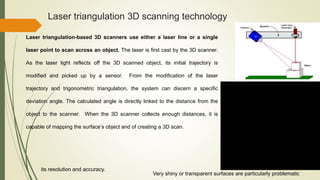
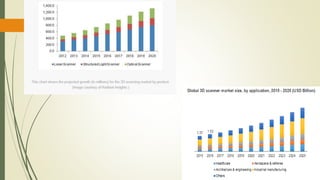
3D scanning technology allows capturing the shape of physical objects and environments digitally. It works by using techniques like laser triangulation, structured light, photogrammetry, or contact-based scanning to obtain high-density 3D measurements. The results can be used for reverse engineering, rapid prototyping, inspection, and analysis. Different scanning methods have advantages and limitations depending on factors like speed, resolution, ability to scan people or outdoor environments, and sensitivity to lighting or surface properties. The document discusses several 3D scanning technologies and their applications in industries like automotive, aeronautics, and entertainment.