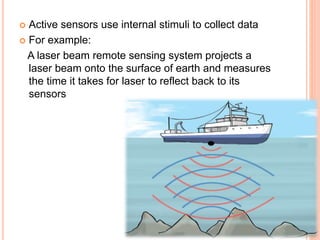
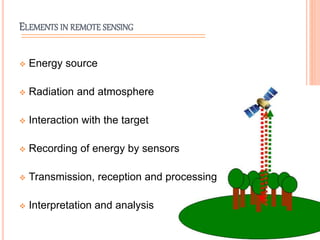
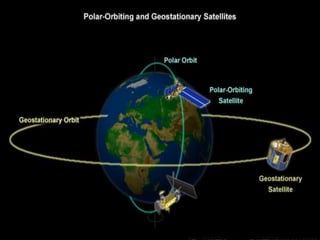
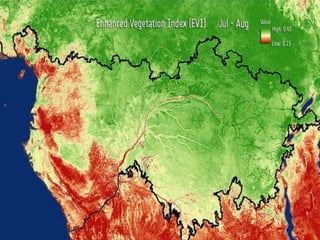
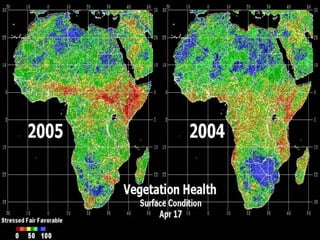
Remote sensing is the science of collecting information about objects or areas from a distance using devices like satellites, radars, and sensors, enabling broad applications in geography, military intelligence, and environmental monitoring. It involves both passive and active sensors to gather data about vegetation and ecosystems, providing valuable insights into habitat mapping, biodiversity, and environmental changes. Limitations include challenges in distinguishing between similar vegetation types, but it remains a crucial tool for various ecological and conservation efforts.