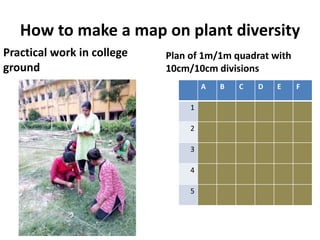
This document provides information about determining plant species diversity using diversity indices. It discusses the Shannon-Wiener and Simpson indices.
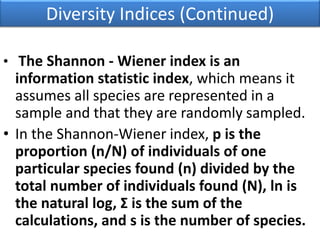
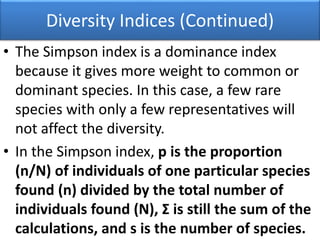
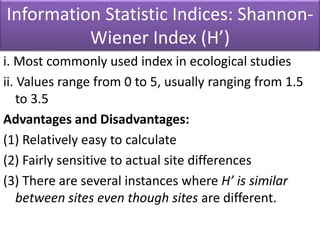
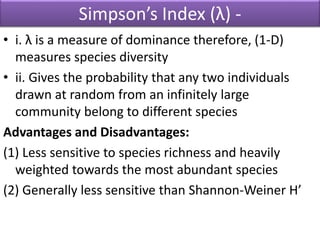
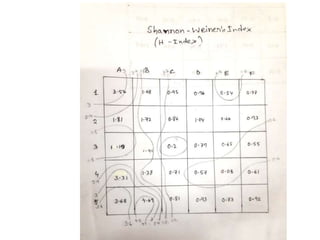
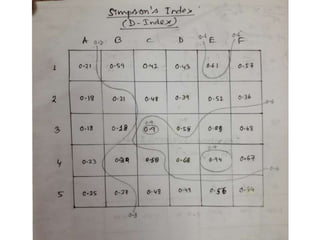
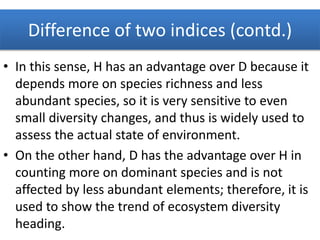
The Shannon-Wiener index is an information statistic index that assumes all species are randomly sampled. The Simpson index is a dominance index that gives more weight to common species.
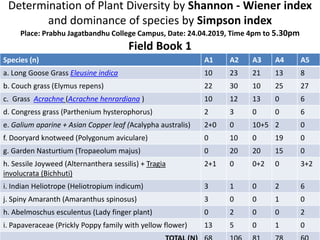
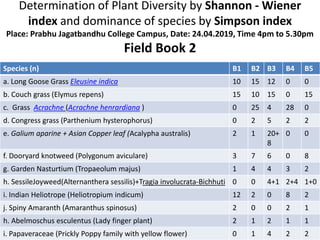
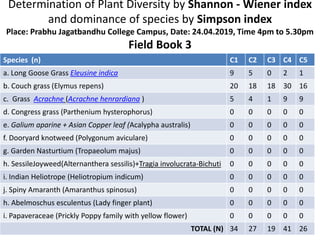
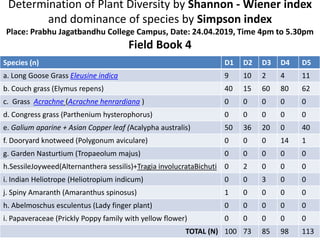
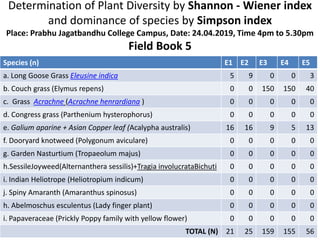
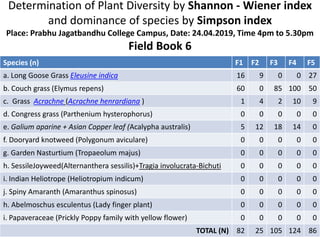
The document also includes field book data from a study measuring various plant species abundance in different quadrats. The species abundances are recorded and will be used to calculate the Shannon-Wiener and Simpson indices to analyze the plant diversity.