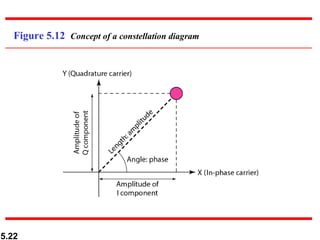
The document discusses digital-to-analog and analog-to-analog conversion. It covers topics such as amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, phase shift keying, and quadrature amplitude modulation. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate bit rates, baud rates, carrier frequencies, and bandwidths for different modulation techniques including ASK, FSK, PSK, and QAM. Diagrams illustrate the constellations for various modulation schemes. Formulas are given for determining the bandwidth requirements of AM, FM, and PM.