This document discusses algorithms for drawing circles and ellipses in computer graphics. It covers:
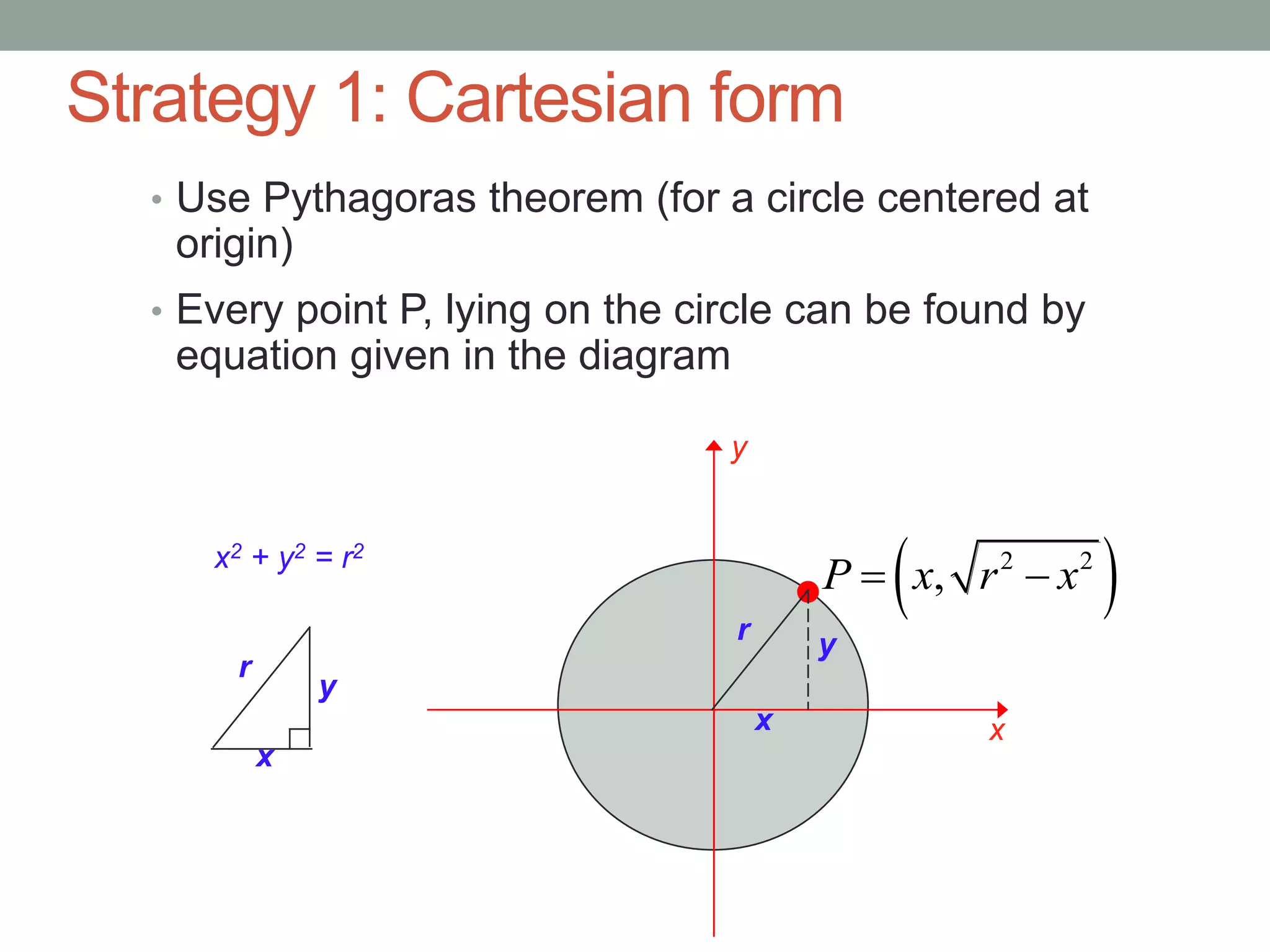
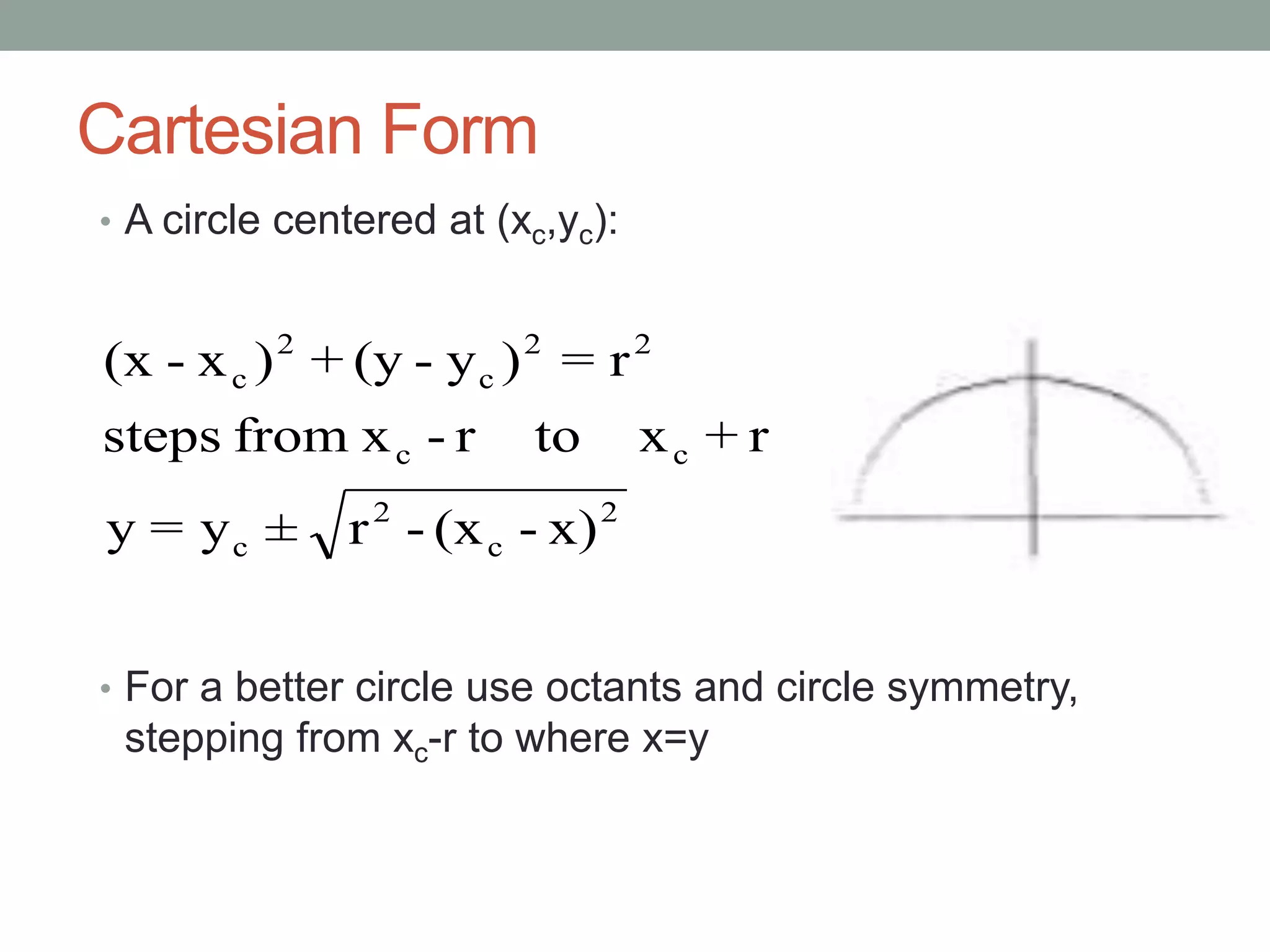
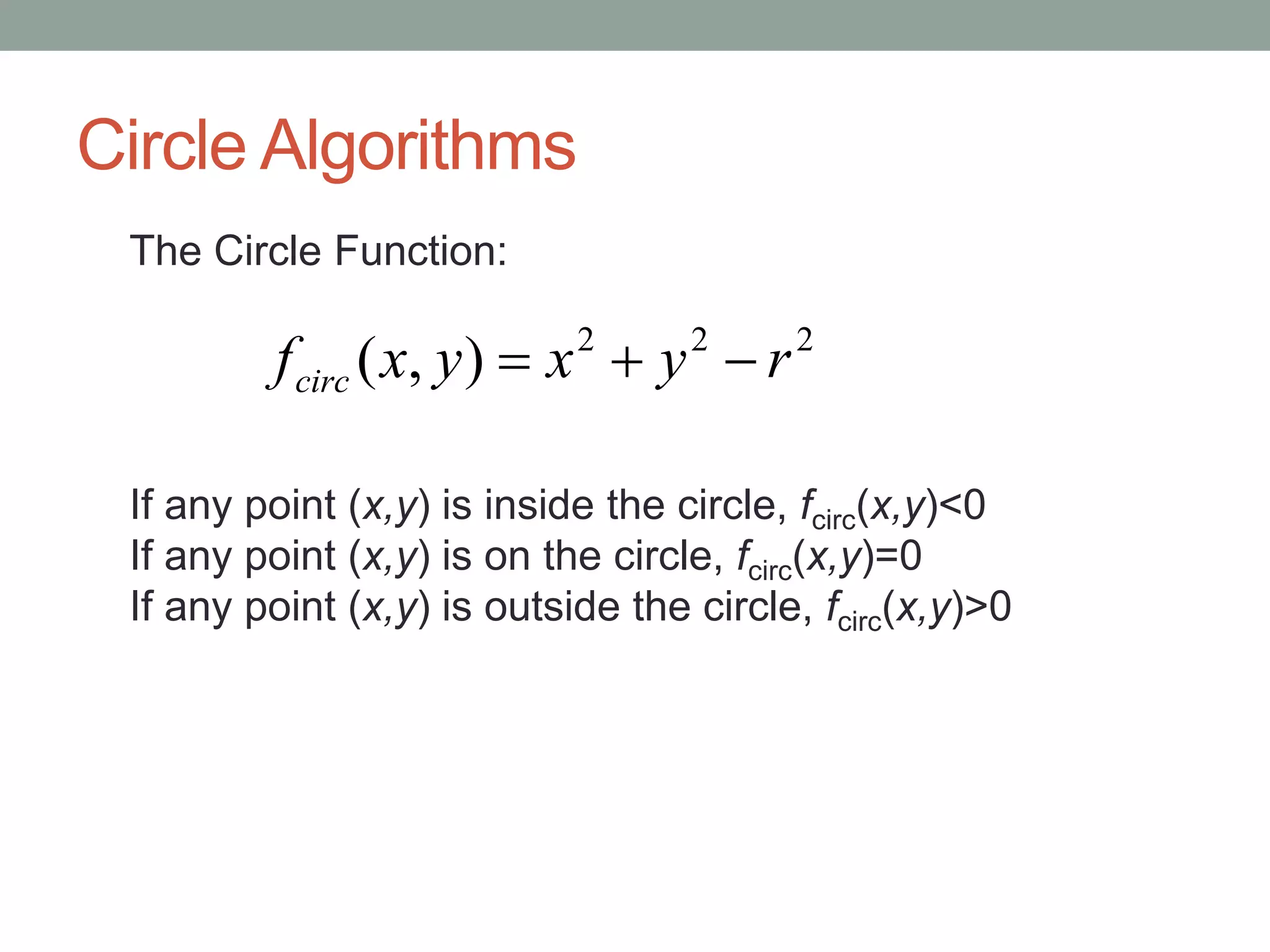
