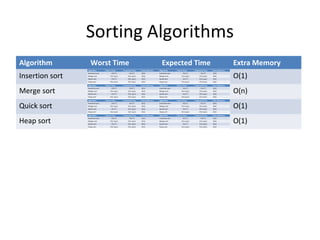
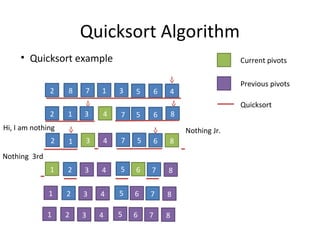
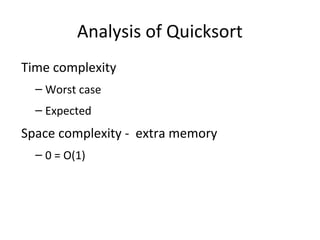
The document discusses quicksort, an efficient sorting algorithm. It begins with a review of insertion sort and merge sort. It then presents the quicksort algorithm, including choosing a pivot, partitioning the array around the pivot, and recursively sorting subarrays. Details are provided on the partition process with examples. Analysis shows quicksort has worst-case time complexity of O(n^2) but expected complexity of O(nlogn) with only O(1) extra memory. Strict proofs are outlined for the worst and expected cases. The document concludes with notes on implementing quicksort in Java for practice.


![Quicksort Algorithm
• Input: A[1, …, n]
• Output: A[1, .., n], where A[1]<=A[2]…<=A[n]
• Quicksort:
1. if(n<=1) return;
2. Choose the pivot p = A[n]
3. Put all elements less than p on the left; put all elements lager
than p on the right; put p at the middle. (Partition)
4. Quicksort(the array on the left of p)
5. Quicksort(the array on the right of p)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150507101206-lva1-app6892/85/3-8-quicksort-4-320.jpg)
![Quicksort Algorithm
• More detail about partition
• Input: A[1, …, n] (p=A[n])
• Output: A[1,…k-1, k, k+1, … n], where A[1, …, k-1]<A[k] and A[k+1, … n] >
A[k], A[k]=p
• Partition:
1. t = the tail of smaller array
2. from i= 1 to n-1{
3. if(A[i]<p) {
4. exchange A[t+1] with A[i];
5. update t to the new tail;
6. }
7. exchange A[t+1] with A[n];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150507101206-lva1-app6892/85/3-8-quicksort-6-320.jpg)
![Quicksort Algorithm
• Partition example
2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4
2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4
2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4
tail
2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4
tail
tail
tail
Exchange 2 with A[tail+1]
Do nothing
Do nothing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150507101206-lva1-app6892/85/3-8-quicksort-7-320.jpg)
![Quicksort Algorithm
• Partition example
2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4
2 871 3 5 6 4
2 8 71 3 5 6 4
tail
tail
Exchange 1 with A[tail+1]
tail
Exchange 3 with A[tail+1]
Do nothing
2 8 71 3 5 6 4
tail
Do nothing
2 871 3 5 64 Final step: exchange A[n]
with A[tail+1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150507101206-lva1-app6892/85/3-8-quicksort-8-320.jpg)




![Strict proof of the expected time complexity
• Given A[1, …, n], after sorting them to , the
chance for 2 elements, A[i] and A[j], to be
compared is .
• The total comparison is calculated as:
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150507101206-lva1-app6892/85/3-8-quicksort-14-320.jpg)
