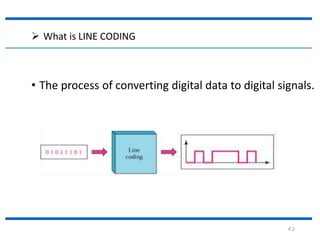
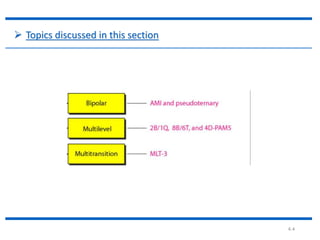
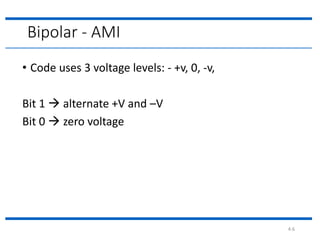
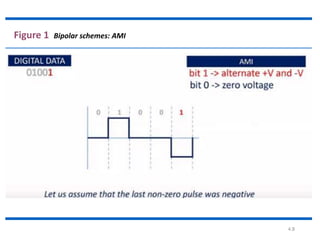
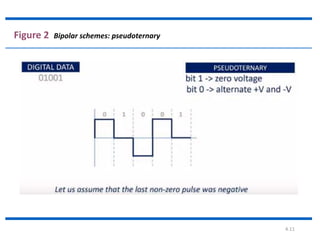
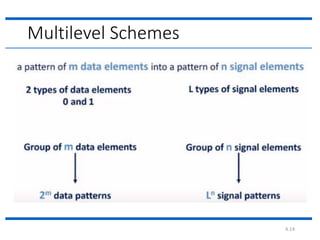
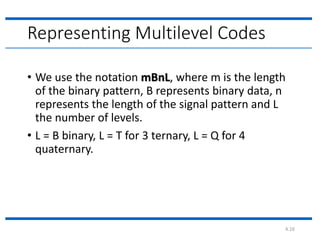
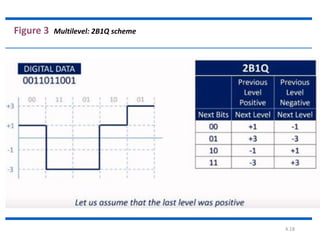
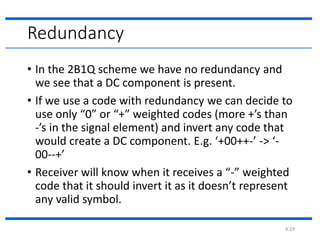
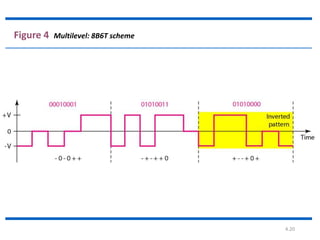
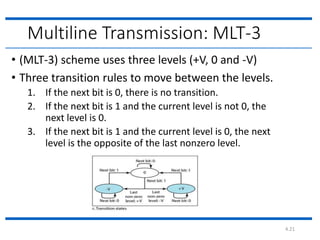
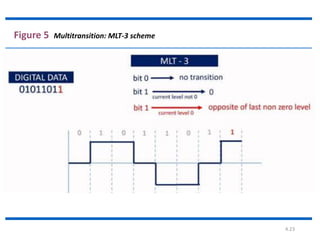
The document discusses different types of line coding techniques used to convert digital data to digital signals for transmission. It describes bipolar AMI and pseudoternary coding which use three voltage levels (+V, 0, -V) to encode bits. Bipolar coding avoids DC components but has no error detection. Multilevel coding techniques like 2B1Q assign symbol patterns to bits for better noise immunity. The 8B6T scheme adds redundancy to avoid DC components. MLT-3 is a multitransition coding that uses transition rules to move between three voltage levels when encoding bits.