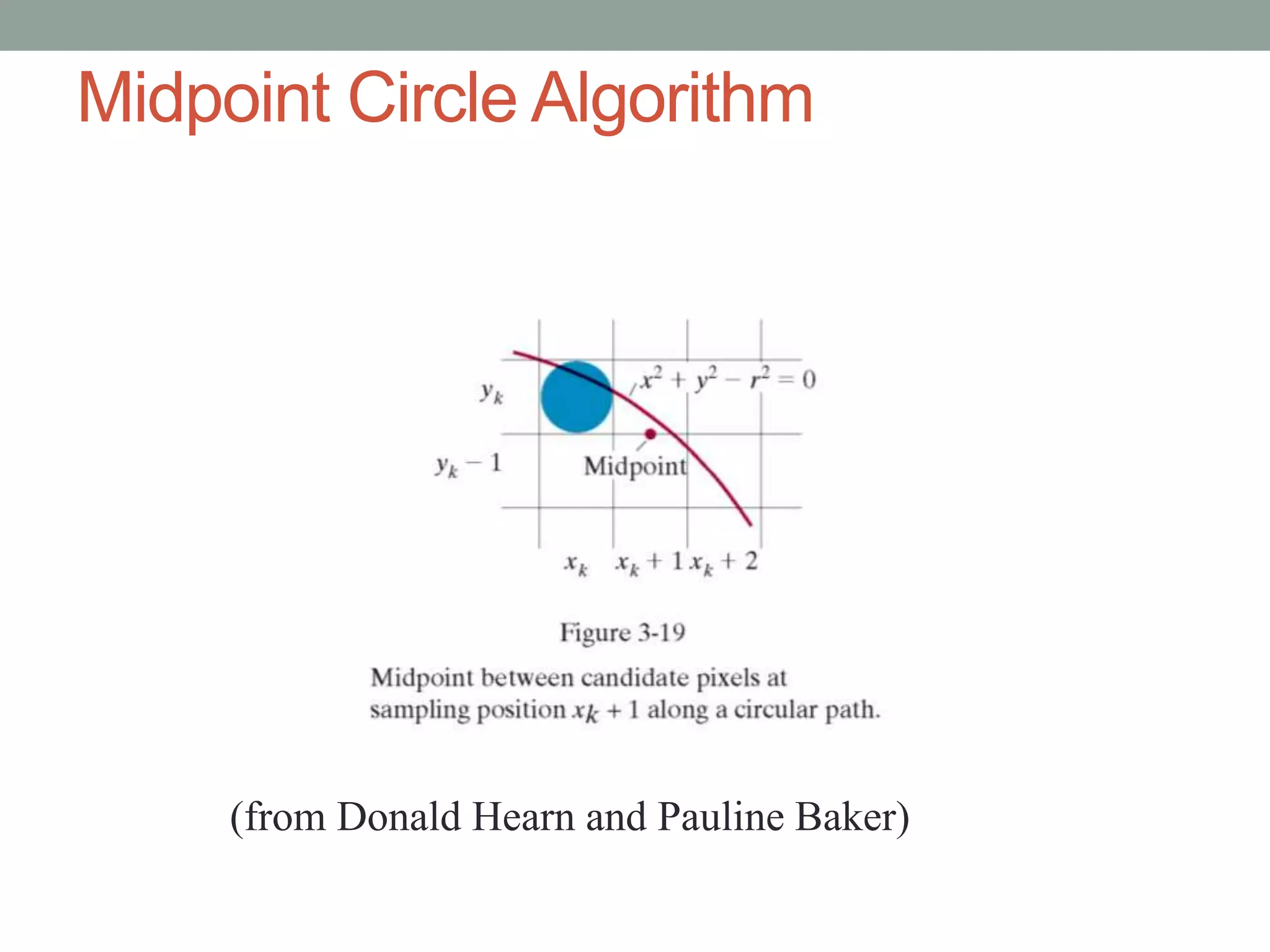
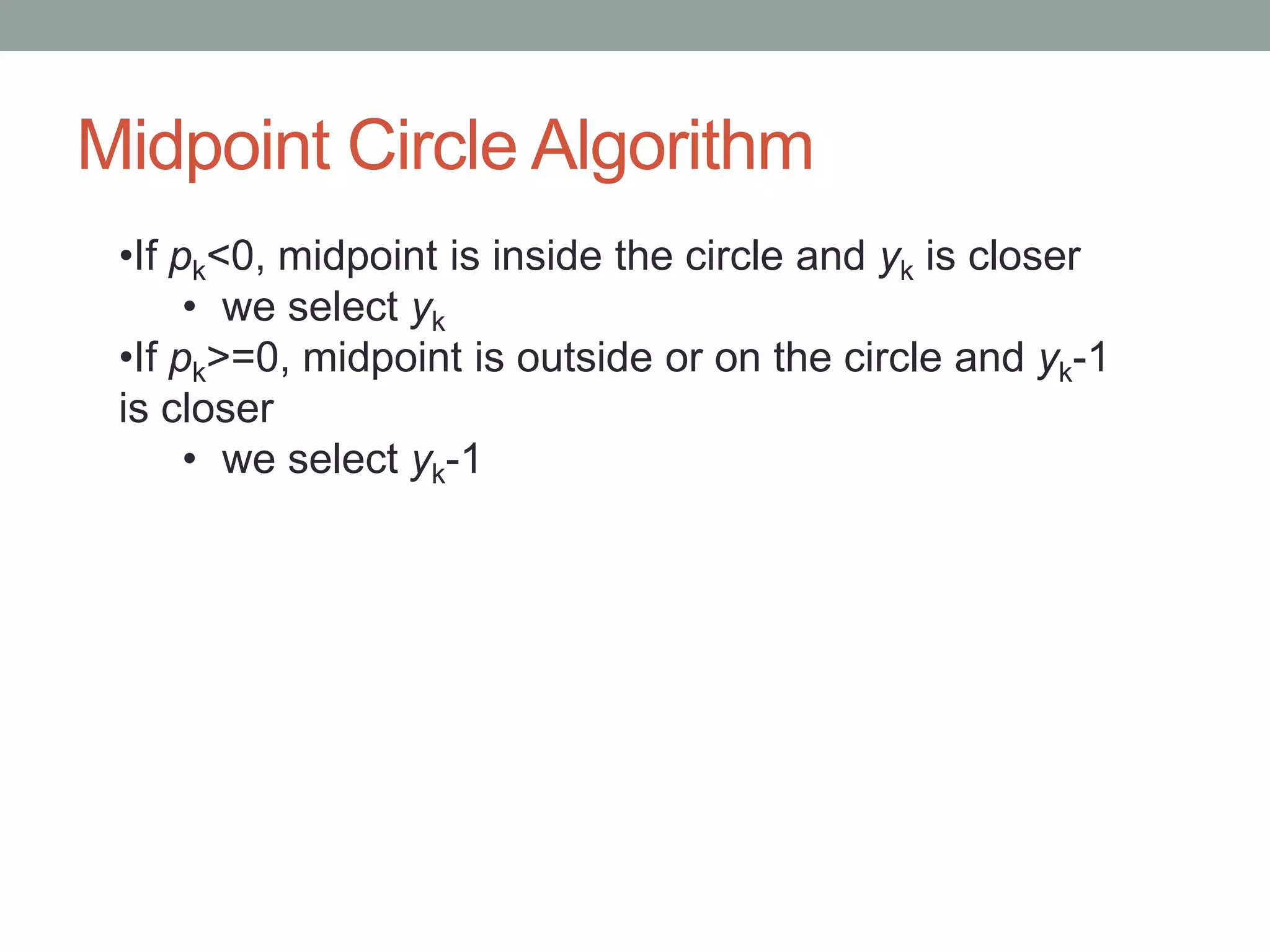
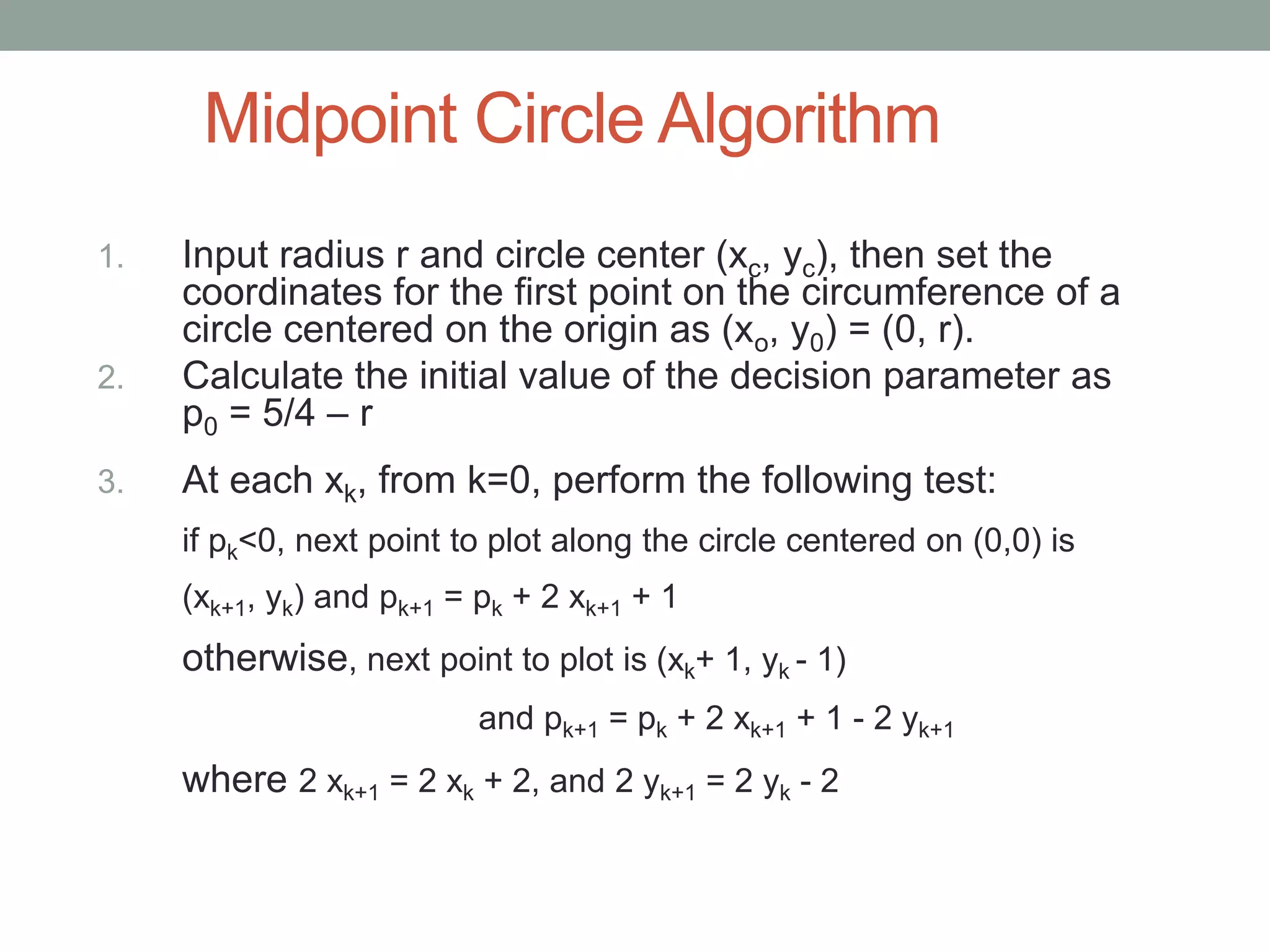
