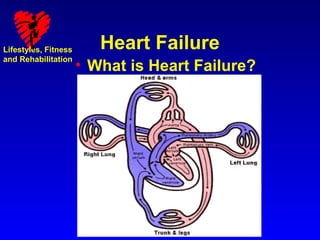
The document discusses heart failure, including its causes, types, signs and symptoms. It defines heart failure as when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Left heart failure involves the left ventricle, and can be systolic or diastolic. Right heart failure usually occurs secondary to left heart failure. Common causes include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Signs and symptoms include shortness of breath, cough, edema, fatigue, lack of appetite, and confusion.