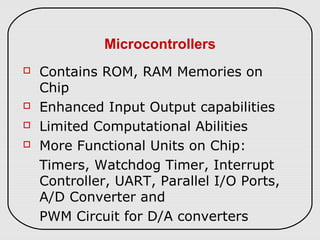
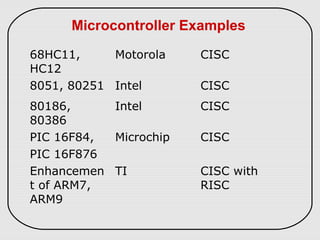
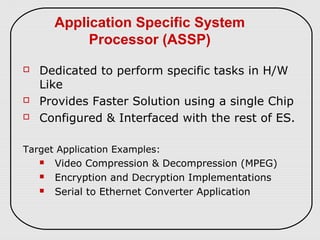
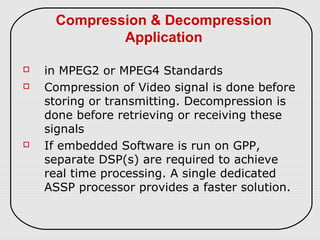
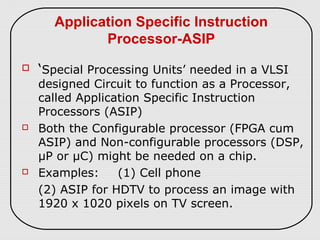
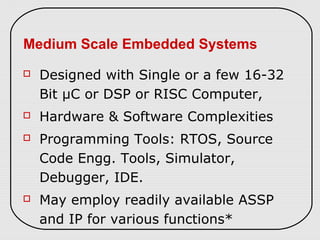
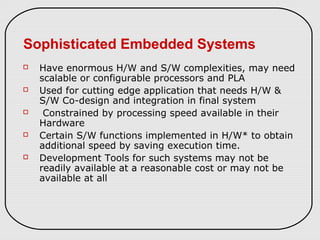
The document describes three types of embedded systems: small scale, medium scale, and sophisticated. Small scale systems use a single microcontroller with little hardware/software complexity. Medium scale systems can use multiple microcontrollers or DSPs with more complex hardware/software. Sophisticated systems have significant hardware/software complexity and may require specialized processors. The document also discusses different types of processors used in embedded systems like microprocessors, microcontrollers, DSPs, and application-specific processors.


![Selection of a Processor
Instruction Set, Pipelining, Super Scalar
Execution.
Data Bus Width (8-16-32 Bits) for Arithmetic.
Floating Point Coprocessor, Cache Memory
On-chip peripheral devices, Clock Frequency,
Availability of Retarget-able Compiler and
Hardware Software Co-design Tools
Power Saving Modes available
Cost [Components, Development tools, NRE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/39245196-intro-es-iii-130624110517-phpapp02/85/39245196-intro-es-iii-6-320.jpg)