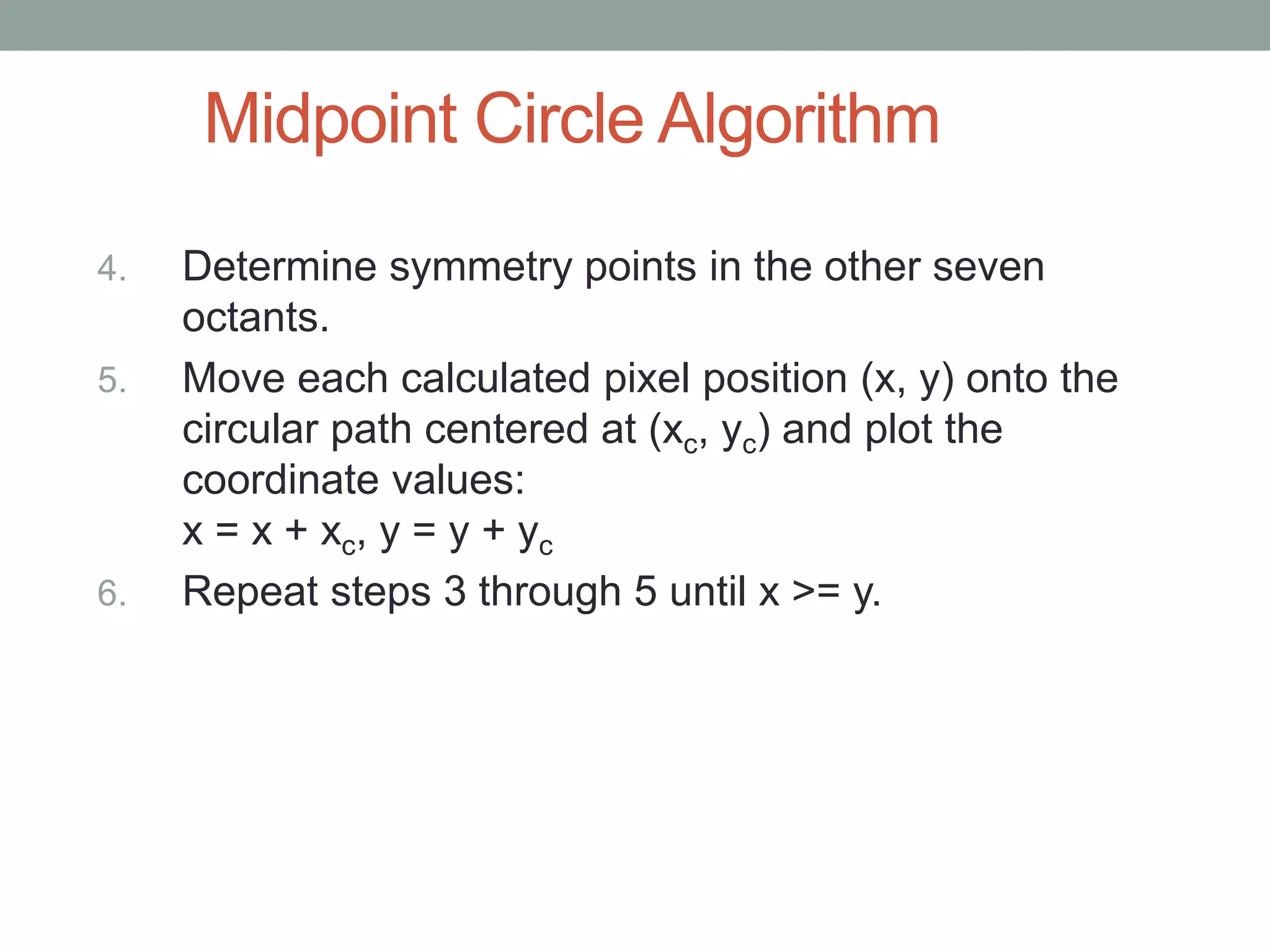
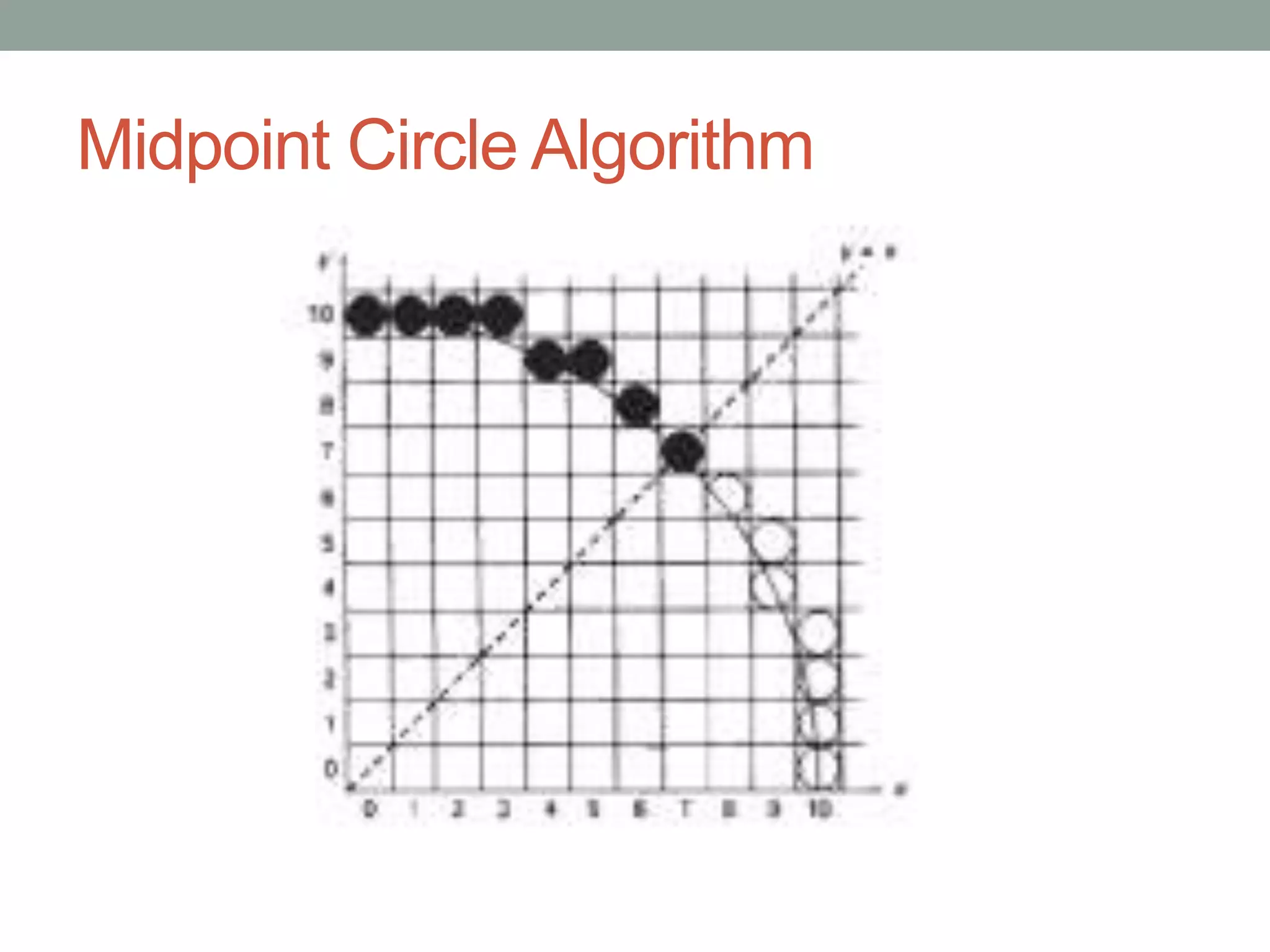
1. Circle drawing algorithms including using Cartesian coordinates, polar coordinates, and the midpoint circle algorithm which iteratively calculates the midpoint between pixels to determine if they are inside, outside, or on the circle.
