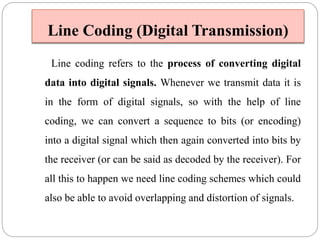
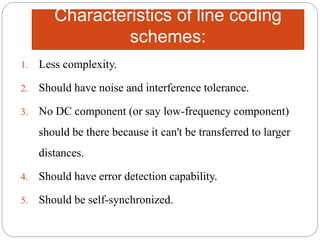
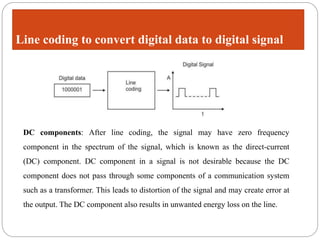
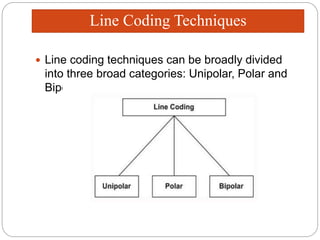
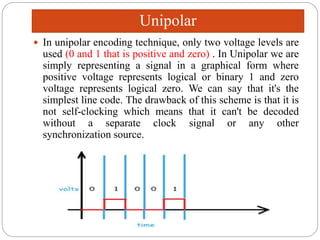
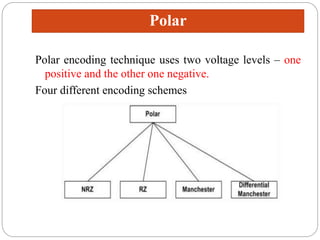
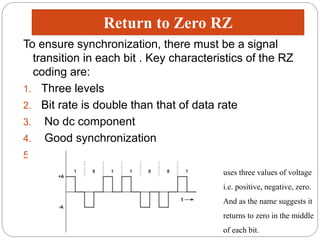
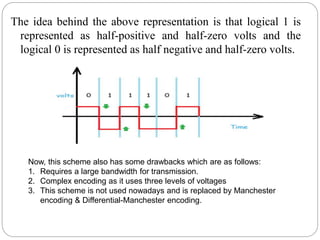
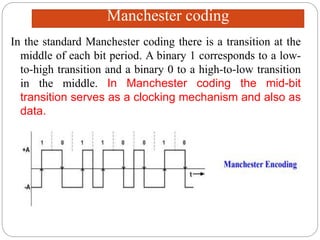
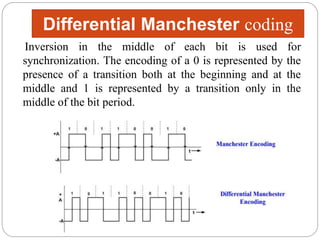
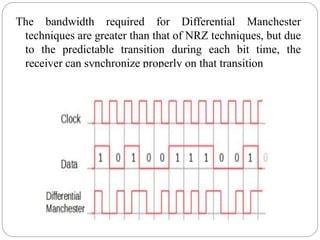
Line coding refers to converting digital data into digital signals for transmission. There are several characteristics line coding schemes should have, such as low complexity, noise tolerance, no DC component, error detection capability, and self-synchronization. Common line coding techniques include unipolar, polar, and bipolar coding. Specific techniques discussed include non-return to zero (NRZ), return to zero (RZ), Manchester, and differential Manchester coding. These techniques vary in their voltage levels, presence of a DC component, synchronization capabilities, and bandwidth requirements.