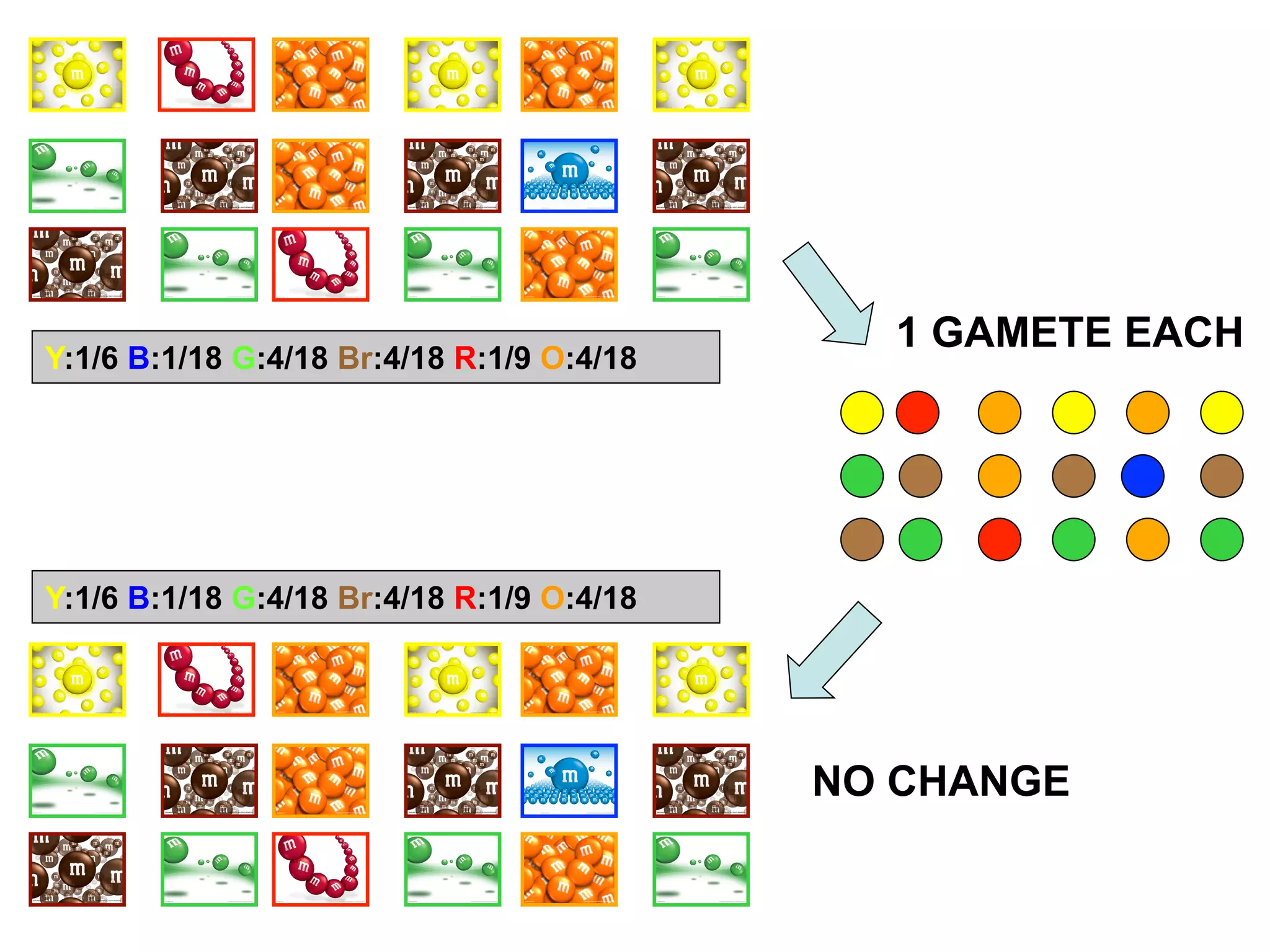
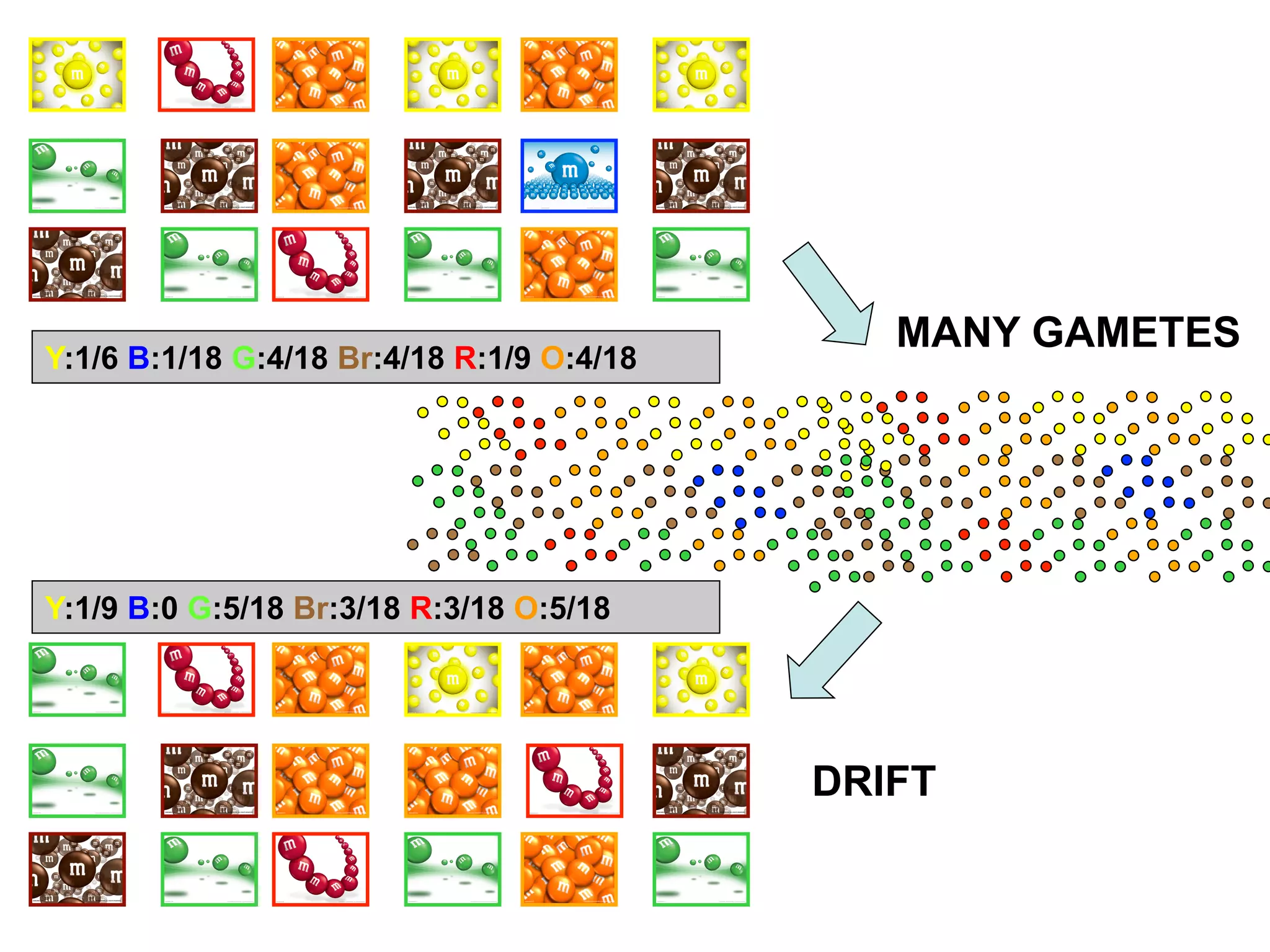
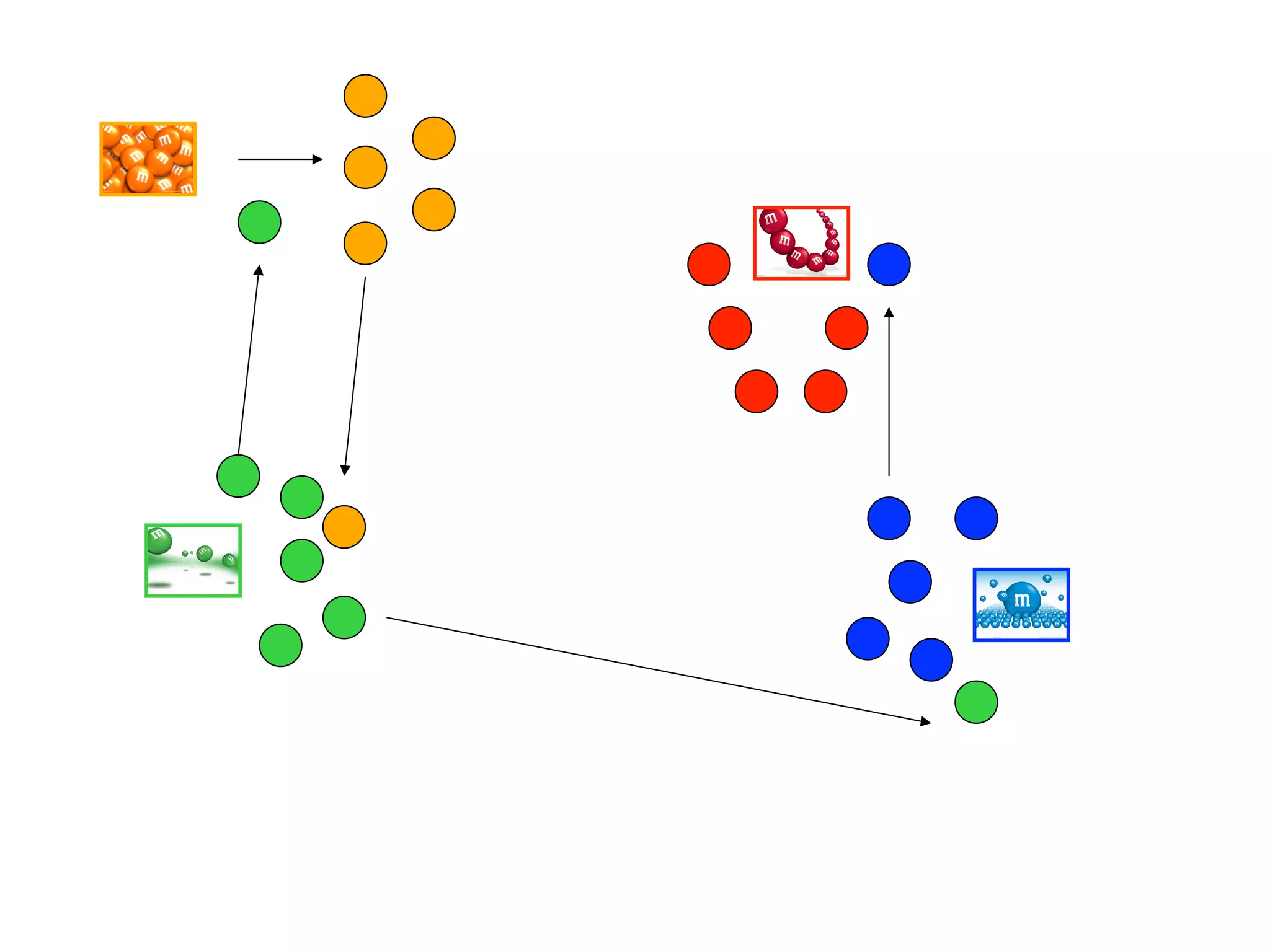
The document discusses the concept of genetic drift, which is the change in allele frequencies over time due to random chance rather than natural selection. It provides examples of genetic drift occurring through bottlenecks, founder effects, and stochastic sampling in populations that have experienced reductions in size. The document then simulates genetic drift through a "Haploid Sex with Chocolate" activity, where students exchange M&M "gametes" over multiple generations to model how drift can change allele frequencies randomly over time in a finite population.