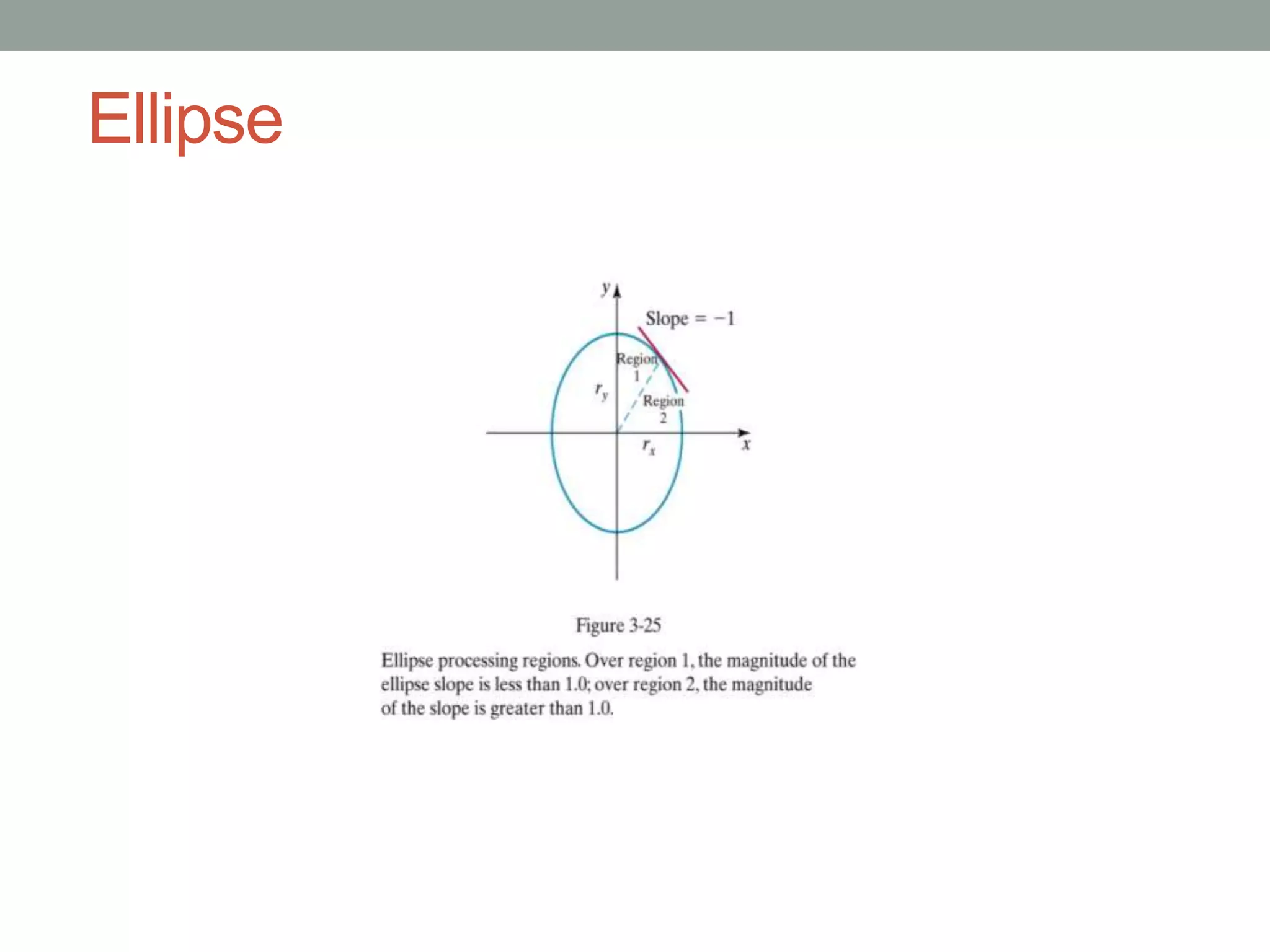
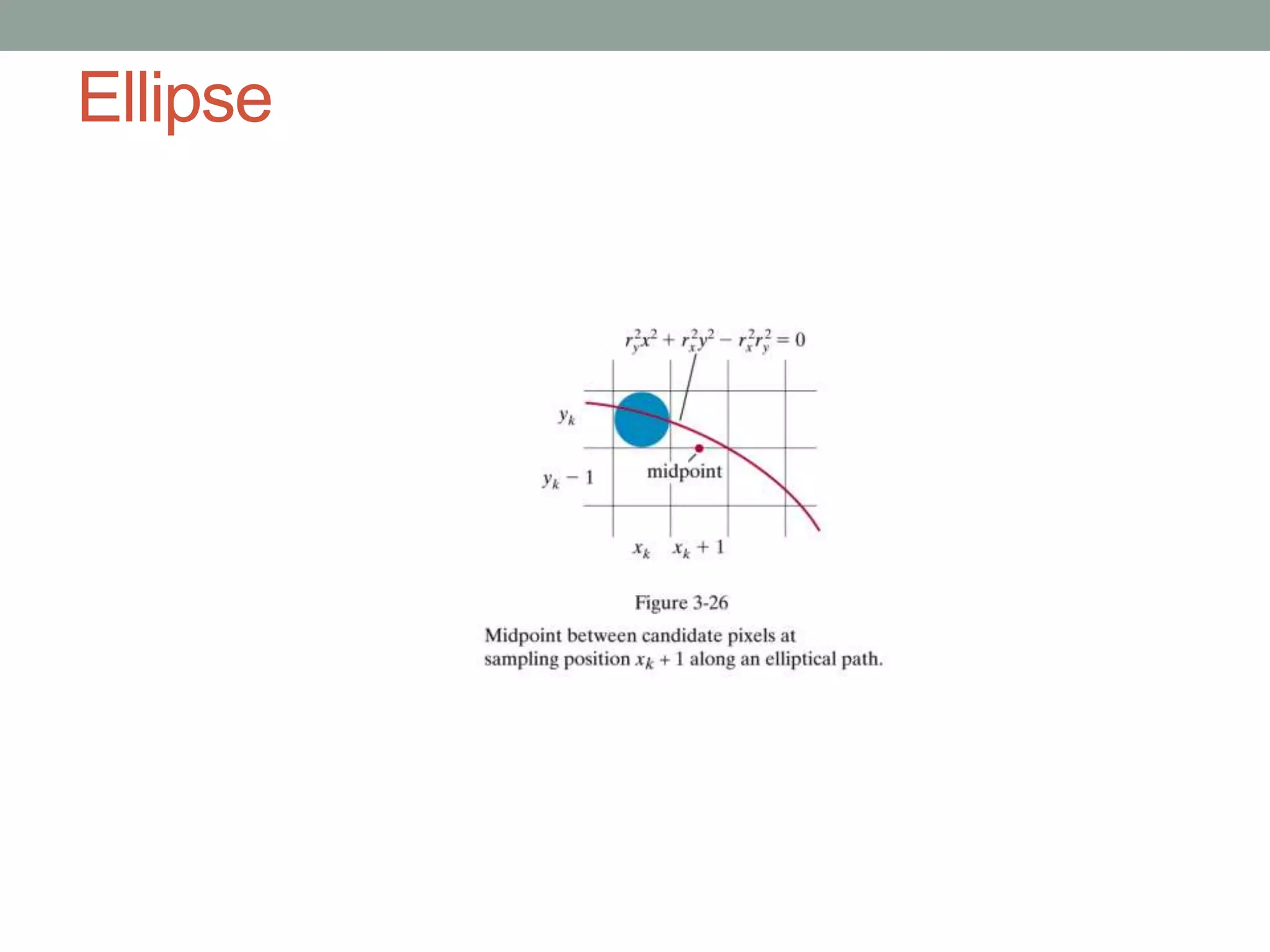
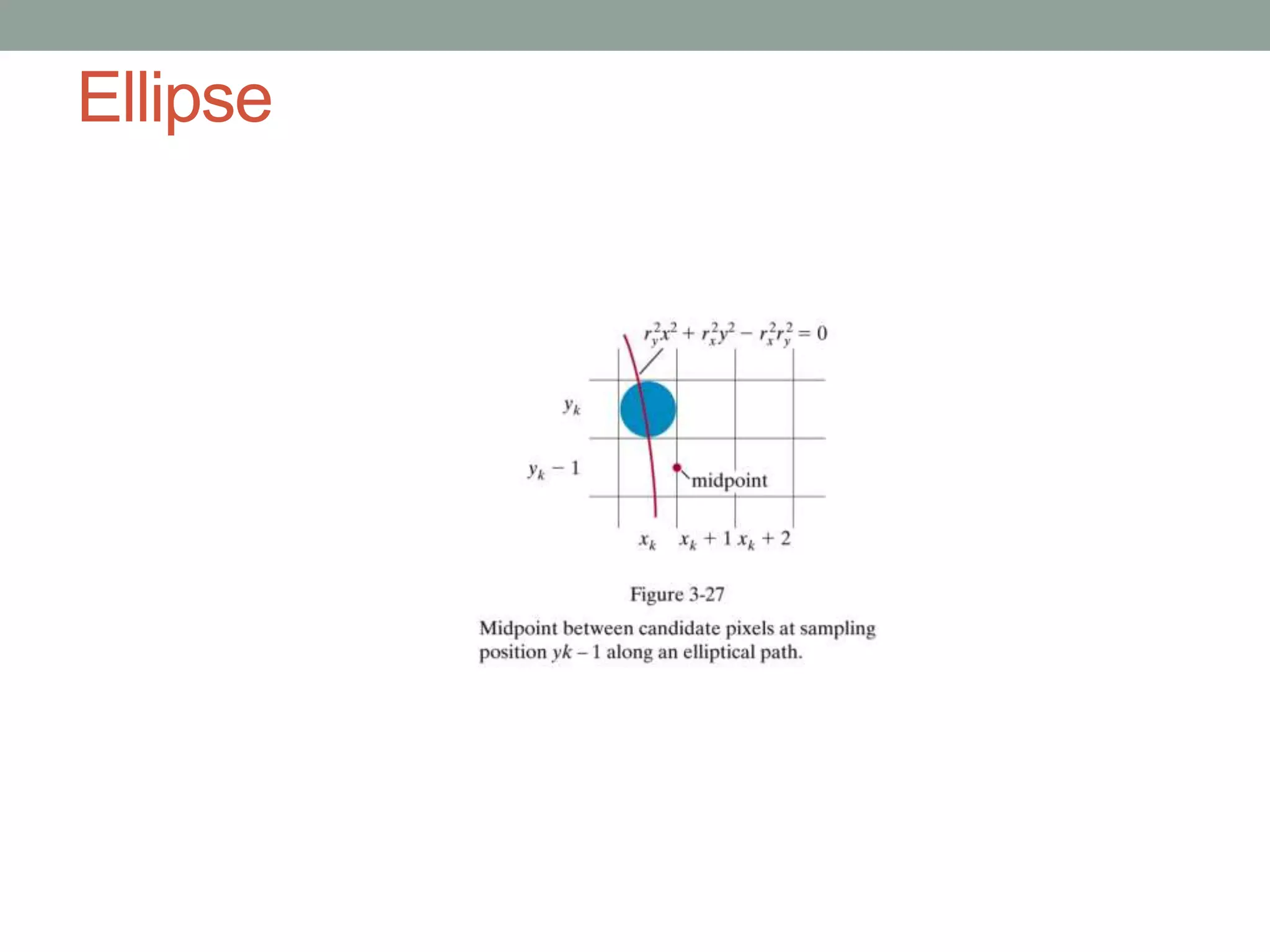
2. The midpoint ellipse algorithm which is similar but uses a modified decision parameter calculation that handles two regions for the first quadrant.
3. Key aspects of the algorithms include using octants and circle symmetry to reduce calculations, and translating the drawn shape to be centered at a given point.