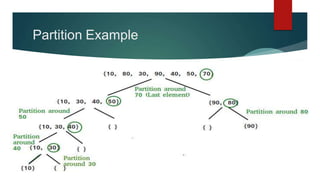
The document provides an overview of the quicksort sorting algorithm, detailing its method of arranging elements in ascending or descending order. It outlines the choice of pivot for partitioning the array and includes pseudocode and a C++ implementation of the algorithm. Quicksort's complexities indicate that it averages O(n log n) efficiency, with a worst-case scenario of O(n²), though the latter can typically be avoided.






![Quicksort Pseudocode
Procedure quicksort(Left ,
Right)
if right-left <= 0
retur
n
else
pivot = A[right]
partition = partitionFunc(left, right, pivot)
quickSort(left,partition-1)
quickSort(partition+1,right)
end if
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-200821092836/85/Quick-sort-by-Sania-Nisar-8-320.jpg)
![Quicksort Implementation
#include < iostream >
using namespace std ;
void quick_sort (int[],int,int); int
partition (int[],int,int);
int main()
{
int a[50],n,i;
cout<<"How many elements?";
cin>>n;
cout<<"n Enter array elements:";
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>a[i];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-200821092836/85/Quick-sort-by-Sania-Nisar-9-320.jpg)
![quick_sort (a,0,n-1);
cout<<"n Array after sorting:";
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
void quick_sort (int a[],int l,int u)
{
int j;
if(l<u)
{
j=partition(a,l,u);
quick_sort(a,l,j-1);
quick_sort(a,j+1,u);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-200821092836/85/Quick-sort-by-Sania-Nisar-10-320.jpg)
![int partition (int a[],int l,int u)
{
int v,i,j,temp;
v=a[l];
i=l;
j=u+1;
do
{
do
i++;
while(a[i]<v&&i<=u);
do
j--;
while(v<a[j]);
if(i<j)
{
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-200821092836/85/Quick-sort-by-Sania-Nisar-11-320.jpg)
![}
while(i<j);
a[l]=a[j];
a[j]=v;
return(j);
}
Output
How many elements?
6
Enter array elements:
9 15 6 7 10 12
Array after
sorting: 6 7 9 10
12 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-200821092836/85/Quick-sort-by-Sania-Nisar-12-320.jpg)




