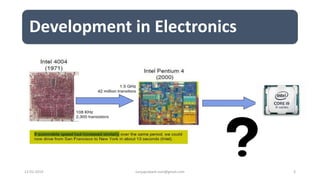
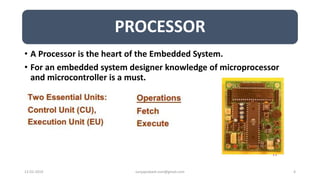
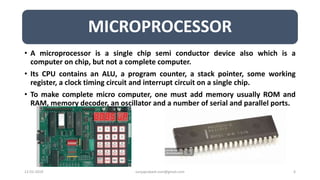
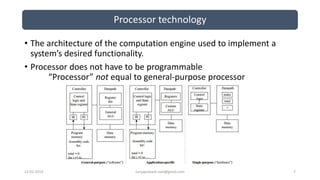
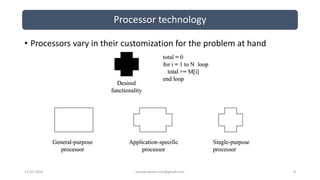
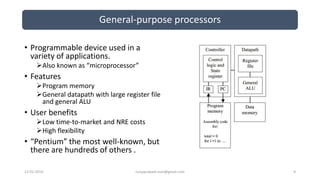
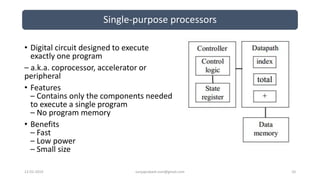
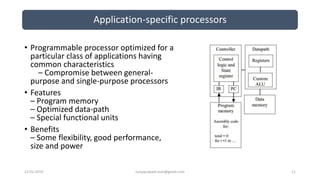
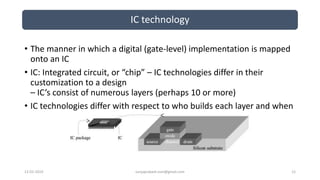
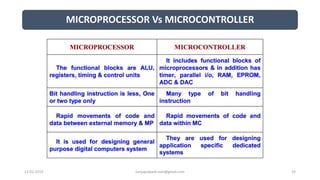
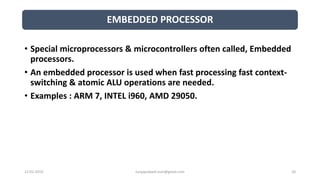
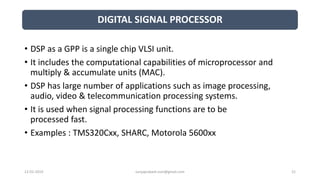
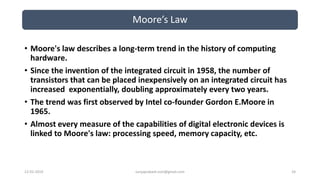
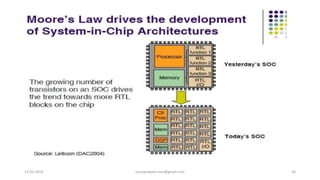
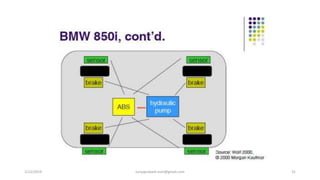
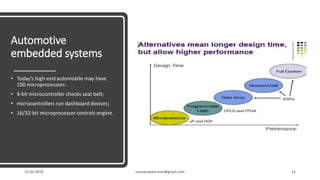
The document discusses different categories of processors used in embedded systems. It describes microprocessors, microcontrollers, embedded processors, digital signal processors, and application specific processors. It also discusses integrated circuit technologies like full-custom, semi-custom ASICs, and programmable logic devices. Microcontrollers integrate a processor, memory and I/O peripherals on a single chip. The document provides examples of processors used in automotive embedded systems and emphasizes finding the cheapest solution that meets requirements.